Seafood offers a rich source of essential nutrients, including omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals important for heart health and brain function. Sustainable fishing practices help maintain ocean biodiversity while providing a steady supply of fresh fish and shellfish. Understanding seafood varieties and their benefits can guide healthier dietary choices and support environmental conservation efforts.
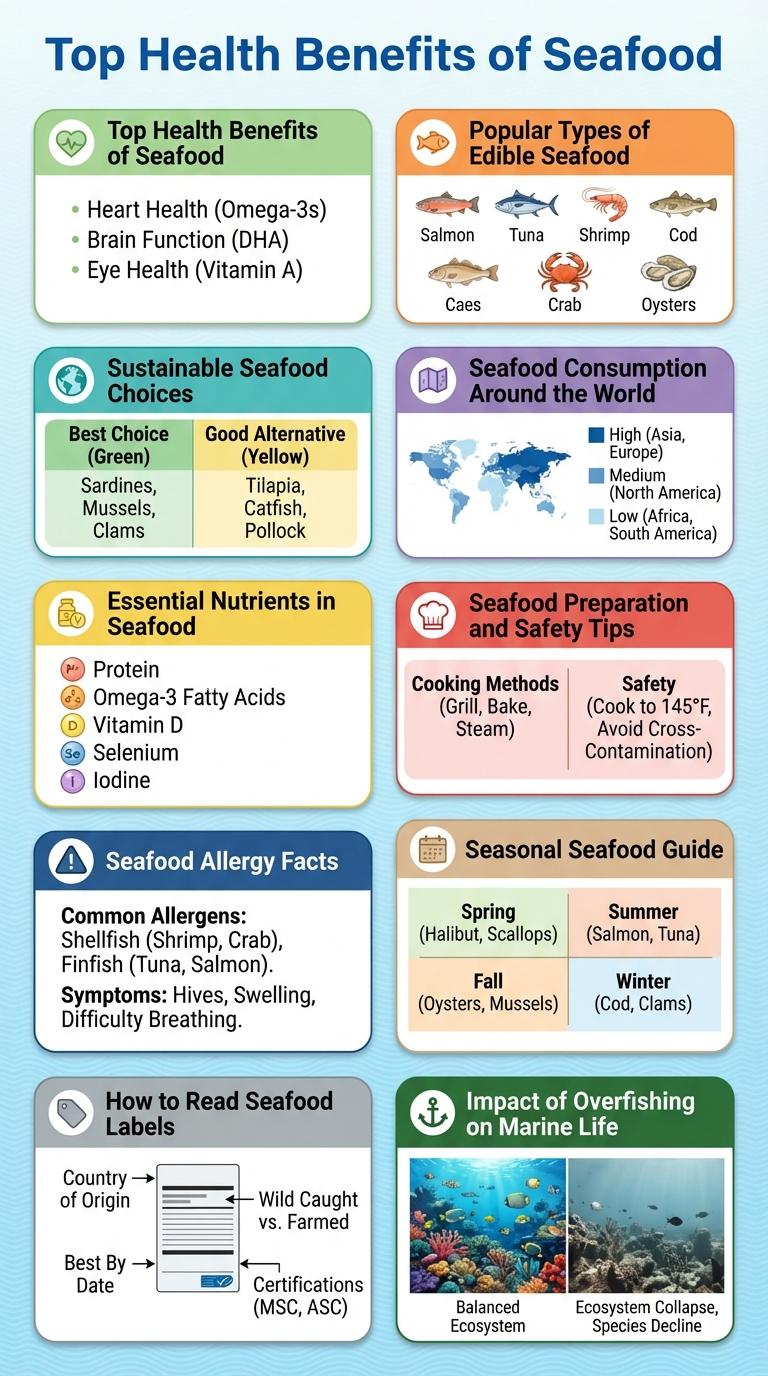
Top Health Benefits of Seafood
Seafood is a rich source of omega-3 fatty acids, which support heart health and reduce inflammation. It provides high-quality protein essential for muscle growth and repair. Regular consumption of seafood can improve brain function and promote healthy vision.
