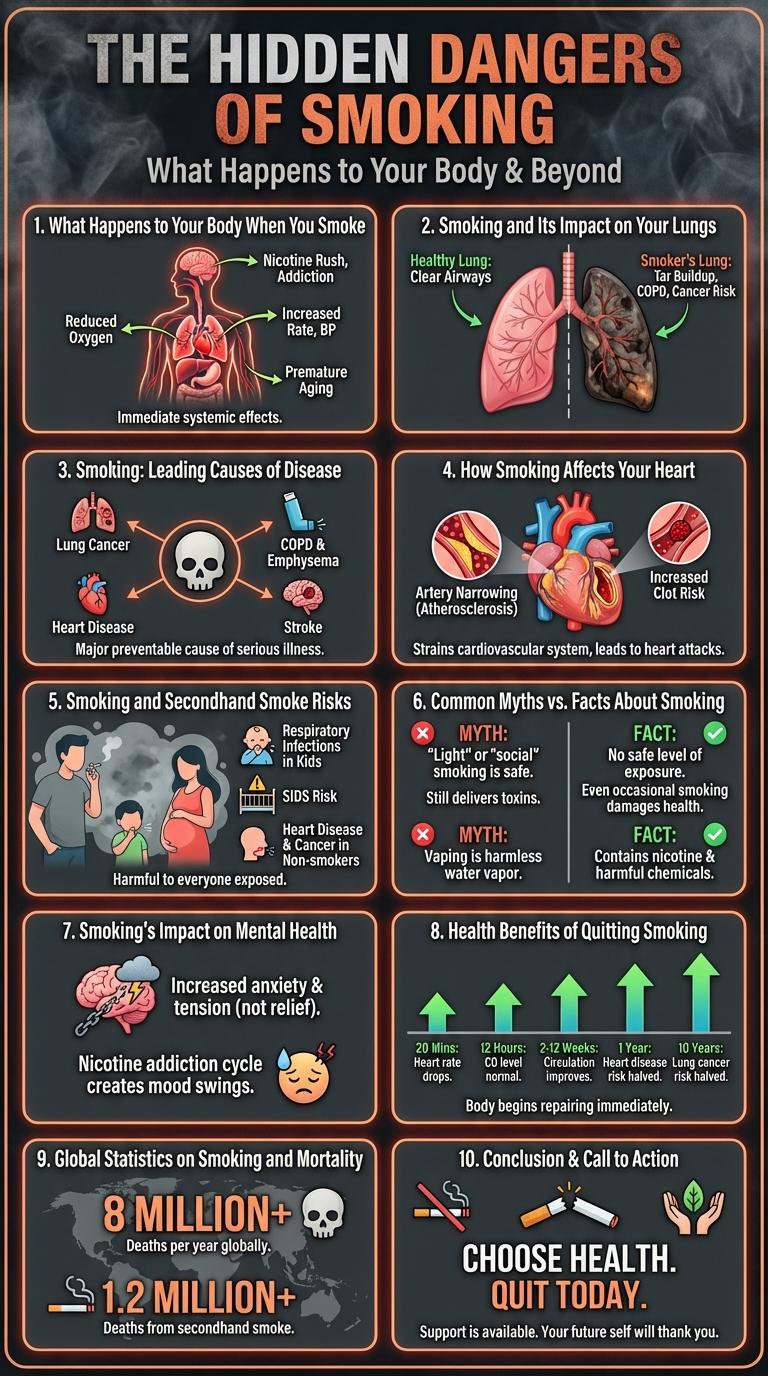
Smoking significantly impacts health by increasing the risk of respiratory diseases, heart conditions, and various cancers. Exposure to harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke damages lung tissue and reduces oxygen flow throughout the body. Visualizing these effects through an infographic highlights the urgent need for awareness and prevention measures.
