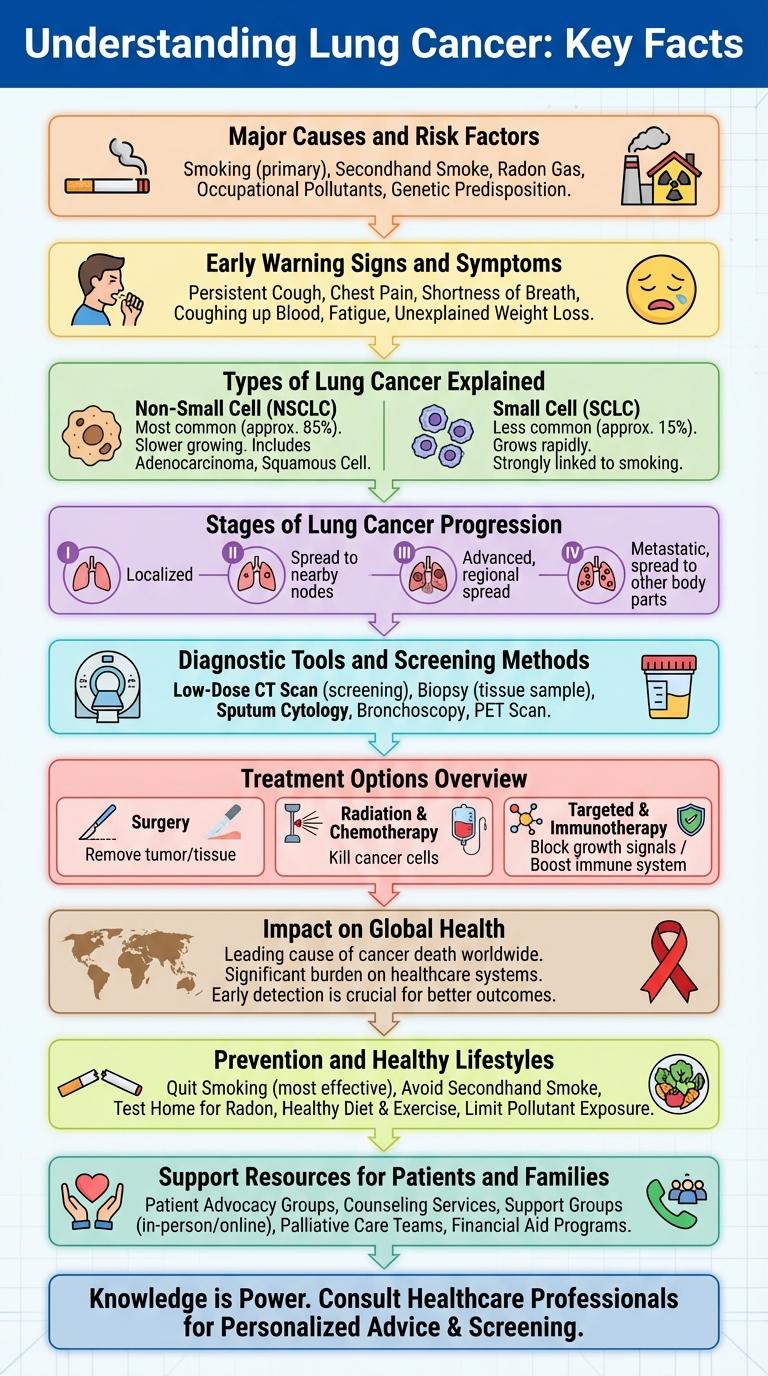
Lung cancer remains one of the most common and deadly cancers worldwide, making awareness and early detection crucial. Infographics provide a clear visual representation of key facts, risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options related to lung cancer. Understanding this information empowers individuals to take preventive measures and seek timely medical advice.
Understanding Lung Cancer: Key Facts
Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, affecting millions each year. It primarily develops in the cells lining the lungs and is strongly linked to smoking and environmental factors.
There are two main types: non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which accounts for about 85% of cases, and small cell lung cancer (SCLC), known for its aggressive nature. Early detection significantly improves survival rates, yet symptoms often appear in advanced stages. Advances in targeted therapies and immunotherapy offer new hope for patients.
Major Causes and Risk Factors
What are the primary causes of lung cancer? Lung cancer mainly arises from tobacco smoke exposure, accounting for about 85% of cases worldwide. Other factors include exposure to radon gas, asbestos, and air pollution, which also significantly increase risk.
Which risk factors contribute most to lung cancer development? Smoking is the leading risk factor, responsible for the majority of lung cancer deaths globally. Genetic predisposition and occupational hazards like exposure to carcinogens in mining and construction further elevate risk.
Early Warning Signs and Symptoms
Lung cancer often develops silently and is diagnosed in advanced stages, making early detection critical. Recognizing early warning signs can improve treatment outcomes and survival rates.
- Persistent Cough - A cough that does not go away or worsens over time can indicate lung abnormalities.
- Chest Pain - Pain or discomfort in the chest area may signal lung tissue involvement or tumor growth.
- Shortness of Breath - Difficulty breathing or shortness of breath can result from airway obstruction or lung function impairment.
Types of Lung Cancer Explained
Lung cancer is primarily classified into two main types based on the characteristics of the cancer cells. Understanding these types helps in choosing the appropriate treatment strategy.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) - The most common type, accounting for about 85% of lung cancer cases, subdivided into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) - A fast-growing type that spreads quickly and is strongly linked to smoking, representing roughly 15% of lung cancer diagnoses.
- Other Rare Types - Includes carcinoid tumors and mesothelioma, which occur less frequently and require specialized treatment approaches.
Stages of Lung Cancer Progression
Lung cancer progresses through four main stages, each indicating the extent of tumor growth and spread. Stage 1 involves a small tumor confined to the lungs, while Stage 4 indicates advanced cancer with metastasis to other organs. Accurate staging is crucial for determining treatment options and predicting patient outcomes.
Diagnostic Tools and Screening Methods
| Diagnostic Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Chest X-ray | Initial imaging to detect lung abnormalities, often used for patients with symptoms or risk factors. |
| Low-Dose Computed Tomography (LDCT) | Recommended for high-risk individuals; detects small lung nodules with reduced radiation exposure. |
| Bronchoscopy | Direct visualization of the airways and collection of tissue samples for biopsy and diagnosis. |
| Biopsy | Extraction of lung tissue to confirm cancer presence and determine histological type. |
| Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Scan | Assess metabolic activity of lung nodules and identify potential metastasis. |
Treatment Options Overview
Lung cancer treatment varies based on the type and stage of the disease. Common options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy.
Early-stage lung cancer often involves surgical removal of tumors, while advanced cases rely more on systemic treatments. Personalized treatment plans improve outcomes and reduce side effects.
Impact on Global Health
Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Its widespread impact severely strains healthcare systems and highlights the urgent need for effective prevention and treatment strategies.
- High Mortality Rate - Lung cancer accounts for nearly 1.8 million deaths annually, making it the deadliest cancer globally.
- Prevalence in Low- and Middle-Income Countries - Over 60% of lung cancer cases are diagnosed in low- and middle-income countries, where access to screening is limited.
- Economic Burden - The cost of lung cancer treatment and lost productivity exceeds billions of dollars each year worldwide.
Raising awareness and improving early detection are critical to reducing the global health impact of lung cancer.
Prevention and Healthy Lifestyles
Lung cancer prevention centers on avoiding tobacco use and exposure to harmful pollutants like radon and asbestos. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, regular exercise, and avoiding secondhand smoke reduces lung cancer risk. Early detection and awareness further improve prevention outcomes, saving lives worldwide.