Popular Types of Edible Seafood
Seafood is a vital source of nutrition worldwide, offering a variety of flavors and health benefits. Popular types of edible seafood include fish, shellfish, and crustaceans, each providing unique textures and tastes.
Salmon, tuna, shrimp, crab, and oysters are among the most sought-after seafood items. These seafood choices are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, vitamins, and minerals essential for a balanced diet.
Sustainable Seafood Choices
| Sustainable Seafood Choice | Key Benefits |
|---|---|
| Wild Alaskan Salmon | Harvested with strict quotas to protect populations, rich in omega-3 fatty acids |
| Mussels | Filter feeders that improve water quality, low environmental impact of farming |
| Pacific Sardines | Fast-growing species with healthy population levels, excellent source of protein |
| Arctic Char | Farmed sustainably in closed systems, requires minimal feed, low carbon footprint |
| Alaskan King Crab | Strictly regulated fisheries, supports local economies, high in important nutrients |
Seafood Consumption Around the World
Seafood consumption varies significantly across different regions, influenced by culture, economy, and access to marine resources. Coastal countries tend to have higher seafood intake compared to landlocked nations.
- Asia leads global seafood consumption - Countries like China, Japan, and Indonesia dominate due to tradition and large populations.
- Europe has diverse seafood preferences - Mediterranean countries favor fish like sardines and anchovies, while northern regions prefer shellfish.
- North America shows moderate consumption - The United States and Canada consume less seafood per capita compared to Asian and European countries.
- Oceania maintains steady seafood intake - Australia and New Zealand rely heavily on sustainable fisheries.
- Africa's seafood consumption is growing - Coastal nations increase seafood intake driven by rising incomes and improved supply chains.
Global seafood demand continues to rise, urging sustainable fishing practices and aquaculture development.
Essential Nutrients in Seafood
Seafood is a rich source of essential nutrients vital for maintaining good health. These nutrients support brain function, improve heart health, and strengthen the immune system.
Key nutrients found in seafood include omega-3 fatty acids, high-quality protein, vitamins D and B12, and minerals such as iodine, zinc, and selenium. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation and promote cardiovascular health. Vitamin B12 is crucial for nerve function and red blood cell formation.
Seafood Preparation and Safety Tips
Proper seafood preparation ensures safety and enhances flavor. Following key safety tips reduces risks of foodborne illnesses.
- Store Seafood Properly - Keep seafood refrigerated at 32degF (0degC) or lower to maintain freshness and prevent bacterial growth.
- Cook Seafood Thoroughly - Cook fish to an internal temperature of 145degF (63degC) to eliminate harmful pathogens.
- Prevent Cross-Contamination - Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw seafood and other foods to avoid spreading bacteria.
Seafood Allergy Facts
Seafood allergies affect approximately 2% of the global population, with shellfish allergy being the most common type. Symptoms can range from mild hives to severe anaphylaxis, requiring immediate medical attention.
Common allergenic seafood includes shrimp, crab, lobster, and various fish species like salmon and tuna. Avoiding cross-contamination in food preparation is crucial for those with seafood allergies to prevent reactions.
Seasonal Seafood Guide
Discover the best seasonal seafood to enjoy fresh and sustainably sourced throughout the year. Spring brings tender scallops and sweet clams, while summer is perfect for juicy blue crabs and flavorful lobster. Fall and winter highlight hearty oysters and rich cod, ensuring delicious seafood options in every season.
| Season | Seafood Highlights |
|---|---|
| Spring | Scallops, Clams |
| Summer | Blue Crab, Lobster |
| Fall | Oysters, Cod |
| Winter | Oysters, Cod |
How to Read Seafood Labels
How can you confidently choose sustainable seafood at the store? Understanding seafood labels helps you make eco-friendly and health-conscious decisions. Labels provide key information about species, origin, and fishing methods.
| Label Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Wild-Caught | Seafood harvested from natural habitats like oceans, rivers, or lakes. |
| Farmed | Seafood raised in controlled aquaculture environments. |
| Certified Sustainable | Seafood verified by organizations like MSC or ASC for eco-friendly practices. |
| Country of Origin | Indicates where the seafood was caught or farmed. |
| Catch Date | The date when the seafood was harvested, reassuring freshness. |
