Eggs are a nutrient-dense food packed with high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and minerals that support overall health. Their versatile nature makes them a staple ingredient in various cuisines worldwide, from breakfast dishes to baked goods. Understanding the nutritional benefits and diverse culinary uses of eggs highlights why they remain a dietary favorite.
The Nutritional Powerhouse of Eggs
Eggs are a rich source of essential nutrients, making them a nutritional powerhouse. They provide high-quality protein and vital vitamins that support overall health.
Incorporating eggs into your diet can enhance muscle strength, brain function, and immune health.
- High-Quality Protein - Eggs contain all nine essential amino acids needed for muscle repair and growth.
- Rich in Vitamins - Eggs supply vitamins B12, D, A, and E that support energy production and cellular function.
- Essential Minerals - Eggs provide important minerals like selenium, iron, and zinc for immune system support.
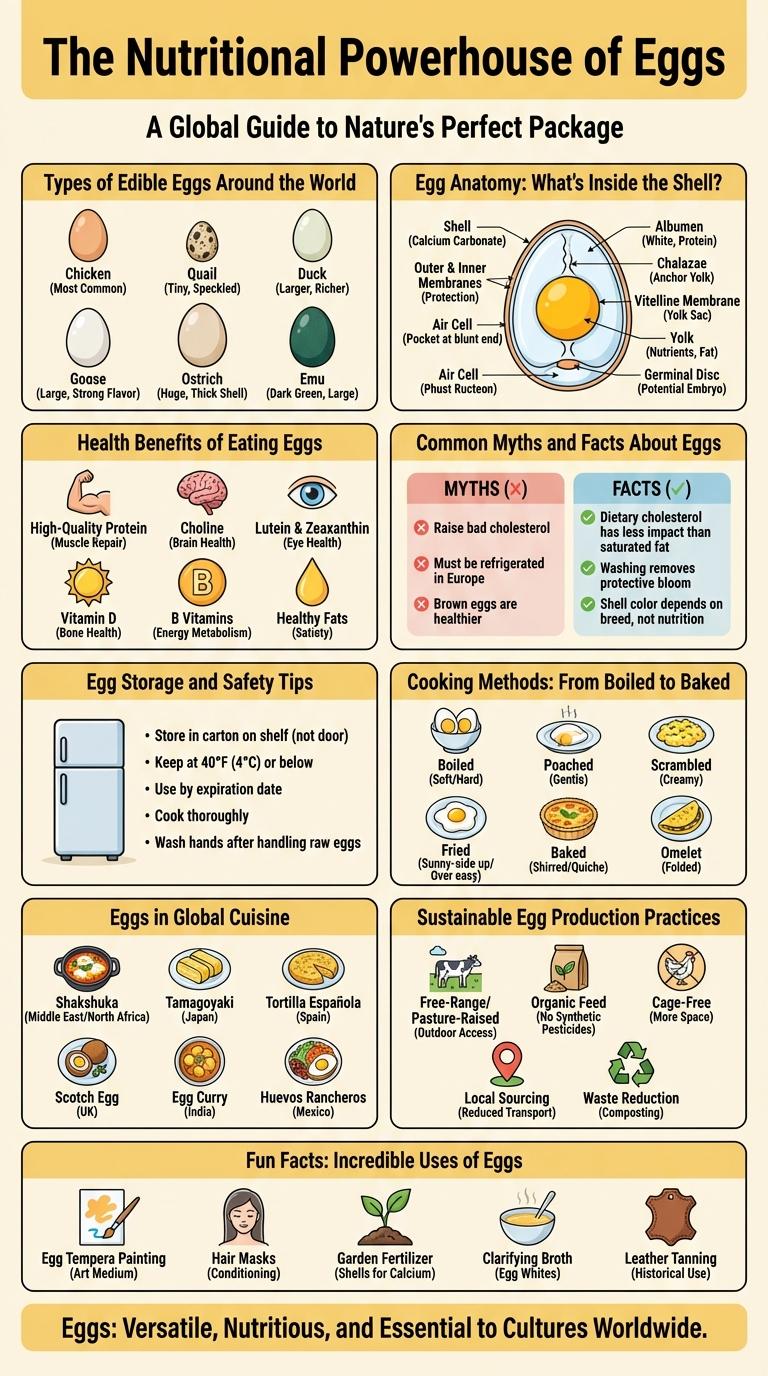
Types of Edible Eggs Around the World
Eggs are a versatile and nutritious food consumed worldwide, coming from various bird species. Different cultures favor unique types of edible eggs based on availability and culinary traditions.