The Hidden Dangers of Smoking
Smoking causes severe damage to the lungs, leading to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. Chemicals in cigarettes harm the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes. Secondhand smoke also poses significant health risks to non-smokers, including respiratory infections and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
What Happens to Your Body When You Smoke
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals into your body that affect almost every organ. These substances cause immediate and long-term damage to your health.
- Respiratory System Impact - Smoking damages your lungs' airways and air sacs, leading to chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
- Cardiovascular Damage - Chemicals in smoke cause blood vessel narrowing, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Immune System Suppression - Smoking weakens your immune defenses, making it harder to fight infections.
Smoking and Its Impact on Your Lungs
Smoking significantly damages lung tissue, leading to reduced lung function and chronic respiratory conditions. Harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke cause inflammation and destruction of alveoli, the tiny air sacs responsible for oxygen exchange. Long-term smoking increases the risk of lung diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer.
Smoking: Leading Causes of Disease
Smoking is a major contributor to numerous chronic diseases worldwide. It significantly increases the risk of life-threatening health conditions.
- Lung Cancer - Smoking causes approximately 85% of lung cancer cases globally.
- Cardiovascular Disease - Tobacco use doubles the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) - Smoking is the leading cause of COPD, a progressive lung disease.
Quitting smoking greatly reduces the risk of these diseases and improves overall health outcomes.
How Smoking Affects Your Heart
| Effect on Heart | Impact |
|---|---|
| Increased Heart Rate | Nicotine raises heart rate, forcing the heart to work harder. |
| High Blood Pressure | Smoking causes narrowing of blood vessels, leading to elevated blood pressure. |
| Reduced Oxygen Supply | Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin, reducing oxygen delivery to the heart muscle. |
| Blood Clot Formation | Chemicals in smoke increase clotting risk, raising chances of heart attack. |
| Coronary Artery Disease | Smoking accelerates plaque buildup in arteries, causing blockage and heart disease. |
Smoking and Secondhand Smoke Risks
Smoking exposes individuals to harmful chemicals that increase the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory issues. Secondhand smoke contains many of the same toxic substances, posing health dangers to non-smokers.
Children and pregnant women are especially vulnerable to secondhand smoke, which can cause developmental problems and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). Reducing exposure to both smoking and secondhand smoke significantly lowers the risk of chronic illnesses and improves overall public health.
Common Myths vs. Facts About Smoking
Is smoking just a harmless stress reliever? Many believe smoking reduces stress, but research shows it actually increases anxiety over time. Nicotine addiction causes mood swings and worsens mental health.
Does smoking only harm the lungs? Smoke affects the entire body, damaging the heart, blood vessels, and organs. Smoking is a leading cause of heart disease and cancer beyond the respiratory system.
Can switching to light or low-tar cigarettes reduce health risks? Light cigarettes deliver similar levels of harmful chemicals, offering no real health benefit. Smokers often inhale more deeply, negating any perceived advantage.
Is quitting smoking too late to improve health? Quitting at any age significantly decreases the risk of disease. Health benefits begin almost immediately and increase the longer one remains smoke-free.
Are smoking-related diseases inevitable for smokers? Risk varies based on genetics and exposure, but quitting smoking greatly lowers chances of disease. Avoiding tobacco remains the most effective prevention strategy.
Smoking's Impact on Mental Health
Smoking significantly affects mental health by increasing the risk of anxiety, depression, and stress-related disorders. Nicotine addiction alters brain chemistry, leading to mood swings and cognitive impairments.
Research indicates smokers are more likely to experience psychological distress compared to non-smokers. Nicotine temporarily boosts dopamine levels but ultimately disrupts emotional regulation. Quitting smoking improves mental well-being and reduces symptoms of anxiety and depression over time.
Health Benefits of Quitting Smoking
Quitting smoking significantly improves lung function and reduces the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease and stroke. Within weeks, circulation and lung capacity begin to improve, enhancing overall physical health.
Long-term benefits include a lowered risk of various cancers and a stronger immune system. Former smokers also experience better respiratory health, increased life expectancy, and improved quality of life.
