HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the production process. The infographic visually breaks down key principles and critical steps, making complex safety protocols easier to understand and implement. Clear visuals highlight the importance of monitoring critical control points to prevent contamination and ensure consumer safety.
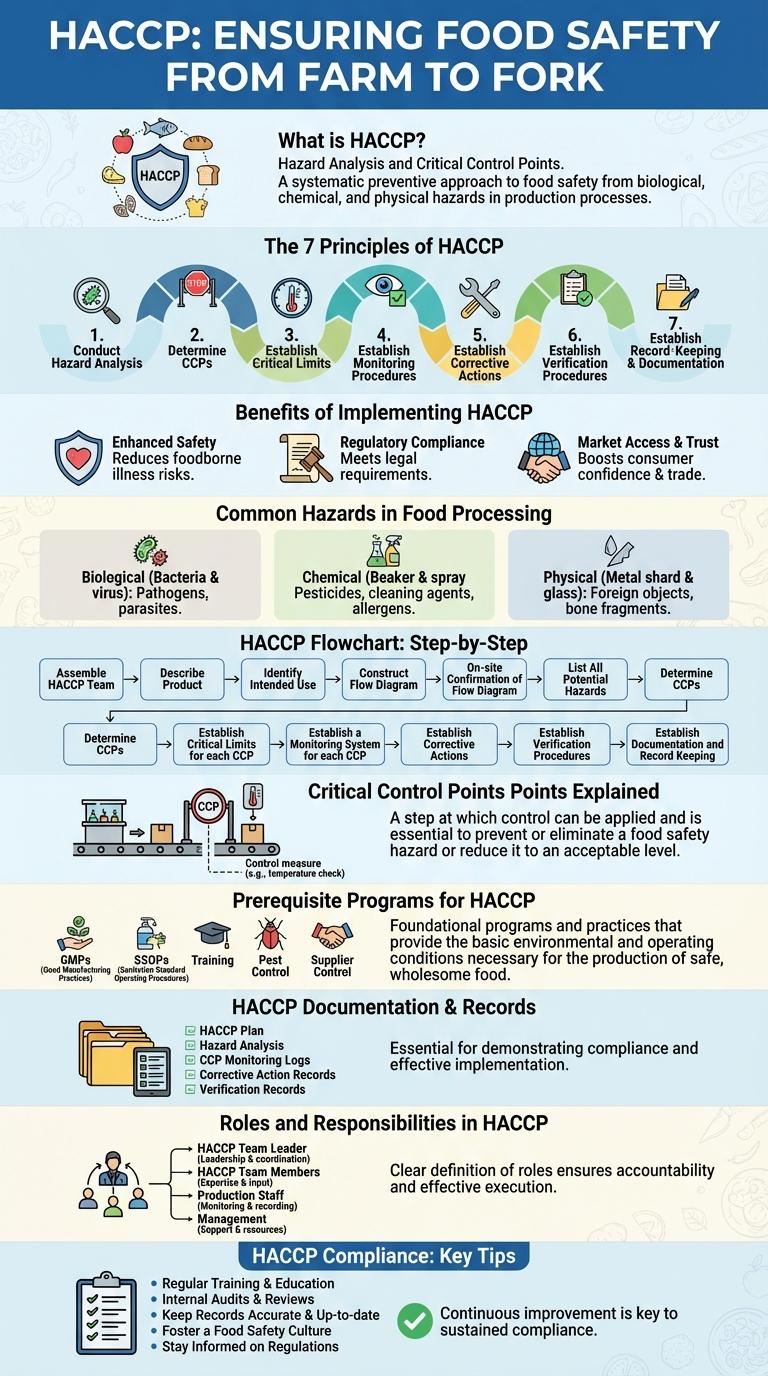
What is HACCP?
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic preventive approach to food safety. It identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the food production process. The goal is to reduce risks of biological, chemical, and physical contaminants to ensure safe food consumption.
