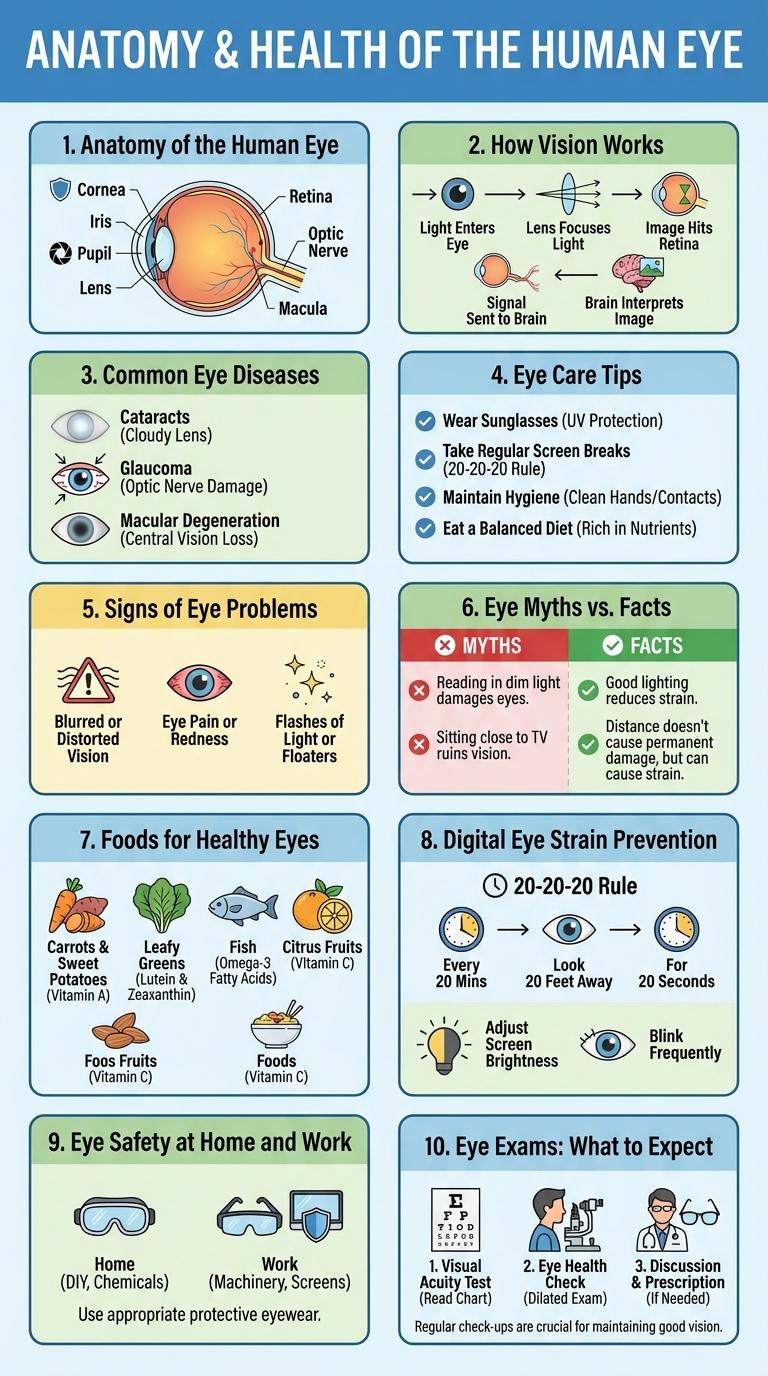
Infographics about eyes provide a clear visual representation of eye anatomy, common conditions, and essential care tips. They highlight key facts such as how the eye processes light and the importance of regular eye exams for maintaining vision health. These informative graphics simplify complex information, making it easier to understand and remember.
Anatomy of the Human Eye
| Part of the Eye | Function |
|---|---|
| Cornea | Transparent outer layer that protects the eye and focuses light |
| Iris | Colored part controlling pupil size to regulate light entry |
| Pupil | Opening that adjusts size to control light amount reaching the retina |
| Lens | Flexible structure that changes shape to focus images on the retina |
| Retina | Layer containing photoreceptor cells that convert light into neural signals |
How Vision Works
How does the human eye process visual information?
