Preventing cross contamination is essential for maintaining food safety and protecting public health. Effective strategies include proper handwashing, using separate utensils, and thoroughly cleaning surfaces. Following these practices minimizes the risk of harmful bacteria spreading between foods.
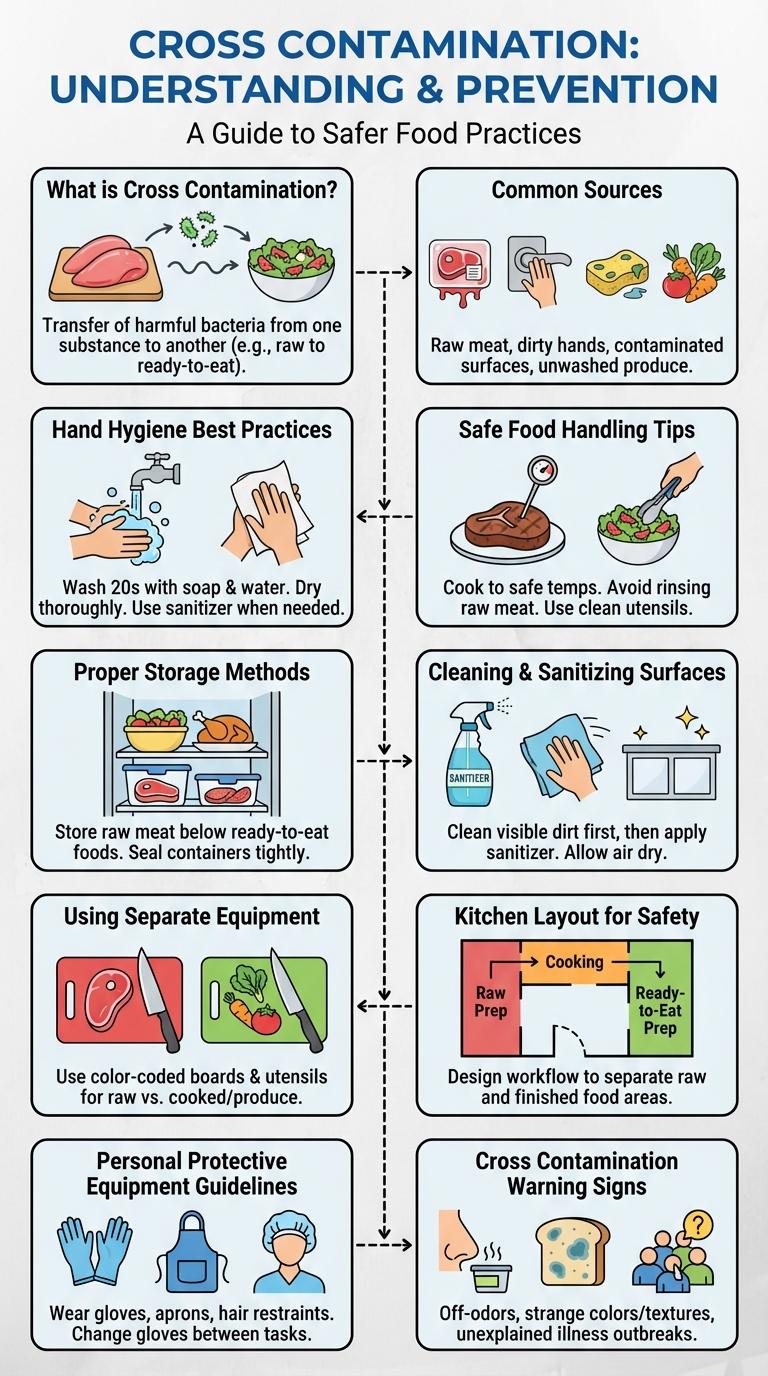
What is Cross Contamination?
Cross contamination occurs when harmful bacteria or allergens transfer from one surface, food, or object to another. This process can lead to foodborne illnesses and allergic reactions, posing serious health risks.