The 7 Principles of HACCP
| HACCP Principle | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Conduct a Hazard Analysis | Identify potential biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production processes. |
| 2. Determine Critical Control Points (CCPs) | Pinpoint stages where hazards can be prevented, eliminated, or reduced to safe levels. |
| 3. Establish Critical Limits | Set maximum or minimum values for temperature, time, pH, or other factors to control hazards. |
| 4. Establish Monitoring Procedures | Implement methods for regular observation and measurement of CCPs to ensure control. |
| 5. Establish Corrective Actions | Define actions to be taken when monitoring indicates deviation from critical limits. |
| 6. Establish Verification Procedures | Confirm that HACCP system is working effectively through validation and audits. |
| 7. Establish Record-Keeping and Documentation | Maintain detailed records of hazard analyses, CCP monitoring, corrective actions, and verification. |
Benefits of Implementing HACCP
What are the benefits of implementing HACCP in food safety management?
Implementing Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) enhances food safety by systematically identifying and controlling potential hazards. It reduces the risk of contamination, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards and boosting consumer confidence.
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Reduction | Identifies critical points to prevent biological, chemical, and physical hazards in food production. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Meets international food safety standards such as FDA, USDA, and Codex Alimentarius requirements. |
| Improved Product Quality | Enhances consistency and quality by controlling production processes and reducing contamination. |
| Cost Savings | Reduces waste, recalls, and liability costs through proactive hazard management. |
| Consumer Trust | Builds brand reputation by demonstrating commitment to food safety and transparent practices. |
Common Hazards in Food Processing
HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) identifies and controls common hazards in food processing to ensure food safety. Understanding these hazards helps prevent contamination and foodborne illnesses.
- Biological Hazards - Includes bacteria, viruses, and parasites that can cause foodborne diseases if not properly controlled.
- Chemical Hazards - Involves harmful substances like pesticides, cleaning agents, and allergens that contaminate food products.
- Physical Hazards - Refers to foreign objects such as metal fragments, glass, or plastic that can injure consumers.
HACCP Flowchart: Step-by-Step
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards. The HACCP flowchart outlines each step in the process to ensure safe food production.
The flowchart begins with identifying potential hazards and determining critical control points (CCPs). Next, it involves establishing critical limits, monitoring procedures, corrective actions, verification, and record-keeping to maintain safety standards.
Critical Control Points Explained
Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) is a systematic approach to food safety that identifies, evaluates, and controls hazards throughout the food production process. Critical Control Points (CCPs) are specific stages where control is essential to prevent or eliminate food safety hazards.
Each CCP has defined limits that must be met to ensure safety, such as temperature thresholds or contamination prevention measures. Monitoring procedures for CCPs include regular checks and documentation to maintain compliance. When deviations occur at a CCP, corrective actions are immediately implemented to protect consumers.
Prerequisite Programs for HACCP
Prerequisite Programs (PRPs) form the foundation of an effective HACCP system by ensuring a hygienic environment and safe food handling practices. These programs address basic operational conditions essential for food safety before applying HACCP principles.
Common PRPs include facility sanitation, pest control, employee hygiene, and equipment maintenance. Implementing robust PRPs minimizes hazards and supports the critical control points identified in HACCP plans.
HACCP Documentation & Records
HACCP Documentation and Records are essential for ensuring food safety and regulatory compliance. They include detailed hazard analyses, critical control points, monitoring procedures, and corrective actions. Proper maintenance of these records supports traceability and continuous improvement in food production processes.
Roles and Responsibilities in HACCP
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to food safety focused on preventing hazards during food production. Clear roles and responsibilities within the HACCP team ensure effective implementation and monitoring of the system.
- HACCP Team Leader - Oversees the development and maintenance of the HACCP plan, ensuring all hazards are identified and controlled.
- Quality Assurance Manager - Verifies compliance with food safety standards and reviews critical control point monitoring records.
- Production Staff - Follows established procedures, monitors critical control points, and reports deviations immediately.
- Sanitation Personnel - Ensures hygiene practices and cleaning schedules minimize contamination risks at all stages.
- Management - Provides resources, training, and enforces HACCP policies throughout the organization.
Effective collaboration among all roles guarantees a robust HACCP system that protects consumer health and complies with regulatory requirements.
