Substance abuse significantly impacts individuals and communities, leading to health complications and social challenges. Visualizing key data through an infographic highlights trends, risks, and preventive measures effectively. Understanding these insights can drive informed decisions and promote healthier lifestyles.
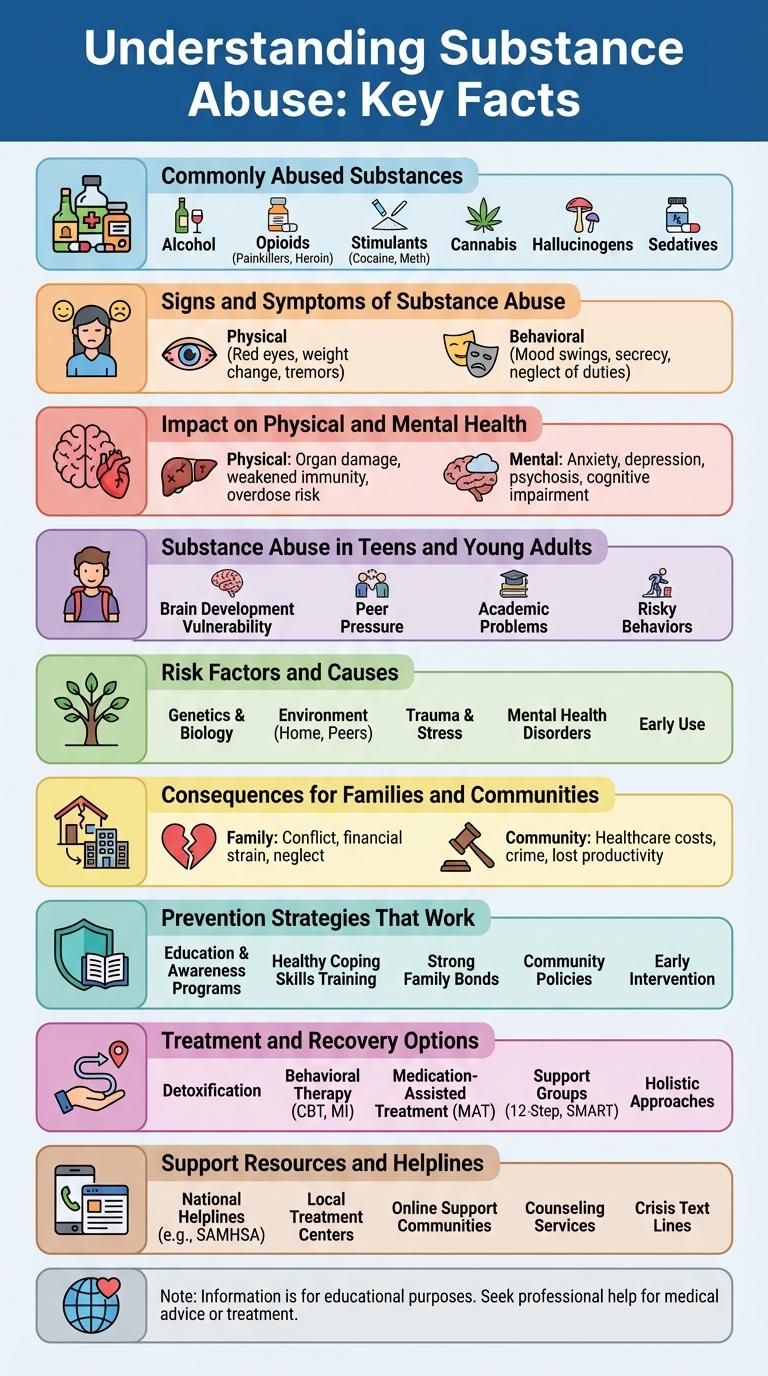
Understanding Substance Abuse: Key Facts
What is substance abuse and why is it a critical issue? Substance abuse involves the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including alcohol and illicit drugs. It poses serious health risks and social challenges worldwide.
How prevalent is substance abuse globally? Over 35 million people suffer from drug use disorders according to the World Health Organization. Alcohol misuse contributes to more than 3 million deaths annually.
