Vaping has rapidly gained popularity as a modern alternative to traditional smoking, offering a variety of devices and e-liquids tailored to different preferences. Infographics provide a clear visual representation of vaping trends, health implications, and regulatory updates, making complex information easy to understand. This infographic highlights key data on vaping demographics, usage patterns, and safety considerations to inform and educate readers effectively.
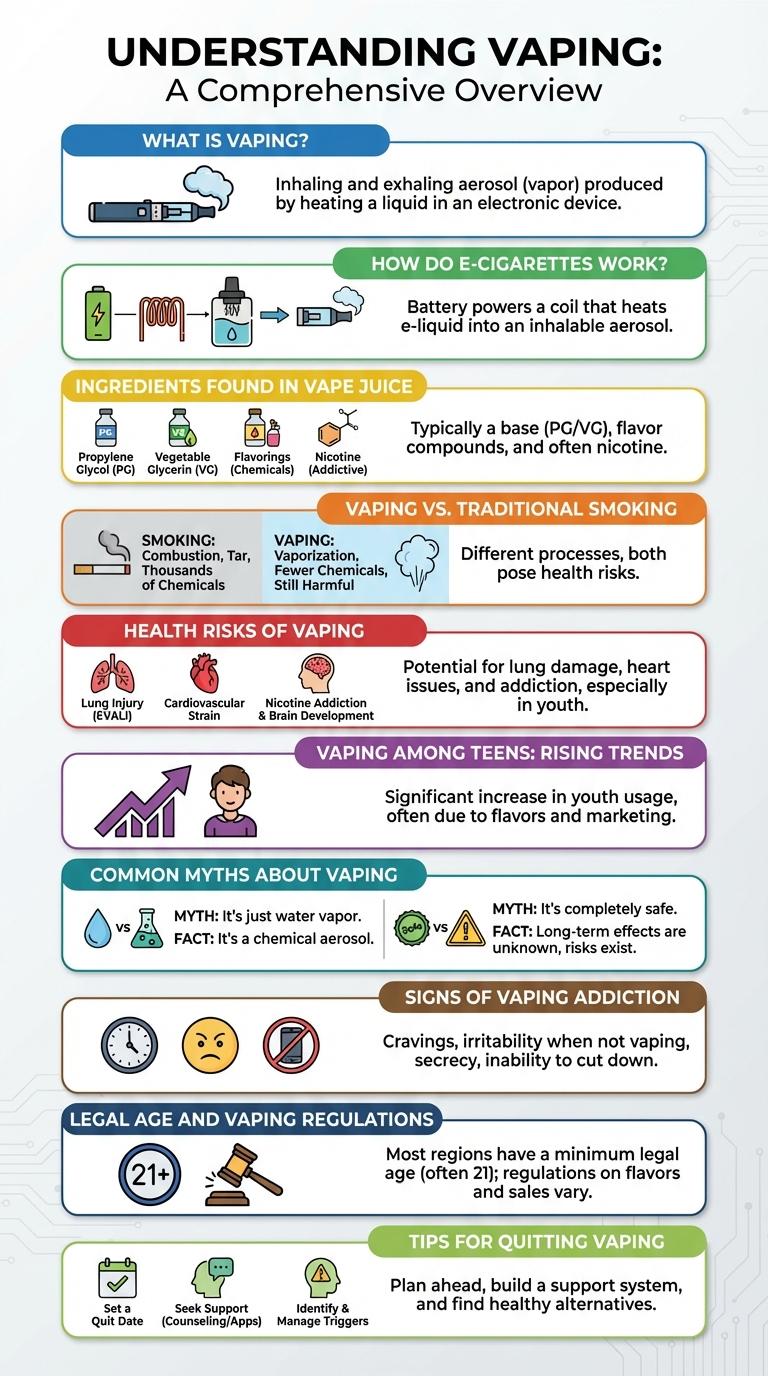
What Is Vaping?
