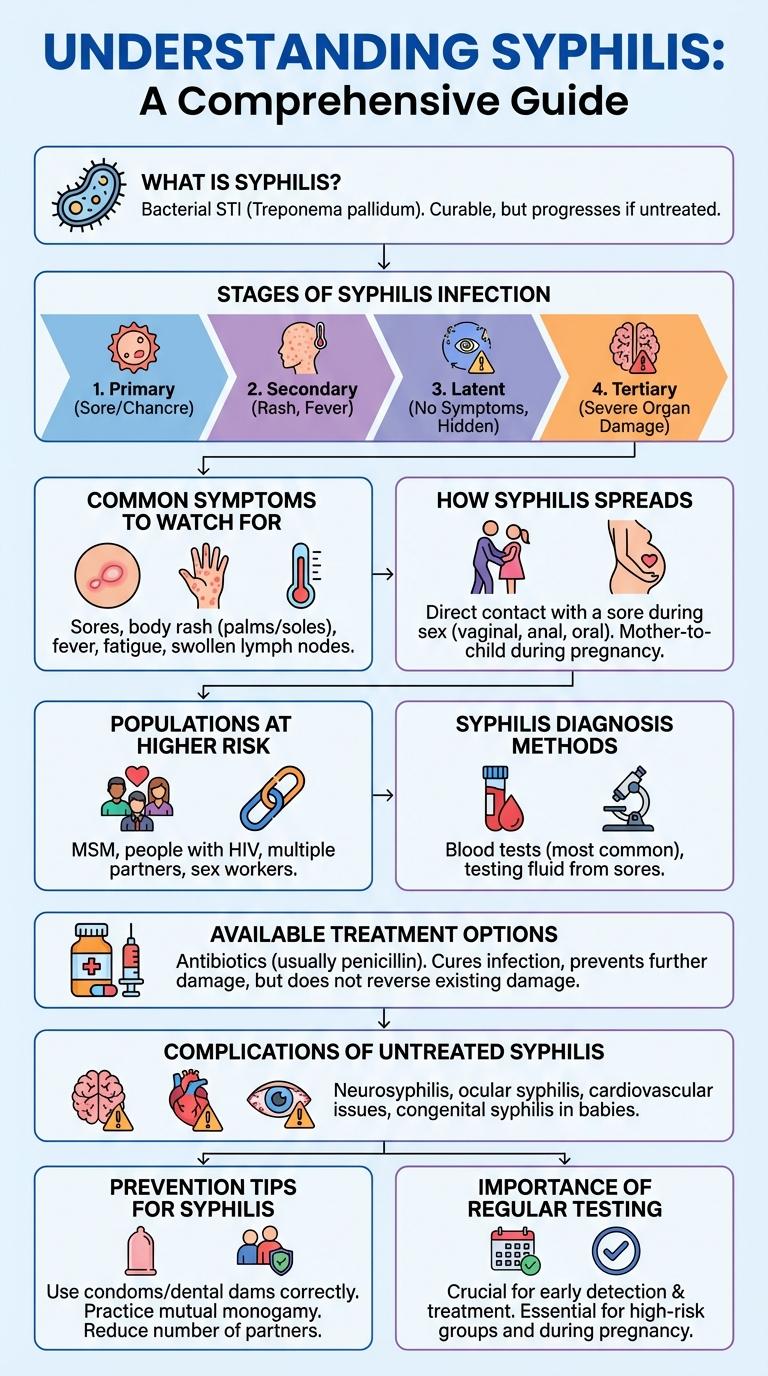
Syphilis is a contagious infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum, primarily spread through sexual contact. Early symptoms include sores and rashes, which can progress to serious complications if left untreated. Understanding the stages, transmission methods, and prevention strategies is crucial for effective management and control of this disease.
What is Syphilis?
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It progresses in stages, starting with sores at the infection site, followed by skin rashes and mucous membrane lesions. Early diagnosis and treatment with antibiotics can prevent serious health complications.
Stages of Syphilis Infection
Syphilis infection progresses through four distinct stages: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary. Each stage exhibits unique symptoms, from painless sores in the primary stage to severe organ damage in the tertiary stage. Early detection and treatment with antibiotics are crucial to prevent complications and transmission.
