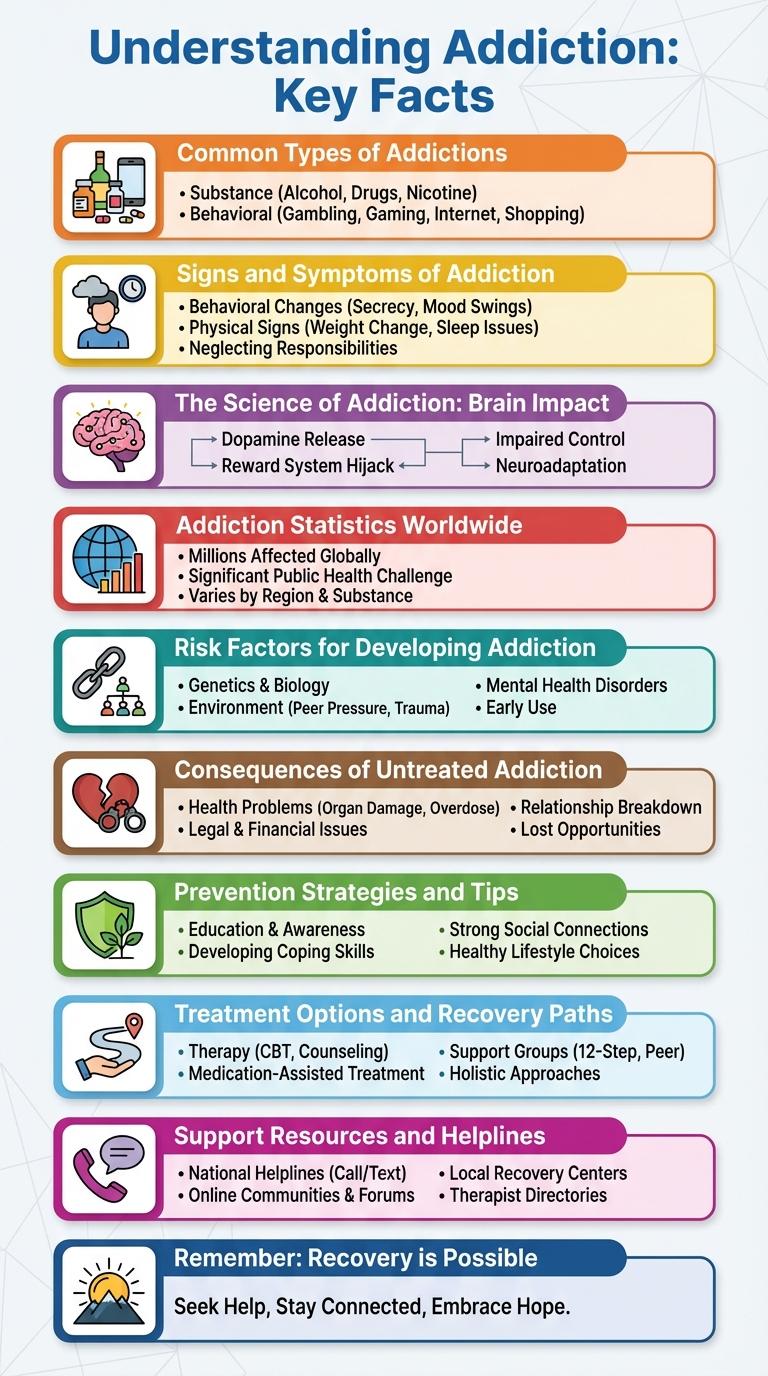
Addiction is a complex condition characterized by compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences. Understanding the causes, effects, and treatment options is essential for effective intervention. This infographic visually presents key data and insights to raise awareness and support recovery efforts.
Understanding Addiction: Key Facts
Addiction is a chronic brain disorder characterized by compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences. It affects the brain's reward, motivation, and memory systems, leading to persistent behavioral changes.
Approximately 21 million people in the United States suffer from addiction to alcohol or drugs. Genetic, environmental, and psychological factors contribute to the development of addiction. Effective treatment involves a combination of medication, therapy, and support systems to aid recovery.
Common Types of Addictions
Addiction affects millions worldwide, disrupting lives and impacting health. Recognizing common types of addictions can aid in prevention and treatment.
- Substance Addiction - Dependence on drugs or alcohol alters brain chemistry, causing physical and psychological symptoms.
- Behavioral Addiction - Compulsive engagement in activities like gambling or gaming leads to significant life impairment.
- Nicotine Addiction - Tobacco use creates strong cravings and withdrawal symptoms, making quitting difficult.
- Prescription Drug Addiction - Misuse of medications such as opioids increases risk of overdose and health complications.
- Food Addiction - Overconsumption of highly palatable foods triggers reward system responses similar to substance abuse.
Signs and Symptoms of Addiction
| Signs of Addiction | Symptoms of Addiction |
|---|---|
| Increased Tolerance | Needing more of the substance to achieve the same effect |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Physical and emotional distress when not using the substance |
| Cravings | Strong, uncontrollable desire to use the substance |
| Neglecting Responsibilities | Ignoring work, school, or family obligations due to substance use |
| Behavioral Changes | Increased secrecy, irritability, or changes in social circles |
The Science of Addiction: Brain Impact
Addiction alters brain function, affecting decision-making and behavior control. These changes reinforce compulsive substance use despite harmful consequences.
- Neurotransmitter Disruption - Addiction increases dopamine release, creating intense feelings of pleasure that reinforce drug-seeking behavior.
- Prefrontal Cortex Impairment - This brain region, responsible for judgment and impulse control, weakens during addiction, reducing self-regulation.
- Memory Formation - The hippocampus encodes addiction-related cues, triggering cravings and relapse even after abstinence.
Understanding the brain's role in addiction reveals targets for effective treatment and recovery strategies.
Addiction Statistics Worldwide
Addiction affects over 35 million people worldwide, with substance use disorders being the most common. Approximately 11% of the global population aged 15-64 has used drugs at least once, contributing to 450,000 annual overdose deaths. Alcohol addiction accounts for 3 million deaths per year, highlighting the urgent need for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Risk Factors for Developing Addiction
Addiction develops through a combination of genetic, environmental, and psychological risk factors. Understanding these factors can help in early identification and prevention.
Genetic predisposition increases vulnerability to addiction by influencing brain chemistry and response to substances. Environmental factors such as exposure to substance use, peer pressure, and stress contribute significantly to addiction risk.
Consequences of Untreated Addiction
Addiction affects brain function and behavior, leading to severe health and social complications when untreated. Early intervention improves recovery chances and quality of life for affected individuals.
- Physical Health Decline - Untreated addiction causes organ damage, weakened immune system, and increased risk of infectious diseases.
- Mental Health Disorders - Prolonged addiction often results in anxiety, depression, and heightened risk of suicide.
- Social Isolation - Addiction leads to strained relationships, job loss, and social withdrawal.
Prevention Strategies and Tips
Addiction prevention strategies focus on education, early intervention, and support systems to reduce risk factors. Key tips include building strong communication skills, fostering healthy relationships, and promoting awareness about the consequences of substance abuse. Effective prevention combines community resources, family involvement, and positive role models to create a supportive environment.
Treatment Options and Recovery Paths
Addiction is a complex condition that requires personalized treatment approaches. Effective recovery often involves a combination of medical, psychological, and social support.
Treatment options include detoxification, medication-assisted therapy, and behavioral counseling. Recovery paths vary from inpatient rehab to outpatient programs and peer support groups.
