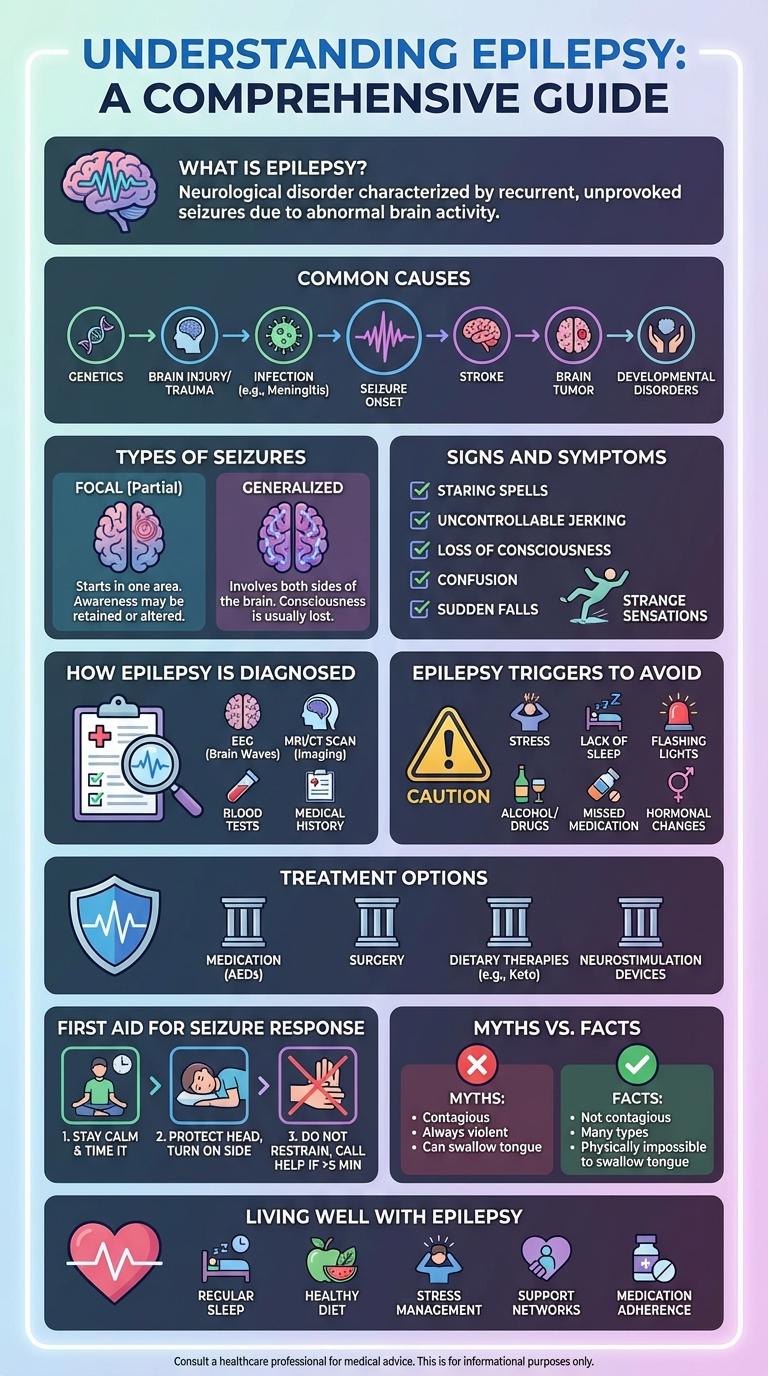
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures affecting millions worldwide. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for effective management and awareness. This infographic provides clear, concise information to help educate and empower individuals about epilepsy.
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, unprovoked seizures. It affects people of all ages worldwide, with varying causes and symptoms.
- Definition - Epilepsy involves abnormal electrical activity in the brain causing seizures.
- Prevalence - Over 50 million people globally live with epilepsy, making it one of the most common neurological conditions.
- Cause - Seizures may result from genetic factors, brain injury, infections, or unknown origins.
Proper diagnosis and treatment can help most individuals control seizures and lead normal lives.
Common Causes of Epilepsy
What are the common causes of epilepsy?
Epilepsy is typically caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain resulting from various conditions. Identifying the underlying cause helps in managing and treating seizures effectively.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Genetic Factors | Inherited gene mutations that increase the risk of seizures. |
| Brain Injury | Traumatic injuries or trauma leading to scar tissue and seizure activity. |
| Stroke | Interrupted blood supply causes brain damage triggering epilepsy. |
| Infections | Encephalitis or meningitis causing inflammation and nerve damage. |
| Developmental Disorders | Conditions like autism or neurofibromatosis increase epilepsy risk. |
Types of Seizures
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal brain activity. Types of seizures include focal seizures, which affect one part of the brain, and generalized seizures, involving both brain hemispheres. Understanding seizure types helps guide treatment and management strategies for individuals with epilepsy.
Signs and Symptoms
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal brain activity. Signs and symptoms vary widely depending on the type of seizure experienced.
Common symptoms include sudden convulsions, loss of consciousness, and uncontrollable jerking movements. Some individuals may experience sensory disturbances, confusion, or brief lapses in awareness.
How Epilepsy is Diagnosed
Epilepsy is diagnosed through a combination of medical history review and diagnostic tests. These steps help differentiate epilepsy from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Doctors begin by evaluating the patient's seizure history and conducting a physical and neurological examination. Electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings are used to detect abnormal brain activity associated with epilepsy. Imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans identify structural brain abnormalities that may contribute to seizures.
Epilepsy Triggers to Avoid
Epilepsy triggers vary but common ones include stress, lack of sleep, and flashing lights. Avoiding these triggers can help reduce the frequency of seizures. Identifying personal triggers through a seizure diary is essential for effective management.
Treatment Options for Epilepsy
Epilepsy treatment varies depending on the type and frequency of seizures. Effective management includes medication, therapy, and sometimes surgery to control symptoms.
Treatment aims to reduce or eliminate seizures and improve quality of life for individuals with epilepsy.
- Anti-Epileptic Drugs (AEDs) - Medications that help control seizures by stabilizing electrical activity in the brain.
- Surgical Intervention - Procedures that remove or alter brain areas causing seizures, considered when medication is ineffective.
- Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS) - A device implanted to stimulate the vagus nerve and reduce seizure frequency.
First Aid for Seizure Response
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures caused by abnormal brain activity. Recognizing and responding promptly to seizures can prevent injury and save lives.
First aid for seizure response involves ensuring the person's safety by clearing the surrounding area to prevent harm. Do not restrain the person or put objects in their mouth during the seizure.
Myths vs. Facts about Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a neurological disorder often misunderstood due to widespread myths. Clarifying facts helps in reducing stigma and improving support for those affected.
- Myth: Epilepsy is contagious - Epilepsy is a brain condition and cannot be transmitted from person to person.
- Fact: People with epilepsy can lead normal lives - With proper treatment, many individuals manage seizures effectively and maintain daily activities.
- Myth: Seizures always involve convulsions - Seizures vary greatly and can include subtle symptoms like staring or brief confusion.
- Fact: Epilepsy affects all ages - This condition can begin in childhood or later in life, affecting diverse populations.
- Myth: Epilepsy is caused by mental illness - Epilepsy is a neurological disorder, distinct from psychiatric conditions.