Which substances are most commonly abused? The most frequently abused substances include alcohol, cannabis, opioids, and stimulants like cocaine and methamphetamine. Prescription medication misuse also significantly contributes to substance abuse statistics.
What are the major health impacts of substance abuse? Substance abuse leads to chronic diseases such as liver cirrhosis, cardiovascular disease, and mental health disorders including anxiety and depression. It also increases the risk of infectious diseases like HIV and hepatitis.
How can substance abuse be effectively prevented and treated? Early education and community support programs reduce the incidence of substance abuse. Evidence-based treatments include behavioral therapy, counseling, and medication-assisted treatment tailored to individual needs.
Commonly Abused Substances
Substance abuse involves the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances. It significantly impacts physical health, mental well-being, and social functioning.
Commonly abused substances include alcohol, tobacco, cannabis, opioids, and stimulants. Alcohol remains the most widely used and abused substance globally. Prescription medications, such as benzodiazepines and opioids, are increasingly misused, leading to addiction and overdose risks.
Signs and Symptoms of Substance Abuse
Substance abuse manifests through physical, behavioral, and psychological signs that indicate a person may be struggling with addiction. Common symptoms include changes in appearance, erratic behavior, and mood swings, along with withdrawal from social activities. Recognizing these signs early can lead to timely intervention and support for recovery.
Impact on Physical and Mental Health
Substance abuse significantly damages both physical and mental health, leading to chronic diseases such as liver cirrhosis, heart disease, and respiratory issues. Mental health effects include anxiety, depression, and increased risk of psychiatric disorders. Early intervention and treatment are critical to mitigate these severe health impacts and improve quality of life.
Substance Abuse in Teens and Young Adults
Substance abuse among teens and young adults remains a critical public health issue with long-term consequences. Early intervention is essential to reduce addiction risks and promote healthier lifestyles.
- Prevalence - Approximately 34% of high school students have tried illicit drugs by age 18, highlighting widespread exposure.
- Impact on Brain Development - Substance use during adolescence can impair cognitive functions and increase vulnerability to mental health disorders.
- Most Common Substances - Alcohol, marijuana, and prescription medications lead in usage rates among youth aged 12 to 25.
Effective prevention programs and family support significantly decrease the likelihood of substance abuse initiation in young populations.
Risk Factors and Causes
Substance abuse stems from a complex mix of risk factors and causes that vary from individual to individual. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective prevention and intervention strategies.
- Genetic Predisposition - A family history of addiction increases the likelihood of substance abuse due to inherited traits.
- Environmental Influences - Exposure to drug use in home or social settings raises the risk of developing substance abuse behaviors.
- Mental Health Disorders - Conditions like depression and anxiety often coexist with or lead to substance misuse as a coping mechanism.
Consequences for Families and Communities
Substance abuse severely impacts families, often leading to emotional distress, financial instability, and disrupted relationships. Children in affected households face higher risks of neglect, abuse, and developmental challenges.
Communities experience increased crime rates, healthcare costs, and reduced workforce productivity due to substance abuse. Public resources are stretched thin, affecting overall social welfare and community safety.
Prevention Strategies That Work
Effective prevention strategies reduce the risk of substance abuse by promoting healthy behaviors and environments. Understanding these methods helps communities and individuals implement successful interventions.
- Education Programs - Comprehensive education increases awareness of substance abuse risks and builds decision-making skills.
- Family Involvement - Strong family bonds and communication lower the likelihood of substance use among youth.
- Community Support - Access to supportive networks and activities offers positive alternatives to drug use.
Treatment and Recovery Options
| Treatment Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Detoxification | Medical process to safely manage withdrawal symptoms during the initial phase of substance abuse treatment. |
| Inpatient Rehab | Residential programs providing 24/7 medical care and structured therapy for severe addiction cases. |
| Outpatient Programs | Flexible treatment allowing patients to attend therapy sessions while maintaining daily routines. |
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) | Evidence-based therapy focused on changing harmful patterns of thinking and behavior related to substance abuse. |
| Support Groups | Peer-led group meetings such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) promoting sustained recovery through shared experiences. |
