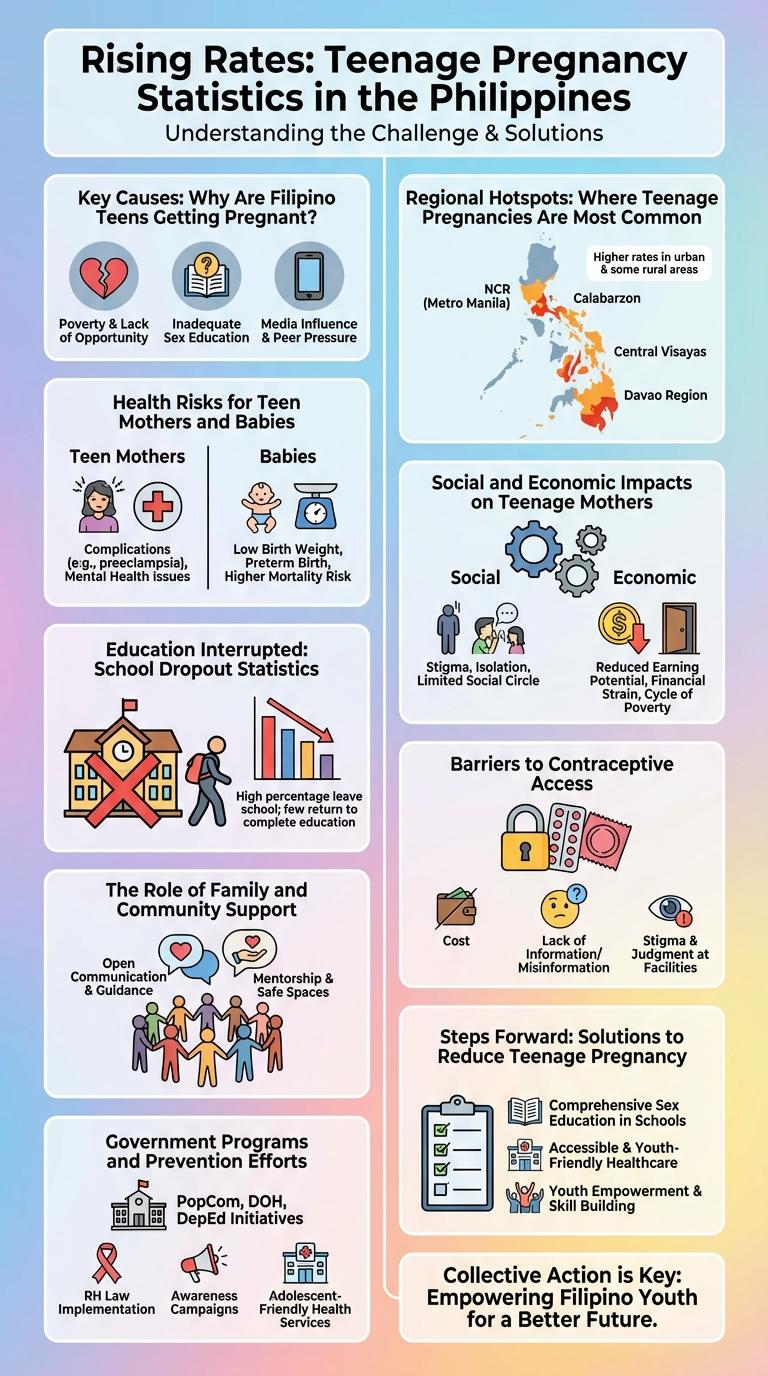
Teenage pregnancy in the Philippines remains a pressing social issue, with significant implications for health, education, and economic outcomes. Infographics provide a clear visual representation of key statistics, trends, and contributing factors, making complex data more accessible and impactful. Understanding these elements is crucial for developing effective policies and support systems to address the challenges faced by young mothers.
Rising Rates: Teenage Pregnancy Statistics in the Philippines
Teenage pregnancy in the Philippines has shown a significant increase over the past decade. This trend poses challenges for the health, education, and economic opportunities of young mothers and their children.
- Rising Teenage Birth Rates - The country recorded approximately 134,000 births among women aged 15-19 in 2022, marking a steady rise from previous years.
- Regional Disparities - Teenage pregnancy rates are highest in the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao and certain rural provinces, reflecting varied access to reproductive health services.
- Impact on Education - Nearly 40% of teenage mothers drop out of school, limiting their future employment and income potential.
Efforts to address teenage pregnancy focus on comprehensive sex education, improved healthcare access, and community support programs across the Philippines.