Chicken eggs remain the most common, known for their balanced flavor and accessibility. Other popular edible eggs include duck, quail, goose, and ostrich, each offering distinct taste and nutritional profiles.
Egg Anatomy: What's Inside the Shell?
Eggs are complex structures providing essential nutrients for embryo development. Understanding egg anatomy reveals the purpose of each component inside the shell.
- Shell - A hard outer layer made mainly of calcium carbonate that protects the egg from physical damage and microbial invasion.
- Egg White (Albumen) - A clear, protein-rich substance that cushions the yolk and provides water and proteins to the developing embryo.
- Yolk - The nutrient-dense center containing fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals essential for embryo growth.
Each layer inside the shell works together to nurture and safeguard the embryo until hatching.
Health Benefits of Eating Eggs
| Health Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Quality Protein | Eggs contain all nine essential amino acids required by the body for muscle building and repair. |
| Rich in Vitamins | Provide important vitamins such as B12, D, A, and riboflavin which support energy production and immune function. |
| Supports Eye Health | Contain antioxidants lutein and zeaxanthin that reduce the risk of cataracts and age-related macular degeneration. |
| Heart Health | Provide choline and healthy fats that help maintain good cholesterol levels and support brain and heart function. |
| Weight Management | High protein content promotes satiety, reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight control. |
Common Myths and Facts About Eggs
Eggs are often surrounded by myths regarding their health effects and nutritional value. Understanding the facts can help make informed dietary choices.
Contrary to popular belief, eggs do not significantly raise cholesterol levels for most people. They are a rich source of high-quality protein, vitamins, and minerals. Regular egg consumption supports muscle health and eye nutrition without increasing heart disease risk in healthy individuals.
Egg Storage and Safety Tips
Proper egg storage is essential to maintain freshness and reduce the risk of foodborne illness. Store eggs in their original carton in the coldest part of the refrigerator, ideally below 40degF (4degC). Avoid placing eggs on the refrigerator door to prevent temperature fluctuations that can compromise safety.
To ensure egg safety, keep eggs refrigerated until use and cook them thoroughly to an internal temperature of 160degF (71degC). Do not consume raw or undercooked eggs, as they can contain harmful bacteria such as Salmonella. Always wash hands and kitchen surfaces after handling raw eggs to minimize contamination.
Check eggs for cracks before purchase or use, as damaged shells increase the risk of bacterial entry. Use eggs within three to five weeks of the purchase date for optimal quality. Discard eggs that have an off smell, unusual appearance, or a floating behavior in water, indicating spoilage.
Cooking Methods: From Boiled to Baked
Eggs are a versatile ingredient used in various cooking methods, each enhancing their texture and flavor. From boiling to baking, these methods transform eggs into delicious and nutritious dishes.
Boiled eggs can be soft or hard depending on cooking time, while poached eggs are gently cooked in simmering water for a delicate texture. Baked eggs involve cooking in an oven or dish, creating rich, creamy results perfect for breakfast or snacks.
Eggs in Global Cuisine
How are eggs used in global cuisine? Eggs serve as a fundamental ingredient in countless dishes across various cultures worldwide. They provide essential proteins, enhance textures, and bind ingredients together in both savory and sweet recipes.
| Region | Popular Egg Dish |
|---|---|
| Japan | Tamago Sushi |
| France | Omelette |
| Mexico | Huevos Rancheros |
| India | Egg Curry |
| United States | Egg Benedict |
Sustainable Egg Production Practices
Sustainable egg production practices prioritize animal welfare, environmental protection, and resource efficiency. These methods include cage-free systems, organic feed, and waste recycling to reduce the carbon footprint of egg farms. Implementing renewable energy sources and water conservation further supports eco-friendly and ethical egg production.
