ADHD significantly impacts attention, impulsivity, and hyperactivity, affecting both children and adults worldwide. Visual representations like infographics simplify complex ADHD symptoms and management strategies, making information easier to understand. This infographic highlights key facts, common signs, and effective coping mechanisms to raise awareness and support.
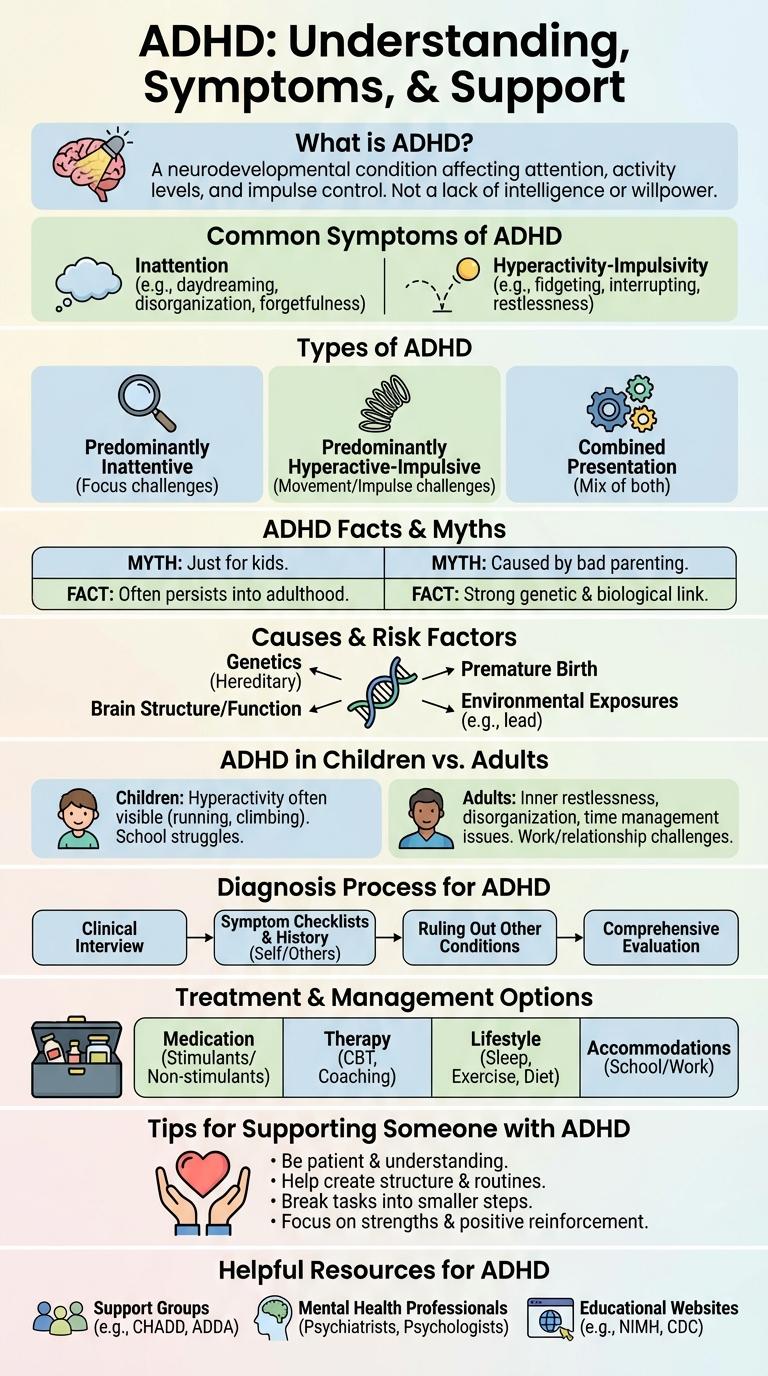
What is ADHD?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental condition affecting focus, impulse control, and activity levels. It is commonly diagnosed in children but often persists into adulthood.
- Symptoms - Include inattentiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness impacting daily life and learning.
- Causes - Involve genetic, neurological, and environmental factors contributing to brain function differences.
- Diagnosis - Based on clinical evaluation of behavior patterns and developmental history by healthcare professionals.
Effective management of ADHD often includes behavioral therapy, medication, and lifestyle adjustments tailored to individual needs.
Common Symptoms of ADHD
ADHD, or Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, is characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Individuals with ADHD often struggle with organizing tasks, sustaining focus, and controlling urges. Recognizing these common symptoms is essential for early diagnosis and effective management.
Types of ADHD
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) primarily includes three types: Predominantly Inattentive, Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive, and Combined Type. Each type presents unique challenges related to attention, impulse control, and activity levels.
Predominantly Inattentive type features difficulty sustaining focus and organization, often leading to forgetfulness and distraction. Predominantly Hyperactive-Impulsive type involves excessive movement, fidgeting, and impulsive decisions without considering consequences.
ADHD Facts & Myths
| ADHD Facts | ADHD Myths |
|---|---|
| ADHD stands for Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. | ADHD is caused by bad parenting styles. |
| Approximately 5-7% of children worldwide have ADHD. | Only children are affected by ADHD. |
| ADHD symptoms include inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. | People with ADHD cannot focus on anything. |
| ADHD has a strong genetic component and can run in families. | ADHD is not a real medical disorder. |
| Medication and behavioral therapy are effective treatments. | Medication for ADHD leads to addiction. |
Causes & Risk Factors
ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder) is influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Family history plays a significant role, with genes affecting brain development and neurotransmitter regulation. Exposure to environmental toxins, premature birth, and low birth weight increase the risk of developing ADHD.
ADHD in Children vs. Adults
How does ADHD manifest differently in children compared to adults?
Children with ADHD often display hyperactivity and impulsiveness, while adults are more likely to experience inattention and restlessness. The symptoms in adults may be less obvious but can significantly impact daily functioning and relationships.
Diagnosis Process for ADHD
Diagnosing ADHD involves a thorough evaluation to accurately identify symptoms and rule out other conditions. The process includes gathering detailed information from multiple sources for a comprehensive assessment.
- Clinical Interview - A healthcare provider conducts interviews with the patient and close contacts to understand symptom history and impact.
- Behavioral Questionnaires - Standardized rating scales and checklists assess symptom severity across different settings.
- Medical Examination - Physical exams and medical history review help exclude other causes of symptoms.
Treatment & Management Options
ADHD treatment includes behavioral therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes designed to improve focus and reduce impulsivity. Effective management integrates personalized plans tailored to individual needs.
Medication options often involve stimulants like methylphenidate or non-stimulants such as atomoxetine. Behavioral strategies emphasize organization, time management, and social skills development.
Tips for Supporting Someone with ADHD
Supporting someone with ADHD requires understanding and patience. Awareness of their challenges can lead to stronger relationships and effective assistance.
Encourage clear communication and consistent routines to help manage daily tasks. Use reminders and organizational tools to reduce forgetfulness. Offer positive reinforcement to boost their confidence and motivation.