The eye captures light through the cornea, which bends it toward the lens. The lens then focuses the light onto the retina, where photoreceptor cells convert it into electrical signals.
What role does the retina play in vision?
The retina contains rods and cones that detect light intensity and color. These photoreceptors transform light into neural signals sent to the brain via the optic nerve.
How does the brain interpret images from the eyes?
The optic nerve transmits visual information to the visual cortex located in the occipital lobe. The brain processes these signals to create detailed, three-dimensional images.
Why is pupil size important in vision?
The pupil controls the amount of light entering the eye by adjusting its size. This regulation helps optimize vision under varying lighting conditions.
What is the significance of the lens adjusting shape?
The lens changes shape through accommodation to focus on objects at different distances. This flexibility ensures clear vision for both near and far objects.
Common Eye Diseases
Eyes are vital organs that enable vision and perception of the world. Maintaining eye health is crucial to prevent common diseases that can impair sight.
Common eye diseases include cataracts, glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetic retinopathy, and conjunctivitis. Cataracts cause clouding of the eye lens, leading to blurred vision. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve, often due to high eye pressure, and can result in vision loss if untreated.
Eye Care Tips
Healthy eyes are essential for clear vision and overall well-being. Proper eye care helps prevent common eye problems and maintain long-term eye health.
- Regular Eye Exams - Schedule comprehensive eye check-ups to detect issues early and maintain optimal vision.
- Protective Eyewear - Wear sunglasses with UV protection to shield eyes from harmful ultraviolet rays.
- Screen Time Management - Follow the 20-20-20 rule to reduce digital eye strain during prolonged device use.
Incorporating these eye care tips into daily routines supports lifelong visual health.
Signs of Eye Problems
Healthy eyes are crucial for clear vision and overall quality of life. Recognizing early signs of eye problems can prevent serious damage and preserve eyesight.
- Blurred Vision - Difficulty focusing or seeing fine details often indicates refractive errors or other eye conditions.
- Eye Pain - Persistent discomfort may signal infections, glaucoma, or inflammation requiring medical attention.
- Flashes and Floaters - Sudden spots, flashes of light, or floating shapes can be symptoms of retinal detachment or vitreous changes.
Eye Myths vs. Facts
Many common beliefs about eyes are myths that can mislead people about eye health and vision. For example, reading in dim light does not damage the eyes, but it can cause temporary eye strain. Understanding the facts about eyes helps promote better eye care and dispels misinformation.
| Eye Myth | Eye Fact |
|---|---|
| Reading in dim light damages your eyes. | It causes eye strain but does not cause permanent damage. |
| Eating carrots significantly improves vision. | Carrots support eye health but don't drastically improve vision. |
| Sitting too close to the TV harms your eyesight. | It strains eyes temporarily but does not cause lasting harm. |
| Wearing glasses makes your eyesight worse. | Glasses correct vision and do not worsen eye health. |
| Eyes need rest only during sleep. | Regular breaks from screens reduce eye strain and promote comfort. |
Foods for Healthy Eyes
Foods rich in antioxidants and essential nutrients play a crucial role in maintaining healthy eyes. Incorporating vitamins A, C, and E, along with omega-3 fatty acids, can help protect against age-related eye conditions.
Leafy greens, colorful fruits, and fish are excellent sources of eye-friendly nutrients. Consistent intake of these foods supports vision clarity and reduces the risk of macular degeneration and cataracts.
Digital Eye Strain Prevention
Digital Eye Strain affects millions worldwide due to prolonged screen exposure, causing symptoms like dryness, headaches, and blurred vision. Preventive measures include the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds to reduce eye fatigue. Proper screen brightness, ergonomic positioning, and regular eye check-ups help maintain optimal eye health in a digital environment.
Eye Safety at Home and Work
Protecting your eyes from injury is essential both at home and in the workplace. Simple precautions can prevent most eye accidents and maintain long-term vision health.
- Wear Protective Eyewear - Use safety goggles or glasses when handling chemicals, power tools, or performing tasks with flying debris.
- Maintain Proper Lighting - Ensure workspaces have adequate lighting to reduce eye strain and prevent accidents caused by poor visibility.
- Keep Hazardous Materials Away - Store cleaning products and sharp objects safely out of reach to avoid accidental splashes or cuts to the eyes.