Key Causes: Why Are Filipino Teens Getting Pregnant?
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health concern in the Philippines, with multiple factors contributing to its prevalence. Understanding these key causes helps address the issue more effectively.
- Lack of Comprehensive Sex Education - Many Filipino teens receive limited or inaccurate information about reproductive health, leading to poor decision-making.
- Poverty and Economic Factors - Economic hardship often drives early pregnancy due to limited access to healthcare and contraceptives.
- Family and Community Influence - Cultural norms and family expectations sometimes encourage early marriage and childbearing among teens.
Regional Hotspots: Where Teenage Pregnancies Are Most Common
Teenage pregnancy remains a significant public health challenge in the Philippines, with certain regions experiencing notably higher rates. Understanding these regional hotspots helps target interventions effectively.
Regions such as the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM), Northern Mindanao, and the Cordillera Administrative Region report the highest teenage pregnancy rates. Socioeconomic factors, limited access to reproductive health education, and cultural influences contribute to these elevated numbers. Local governments are focusing efforts on education and healthcare services to address the issue.
Health Risks for Teen Mothers and Babies
What are the health risks associated with teenage pregnancy in the Philippines? Teenage mothers face higher chances of complications such as anemia, preeclampsia, and premature labor. Babies born to teen mothers are more likely to experience low birth weight, respiratory issues, and developmental delays.
How does teenage pregnancy impact maternal health in the Philippines? Teenage mothers often encounter increased risks of obstetric fistula, maternal mortality, and inadequate prenatal care. Limited access to healthcare exacerbates these health challenges, leading to poorer outcomes for mother and child.
| Health Risk | Description |
|---|---|
| Anemia | Reduced oxygen supply causing fatigue and weakness in teen mothers. |
| Preterm Birth | Increased likelihood of babies born before 37 weeks gestation. |
| Low Birth Weight | Newborns weighing less than 2,500 grams with higher mortality risk. |
| Obstetric Fistula | Childbirth injury causing urinary or fecal incontinence in teens. |
| Maternal Mortality | Higher risk of death during pregnancy or childbirth among adolescents. |
Social and Economic Impacts on Teenage Mothers
Teenage pregnancy in the Philippines significantly affects young mothers' social lives, often leading to stigma and isolation within their communities. Many teenage mothers face interrupted education, limiting their job opportunities and perpetuating cycles of poverty. Economic hardships increase as these young women struggle to balance childcare responsibilities with the need for financial stability.
Education Interrupted: School Dropout Statistics
| Statistic | Data |
|---|---|
| Teenage pregnancy rate | Approximately 12% of Filipino girls aged 15-19 have given birth |
| School dropout rate among pregnant teens | Over 50% of pregnant teenagers discontinue their education |
| Reasons for leaving school | Pregnancy, financial difficulties, stigma |
| Impact on education | Interrupted or early termination of secondary education |
| Programs supporting teenage mothers | Alternative learning systems, scholarship grants, counseling services |
Barriers to Contraceptive Access
Teenage pregnancy in the Philippines remains a critical public health issue with significant social and economic consequences. Barriers to contraceptive access contribute heavily to high rates of adolescent pregnancies.
The following key obstacles limit Filipino teens' ability to obtain effective contraception:
- Lack of Comprehensive Sex Education - Many adolescents do not receive accurate information about reproductive health and contraception options in schools.
- Cultural and Religious Stigma - Strong societal norms and religious beliefs discourage open discussion and use of contraceptives among teenagers.
- Limited Access to Youth-Friendly Health Services - Health centers often lack confidential and adolescent-focused contraceptive services.
- Financial Constraints - Many teenagers cannot afford contraceptives due to poverty or lack of subsidy programs.
- Legal and Policy Barriers - Restrictions on distributing contraceptives to minors without parental consent limit accessibility.
The Role of Family and Community Support
Teenage pregnancy in the Philippines remains a significant social issue, with family and community support playing a crucial role in addressing it. Strong family bonds and guidance help young mothers continue their education and improve their wellbeing.
Communities that offer counseling, health services, and educational programs contribute significantly to reducing teenage pregnancy rates. Collective efforts foster a supportive environment that empowers teenagers to make informed choices about their futures.
Government Programs and Prevention Efforts
The Philippine government implements comprehensive programs to address teenage pregnancy, such as the Adolescent Health and Development Program, which provides reproductive health education and counseling. Local government units collaborate with schools and communities to promote awareness campaigns and access to contraceptive services. These prevention efforts aim to empower Filipino youth with knowledge and resources to make informed decisions about their sexual health.
