Obesity affects millions worldwide, posing significant health risks such as diabetes, heart disease, and stroke. This infographic highlights key statistics, causes, and prevention strategies to raise awareness and promote healthier lifestyles. Understanding these factors is essential for tackling the obesity epidemic effectively.
Understanding Obesity: Key Facts
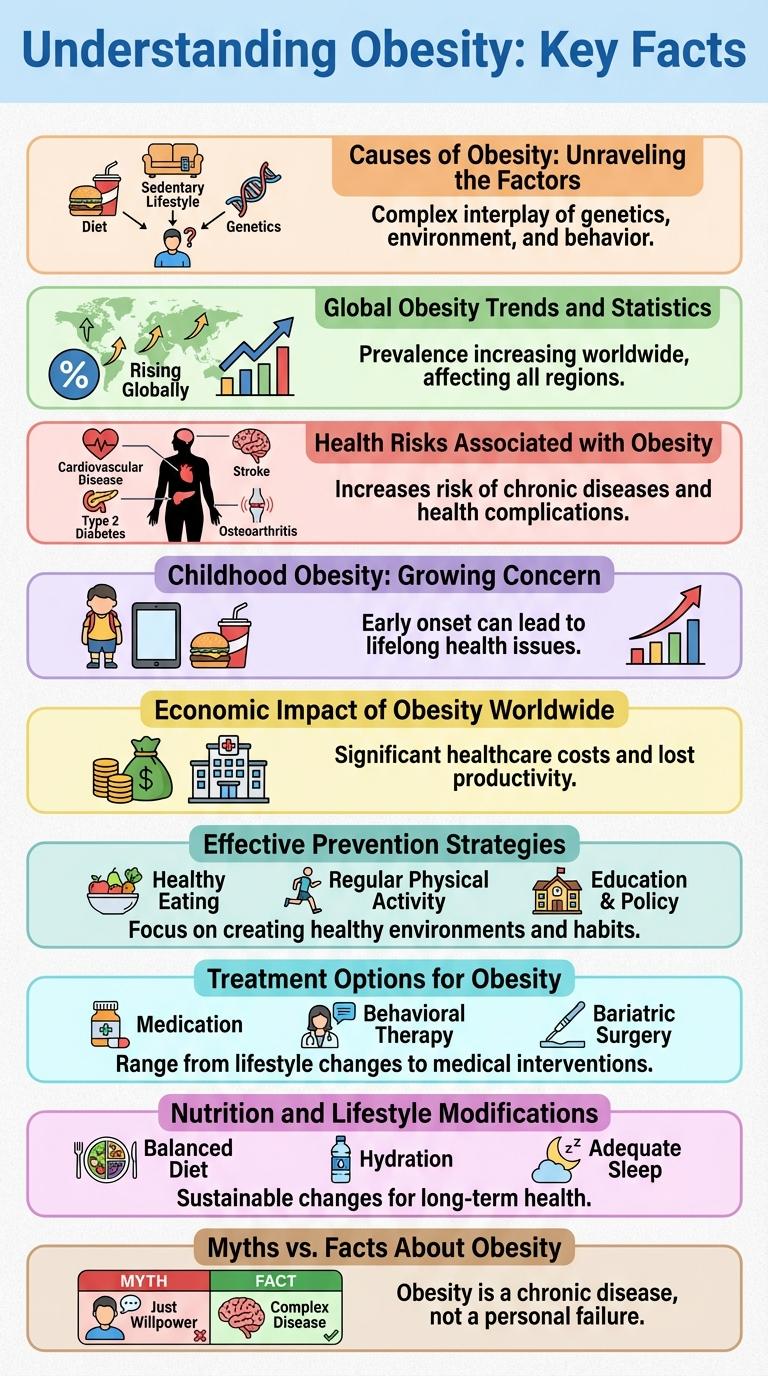
Obesity is a chronic condition characterized by excessive body fat accumulation, impacting overall health. It increases the risk of diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and certain cancers. Understanding obesity involves recognizing its causes, including genetics, diet, and physical inactivity.
Causes of Obesity: Unraveling the Factors
Global Obesity Trends and Statistics
Global obesity rates have nearly tripled since 1975, affecting over 650 million adults worldwide as of 2023. The World Health Organization reports that 39% of adults aged 18 and over are overweight, with 13% classified as obese. Rising obesity levels pose significant health risks, including increased rates of heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Health Risks Associated with Obesity
Obesity significantly increases the risk of developing multiple chronic health conditions. Understanding these risks is crucial for prevention and management.
- Heart Disease - Excess body fat strains the heart and arteries, raising the likelihood of heart attacks and stroke.
- Type 2 Diabetes - Obesity causes insulin resistance, leading to elevated blood sugar levels and diabetes.
- Joint Problems - Increased weight puts pressure on joints, causing pain and osteoarthritis.
Childhood Obesity: Growing Concern
Childhood obesity has become a significant health challenge worldwide, with rates tripling over the past three decades. This condition increases the risk of various chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular problems in children.
Factors influencing childhood obesity include poor diet, sedentary lifestyle, and genetic predisposition. Early intervention through balanced nutrition, physical activity, and education remains critical to reversing this alarming trend.
Economic Impact of Obesity Worldwide
Obesity contributes significantly to global economic burdens affecting healthcare systems and workforce productivity. The financial strain from obesity-related diseases challenges both developed and developing economies.
The rising costs associated with obesity include direct medical expenses and indirect costs such as lost income and lower productivity.
- Healthcare Expenditure - Obesity accounts for nearly 2-7% of total healthcare costs in many countries worldwide.
- Workforce Impact - Obesity-related illnesses lead to increased absenteeism and reduced work efficiency, costing billions annually.
- Global Economic Loss - The global economy faces an estimated loss of $2 trillion per year due to obesity's impact on health and productivity.
Effective Prevention Strategies
Obesity is a global health challenge affecting millions, increasing the risk of chronic diseases like diabetes and heart conditions. Effective prevention strategies focus on lifestyle changes and community support to reduce obesity rates.
Healthy eating habits, including balanced diets rich in fruits and vegetables, play a critical role in preventing obesity. Regular physical activity, such as at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, helps maintain a healthy weight. Public health initiatives that promote awareness, accessibility to healthy foods, and safe environments for exercise can significantly reduce obesity prevalence.
Treatment Options for Obesity
Obesity treatment involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medical interventions, and sometimes surgical procedures. Effective treatment plans are personalized based on the patient's health status and degree of obesity.
Lifestyle modifications include a balanced diet and increased physical activity to achieve gradual weight loss. Medications such as orlistat and GLP-1 receptor agonists aid in appetite control and fat absorption reduction.
Bariatric surgery options like gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy provide significant weight loss for severe obesity cases. These procedures improve metabolic health and reduce obesity-related complications.
Behavioral therapy supports sustainable lifestyle changes by addressing eating habits and motivation. Ongoing medical monitoring ensures treatment safety and effectiveness over time.
Nutrition and Lifestyle Modifications
Obesity is a complex health condition influenced by dietary habits and physical activity levels. Effective management requires targeted nutrition and lifestyle modifications to improve overall health.
- Balanced Diet - Consuming nutrient-rich foods with appropriate calorie intake supports weight management and reduces obesity risk.
- Regular Physical Activity - Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly promotes fat loss and cardiovascular health.
- Behavioral Changes - Incorporating mindful eating and consistent meal patterns helps prevent overeating and supports sustainable weight loss.
Implementing these nutrition and lifestyle changes significantly improves obesity outcomes and long-term well-being.
