Protein is a vital macronutrient essential for building and repairing tissues, producing enzymes, and supporting overall bodily functions. This infographic breaks down the key sources, daily requirements, and health benefits of protein intake. Understanding these elements can help optimize nutrition and enhance well-being.
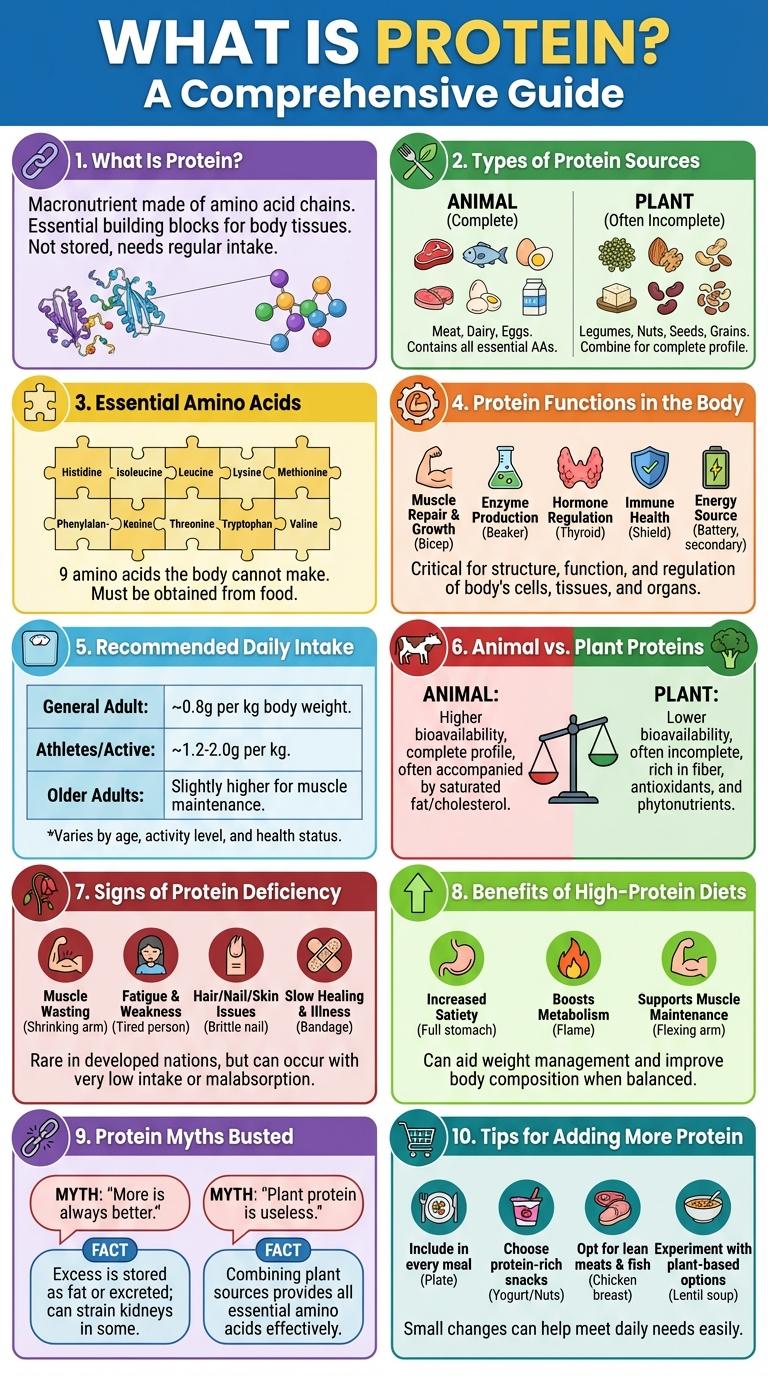
What Is Protein?
Protein is a vital macronutrient essential for building and repairing tissues. It plays a crucial role in the structure, function, and regulation of the body's cells and organs.
- Building Blocks - Proteins are made of amino acids, which are the fundamental units for constructing body tissues.
- Metabolic Functions - Enzymes and hormones are proteins that regulate biochemical reactions and physiological processes.
