Drug awareness and prevention infographic highlights key facts about substance abuse, its impacts, and effective strategies to reduce risks. It visually presents statistics, warning signs, and resources to educate individuals on making informed decisions. Emphasizing early intervention and community support promotes healthier lifestyles and decreases drug-related harm.
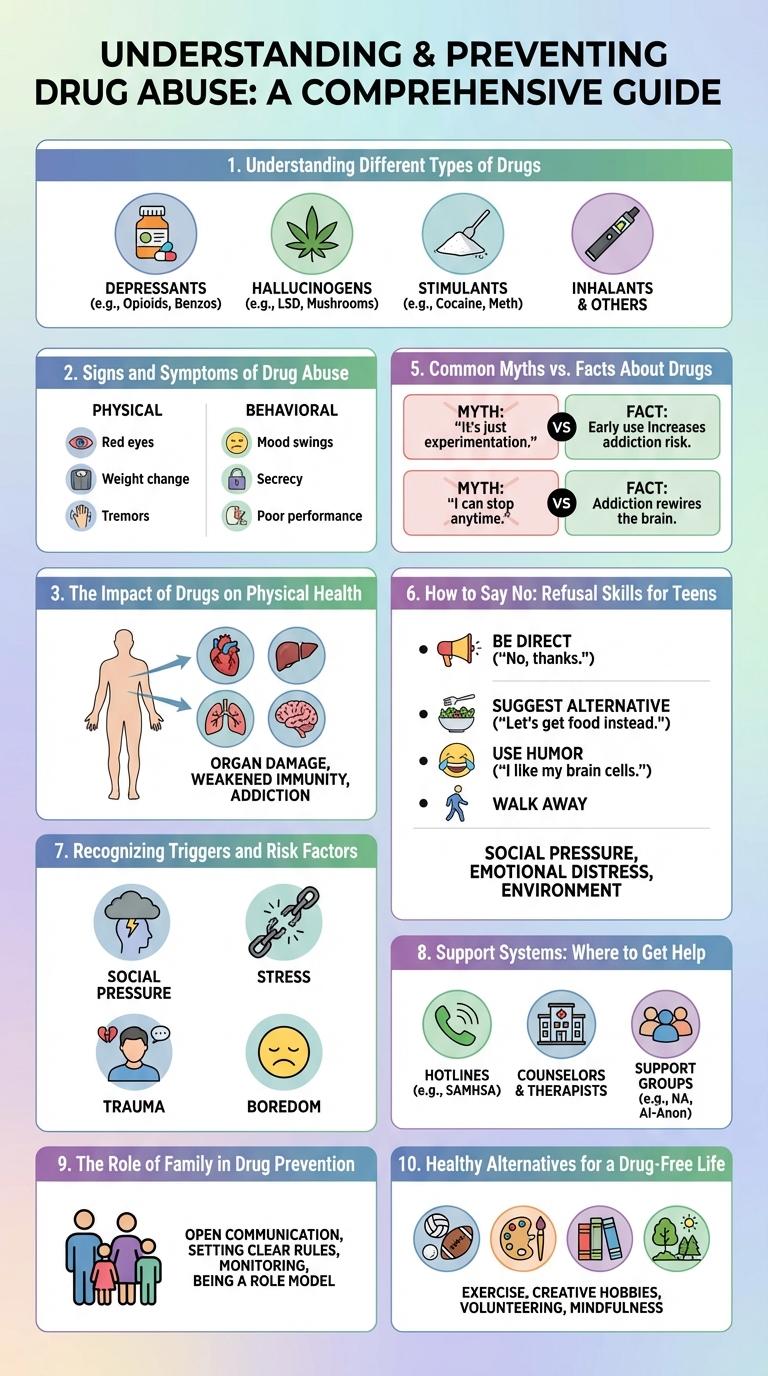
Understanding Different Types of Drugs
| Drug Type | Description & Effects |
|---|---|
| Stimulants | Increase alertness and energy; examples include cocaine and amphetamines. Risk of heart problems and addiction. |
| Depressants | Slow down brain activity; includes alcohol, benzodiazepines. Can cause drowsiness, impaired coordination, and overdose risk. |
| Opioids | Used for pain relief; examples are heroin, morphine, prescription painkillers. High risk of addiction and respiratory failure. |
| Hallucinogens | Alter perception and consciousness; includes LSD, psilocybin. Can cause hallucinations and unpredictable psychological effects. |
| Cannabis | Produces relaxation and altered senses; includes marijuana. Possible memory issues and impaired coordination. |
Signs and Symptoms of Drug Abuse
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of drug abuse is crucial for early intervention and prevention. Changes in behavior, appearance, and physical health often indicate substance misuse.