Vaping involves inhaling vapor produced by an electronic cigarette or similar device. These devices heat a liquid, often containing nicotine, flavorings, and other chemicals, to create an aerosol.
Unlike traditional smoking, vaping does not burn tobacco but delivers nicotine through vapor. This method is popular among those seeking alternatives to cigarettes or methods to quit smoking.
How Do E-Cigarettes Work?
E-cigarettes are battery-powered devices that heat a liquid to create an inhalable vapor. They are designed as an alternative to traditional tobacco smoking by simulating the experience without burning tobacco.
- Battery Activation - The device uses a rechargeable battery to power the heating element when the user inhales or presses a button.
- Heating Coil - A coil heats the e-liquid to a temperature that turns it into vapor without combustion.
- E-Liquid Composition - The liquid typically contains nicotine, flavorings, and a base of propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin.
The vapor produced delivers nicotine and flavors to the user's lungs, mimicking the sensation of traditional smoking.
Ingredients Found in Vape Juice
Vape juice, also known as e-liquid, primarily contains propylene glycol, vegetable glycerin, nicotine, and flavorings. Propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin create the vapor when heated, while nicotine is the addictive component. Flavorings add taste but may include chemicals with unknown long-term health effects.
Vaping vs. Traditional Smoking
| Vaping | Traditional Smoking |
|---|---|
| Uses e-liquids with nicotine or nicotine-free options | Burns tobacco releasing nicotine and harmful tar |
| Produces vapor containing fewer toxic chemicals | Generates smoke containing thousands of harmful chemicals including tar and carbon monoxide |
| Less odor and residue compared to smoke | Strong and persistent odor with sticky residue on surfaces |
| Long-term health effects still under study but considered less harmful than smoking | Proven to cause lung cancer, heart disease, and chronic respiratory illnesses |
| Instant vapor inhalation and fewer toxins inhaled | Combustion process leads to inhalation of smoke and carcinogens |
Health Risks of Vaping
Vaping introduces harmful chemicals such as nicotine, formaldehyde, and acrolein into the lungs, increasing the risk of respiratory issues and lung damage. Studies link vaping to conditions like bronchitis, asthma exacerbation, and potential long-term cardiovascular problems. Awareness of these health risks is crucial for making informed decisions about vaping habits.
Vaping Among Teens: Rising Trends
Why is vaping among teens becoming a significant concern?
Recent studies show a sharp increase in teen vaping rates, with over 25% of high school students reporting e-cigarette use in the past month. This rise poses health risks related to nicotine addiction and respiratory problems.
Common Myths About Vaping
Vaping has become increasingly popular, but many misconceptions surround its use and safety. Understanding the facts helps users make informed decisions about vaping.
- Vaping is completely safe - Vaping is not risk-free; it contains nicotine and other harmful chemicals that can affect health.
- Vaping helps everyone quit smoking - While vaping can aid some smokers, it is not a guaranteed cessation method for everyone.
- Vaping produces only harmless water vapor - The aerosol from vaping contains nicotine, flavorings, and potentially toxic substances.
Signs of Vaping Addiction
Vaping addiction occurs when the use of e-cigarettes becomes a compulsive habit despite negative consequences. Recognizing the signs early can help prevent long-term health issues.
Common signs of vaping addiction include frequent cravings and inability to quit or reduce usage. Other indicators are increased tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, and neglect of daily responsibilities.
Legal Age and Vaping Regulations
Vaping regulations and legal age requirements vary significantly across different regions. Understanding these laws helps ensure compliance and promotes responsible vaping.
- Legal Age - Most countries set the minimum vaping age at 18 or 21 to restrict access by minors.
- Sales Restrictions - Retailers are often required to verify age before selling vaping products to prevent underage purchases.
- Advertising Limits - Many regulations prohibit marketing vaping products to youth to reduce appeal and exposure.
- Flavor Bans - Some jurisdictions ban flavored e-liquids to minimize youth vaping initiation.
- Usage Restrictions - Vaping is commonly banned in indoor public spaces similar to smoking laws.