- Dietary Sources - Common protein sources include meat, dairy, legumes, and nuts, providing essential amino acids for health.
Types of Protein Sources
Proteins are essential macronutrients found in various food sources, critical for muscle repair, enzyme function, and overall body maintenance. Understanding different protein sources helps in crafting a balanced diet that meets individual nutritional needs.
Animal-based proteins include meat, dairy, eggs, and fish, offering complete protein profiles with all essential amino acids. Plant-based proteins, such as beans, lentils, nuts, and seeds, provide vital nutrients and support vegetarian and vegan diets.
Essential Amino Acids
Proteins are composed of essential amino acids, which the body cannot synthesize and must obtain from food. These amino acids play a crucial role in building muscle, repairing tissues, and supporting immune function. A balanced diet including sources like meat, dairy, and legumes ensures adequate intake of all essential amino acids.
Protein Functions in the Body
| Protein Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Muscle Repair and Growth | Proteins provide amino acids that rebuild muscle tissue after exercise or injury. |
| Enzyme Production | Proteins act as enzymes to speed up biochemical reactions essential for metabolism. |
| Hormone Synthesis | Some hormones, like insulin, are proteins that regulate physiological processes. |
| Immune Response | Antibodies are protein-based and help identify and neutralize pathogens. |
| Cell Structure and Support | Structural proteins like collagen provide support and strength to cells and tissues. |
Recommended Daily Intake
Protein is a vital macronutrient essential for muscle repair, immune function, and overall health. The Recommended Daily Intake (RDI) varies based on age, sex, and activity level to meet individual nutritional needs.
For most adults, the RDI is approximately 50 grams per day, equating to 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. Athletes and pregnant women require higher protein intakes to support increased physiological demands.
Animal vs. Plant Proteins
Proteins are essential macronutrients found in both animal and plant sources, vital for muscle repair and overall health. Understanding the differences between animal and plant proteins helps optimize dietary choices for better nutrition.
- Amino Acid Profile - Animal proteins contain all nine essential amino acids, making them complete proteins, while most plant proteins lack one or more essential amino acids.
- Digestibility - Animal proteins generally have higher digestibility scores, meaning the body absorbs them more efficiently compared to plant proteins.
- Additional Nutrients - Animal proteins provide nutrients like vitamin B12, heme iron, and omega-3 fatty acids not commonly found in plant proteins.
Combining diverse plant protein sources can create a complete amino acid profile to meet nutritional needs effectively.
Signs of Protein Deficiency
Protein is essential for muscle growth, tissue repair, and immune function. A lack of protein can lead to serious health issues if not addressed promptly.
Common signs of protein deficiency include fatigue, weakened immunity, and muscle loss. Hair thinning or hair loss may also occur due to insufficient protein intake. Swelling or edema can result from low protein levels affecting fluid balance in the body.
Benefits of High-Protein Diets
High-protein diets support muscle growth, weight management, and overall health. Proteins are essential macronutrients that play a critical role in body functions.
- Muscle Repair and Growth - Protein provides amino acids needed for muscle tissue repair and growth.
- Weight Management - High-protein intake increases satiety, reducing overall calorie consumption.
- Metabolism Boost - Protein has a higher thermic effect, enhancing calorie burning during digestion.
Protein Myths Busted
Is eating more protein always better for muscle growth? Consuming excess protein beyond your body's needs does not necessarily boost muscle gain and can strain your kidneys. Balanced intake tailored to activity level is essential for optimal health.
Do plant-based proteins lack essential amino acids? Many plant proteins provide all nine essential amino acids when combined properly throughout the day. Quinoa, soy, and buckwheat are complete plant protein sources suitable for diverse diets.
Does protein cause weight gain? Protein itself does not cause weight gain; calories in excess of what the body burns lead to fat accumulation. High-protein diets can support weight loss by increasing satiety and preserving lean muscle mass.
Is it true protein supplements are necessary for everyone? Most people can meet their protein requirements through whole foods without supplements. Protein powders are beneficial primarily for convenience or specific dietary needs.
Does eating protein late at night disrupt sleep or cause fat gain? Consuming protein before bed does not inherently cause fat gain and may aid muscle repair during sleep. Timing should fit individual lifestyle and total daily protein goals.