Common signs include sudden mood swings, secretive behavior, and neglect of personal hygiene. Physical symptoms may involve bloodshot eyes, unusual odors, and unexplained weight changes.
The Impact of Drugs on Physical Health
Drug abuse significantly damages physical health, affecting multiple organs and systems. Understanding these effects is crucial for prevention and promoting healthy lifestyles.
- Cardiovascular Damage - Drugs like cocaine and methamphetamine increase heart rate and blood pressure, leading to heart attacks and strokes.
- Respiratory Issues - Smoking drugs such as tobacco and marijuana causes lung damage, chronic bronchitis, and increased risk of lung cancer.
- Liver Toxicity - Alcohol and certain prescription drugs can cause liver inflammation, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis.
Preventing drug use helps preserve physical health and reduces the risk of chronic diseases.
Effects of Drug Abuse on Mental Wellbeing
Drug abuse significantly impacts mental wellbeing, leading to disorders such as depression, anxiety, and psychosis. Prolonged substance use disrupts brain chemistry, impairing cognitive function and emotional regulation. Early prevention and awareness are crucial to protect mental health and promote recovery.
Common Myths vs. Facts About Drugs
Is it true that all drugs are equally harmful? Different drugs pose varying levels of risk depending on their chemical properties and how they are used.
Do prescription drugs have no potential for abuse? Some prescription medications can be addictive and harmful if misused or taken without medical supervision.
Does occasional drug use cause no long-term damage? Even occasional use can impact brain function and increase the risk of addiction over time.
Can using drugs improve performance or creativity? Drugs may impair judgment and coordination, ultimately hindering productivity and creative processes.
Is addiction solely a failure of willpower? Addiction is a complex brain disorder influenced by genetic, environmental, and psychological factors.
How to Say No: Refusal Skills for Teens
Teaching refusal skills empowers teens to confidently say no to drugs and avoid peer pressure. Effective communication techniques help maintain personal boundaries and promote healthy choices.
- Be Assertive - Use a firm and clear tone to express your refusal without hesitation.
- Suggest Alternatives - Offer other activities or ideas to divert the situation away from drug use.
- Use Body Language - Maintain eye contact and an upright posture to reinforce your decision.
Recognizing Triggers and Risk Factors
Understanding triggers and risk factors is essential for effective drug awareness and prevention. Identifying these elements helps individuals and communities take proactive steps to reduce substance abuse.
- Environmental Triggers - Exposure to high-risk environments like parties or peer groups increases the likelihood of drug use.
- Emotional Stress - Stress, anxiety, and depression often serve as catalysts for substance misuse as individuals seek coping mechanisms.
- Genetic Predisposition - A family history of addiction can elevate the risk of developing similar behaviors due to inherited traits and learned habits.
Support Systems: Where to Get Help
Support systems play a crucial role in drug awareness and prevention by offering accessible resources and guidance. Key places to seek help include local health clinics, community support groups, and national helplines specializing in substance abuse. Utilizing these support networks enhances recovery chances and promotes informed decision-making.
The Role of Family in Drug Prevention
Families play a crucial role in preventing drug abuse by providing emotional support and setting clear expectations. Strong family bonds reduce the likelihood of substance use among youth.
Open communication within families helps teens understand the risks of drug use and develop healthy coping strategies. Parents who monitor activities and maintain consistent discipline create a protective environment. Family involvement in education and community programs enhances prevention efforts significantly.