Common Symptoms to Watch For
| Common Symptoms | Description |
|---|---|
| Chancre | Painless sore appearing at the infection site, typically on genitals, mouth, or anus. |
| Rash | Red or reddish-brown spots on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet, often non-itchy. |
| Fatigue | Persistent tiredness and weakness experienced during secondary syphilis stage. |
| Fever | Low-grade fever accompanying early infection phases. |
| Swollen Lymph Nodes | Enlarged lymph nodes near the site of infection or throughout the body. |
How Syphilis Spreads
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. It primarily spreads through direct contact with syphilitic sores during vaginal, anal, or oral sex.
These sores, also called chancres, are highly infectious and can appear on the genitals, rectum, or mouth. Transmission can occur even when sores are not visible, due to microscopic lesions. Mother-to-child transmission is possible during pregnancy, leading to congenital syphilis.
Populations at Higher Risk
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection that disproportionately affects certain high-risk groups. Awareness of populations at higher risk is crucial for targeted prevention and treatment efforts.
- Men who have sex with men (MSM) - This group experiences the highest rates of syphilis due to network patterns and exposure risks.
- People living with HIV - Co-infection with syphilis is common among individuals with HIV, complicating treatment and transmission dynamics.
- Sex workers - Frequent partner changes and limited access to healthcare increase syphilis risk in sex workers.
- Pregnant women - Untreated syphilis in pregnancy can lead to serious complications such as congenital syphilis.
- Individuals with multiple sexual partners - High partner turnover elevates the likelihood of encountering an infected partner.
Syphilis Diagnosis Methods
Syphilis diagnosis relies on a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to detect the presence of Treponema pallidum. Accurate diagnosis is essential for timely treatment and preventing complications.
- Darkfield Microscopy - Direct visualization of Treponema pallidum from lesion samples under a microscope confirms infection in early stages.
- Non-treponemal Tests - Rapid plasma reagin (RPR) and Venereal Disease Research Laboratory (VDRL) tests detect antibodies indicating active syphilis infection.
- Treponemal Tests - Fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption (FTA-ABS) and enzyme immunoassays (EIA) confirm past or current syphilis exposure by detecting specific antibodies.
Combining these diagnostic methods improves accuracy and guides effective treatment decisions.
Available Treatment Options
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent serious health complications.
Penicillin remains the most effective treatment option for all stages of syphilis. Alternative antibiotics, such as doxycycline or azithromycin, are available for those allergic to penicillin.
Prevention Tips for Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial infection primarily transmitted through sexual contact. Preventing syphilis involves proactive measures that reduce the risk of infection and promote early detection.
- Practice Safer Sex - Use condoms consistently and correctly during all sexual activities to lower syphilis transmission risk.
- Regular Testing - Get routine syphilis screenings, especially if you have multiple partners or engage in high-risk behaviors.
- Limit Sexual Partners - Reducing the number of sexual partners decreases exposure to syphilis and other sexually transmitted infections.
Complications of Untreated Syphilis
What are the complications of untreated syphilis? Untreated syphilis can cause serious health problems affecting multiple organ systems. It often progresses through stages, leading to severe and potentially life-threatening conditions.
How does untreated syphilis impact the nervous system? Neurosyphilis can develop, causing headaches, difficulty coordinating muscle movements, paralysis, numbness, and dementia. This occurs when the infection spreads to the brain and spinal cord.
Can untreated syphilis cause cardiovascular problems? Yes, cardiovascular syphilis can damage the heart and blood vessels, leading to aneurysms or inflammation of the aorta. These complications may result in heart failure or stroke if not managed.
What effects does untreated syphilis have during pregnancy? It can lead to congenital syphilis, causing stillbirth, neonatal death, or serious deformities in the newborn. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical to prevent such outcomes.
Are there chronic complications from untreated syphilis? Chronic untreated syphilis can result in gummatous lesions, permanent organ damage, and increased vulnerability to HIV infection. Long-term health consequences highlight the importance of timely treatment.