Preventing cross contamination involves proper food handling, cleaning, and storage practices. Understanding the sources and pathways of contamination is essential to maintain food safety in kitchens and food preparation areas.
Common Sources of Cross Contamination
What are the common sources of cross contamination in food handling?
Cross contamination often occurs through raw meat, poultry, and seafood coming into contact with ready-to-eat foods. Contaminated kitchen tools like cutting boards and utensils also play a significant role in spreading harmful bacteria.
Hand Hygiene Best Practices
Hand hygiene is the most effective way to prevent cross contamination in any environment. Regular and thorough hand washing removes harmful pathogens that can spread to food, surfaces, and people.
Use soap and warm water to wash hands for at least 20 seconds, covering all surfaces including between fingers and under nails. When handwashing is not possible, use an alcohol-based hand sanitizer with at least 60% alcohol. Always wash hands before handling food, after using the restroom, and after touching potentially contaminated surfaces.
Safe Food Handling Tips
Cross contamination is a leading cause of foodborne illnesses. Proper food handling techniques can prevent harmful bacteria from spreading.
- Separate Raw and Cooked Foods - Use different cutting boards and utensils for raw meats and ready-to-eat foods to avoid bacterial transfer.
- Wash Hands Thoroughly - Clean hands with soap and warm water for at least 20 seconds before handling food.
- Clean Surfaces Regularly - Disinfect countertops and kitchen tools after each use to eliminate pathogens.
Proper Storage Methods
| Proper Storage Method | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|
| Separate Raw and Cooked Foods | Use different containers and shelves to avoid contact and drip contamination |
| Use Airtight Containers | Prevent exposure to contaminants and maintain food safety |
| Label and Date Food Items | Ensure correct rotation using FIFO (First In, First Out) to avoid spoilage |
| Store at Correct Temperatures | Keep refrigeration below 40degF (4degC) and freezing below 0degF (-18degC) to inhibit bacterial growth |
| Clean and Sanitize Storage Areas | Regularly clean shelves and containers to minimize risk of cross contamination |
Cleaning & Sanitizing Surfaces
Effective cleaning and sanitizing of surfaces are crucial steps in preventing cross contamination in any environment. Use appropriate detergents to clean surfaces first, removing dirt and debris before applying sanitizers that kill harmful bacteria and viruses. Regularly sanitize high-touch areas such as countertops, cutting boards, and utensils to maintain a safe and hygienic workspace.
Using Separate Equipment
Preventing cross contamination is essential in maintaining food safety and avoiding foodborne illnesses. Using separate equipment for different food types significantly reduces the risk of harmful bacteria transfer.
- Color-Coded Tools - Assign specific colors to cutting boards and knives for raw meat, vegetables, and cooked foods to prevent cross-use.
- Dedicated Equipment - Use separate utensils and appliances for allergen-containing ingredients to protect individuals with allergies.
- Proper Storage - Store equipment used for raw and cooked foods separately to avoid inadvertent contamination.
Kitchen Layout for Safety
Effective kitchen layout plays a crucial role in preventing cross contamination by separating raw and cooked food areas. Designated zones for washing, prepping, cooking, and storing reduce the risk of bacteria transfer.
Separate sinks and cutting boards for raw meats and vegetables enhance hygiene and safety. Clear workflows and physical barriers minimize contact between allergens and other foods, ensuring a safer cooking environment.
Personal Protective Equipment Guidelines
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) plays a crucial role in preventing cross contamination in various environments. Proper use of PPE minimizes the transfer of harmful microorganisms between surfaces and individuals.
- Gloves must be worn and changed frequently - This reduces the risk of contaminating clean surfaces and food products after contact with potentially hazardous materials.
- Face masks prevent the spread of respiratory droplets - Wearing masks limits the transmission of airborne pathogens during interactions or food handling.
- Protective clothing should be laundered regularly - Clean uniforms and aprons reduce the buildup of contaminants and protect against cross contamination.
Strict adherence to PPE guidelines helps maintain a safe and hygienic environment, significantly lowering contamination risks.
