Sleep plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health, influencing everything from cognitive function to immune system performance. Understanding the stages of sleep and the factors that affect its quality can help improve rest and boost daily productivity. Infographics visually break down complex sleep data, making it easier to grasp essential information at a glance.
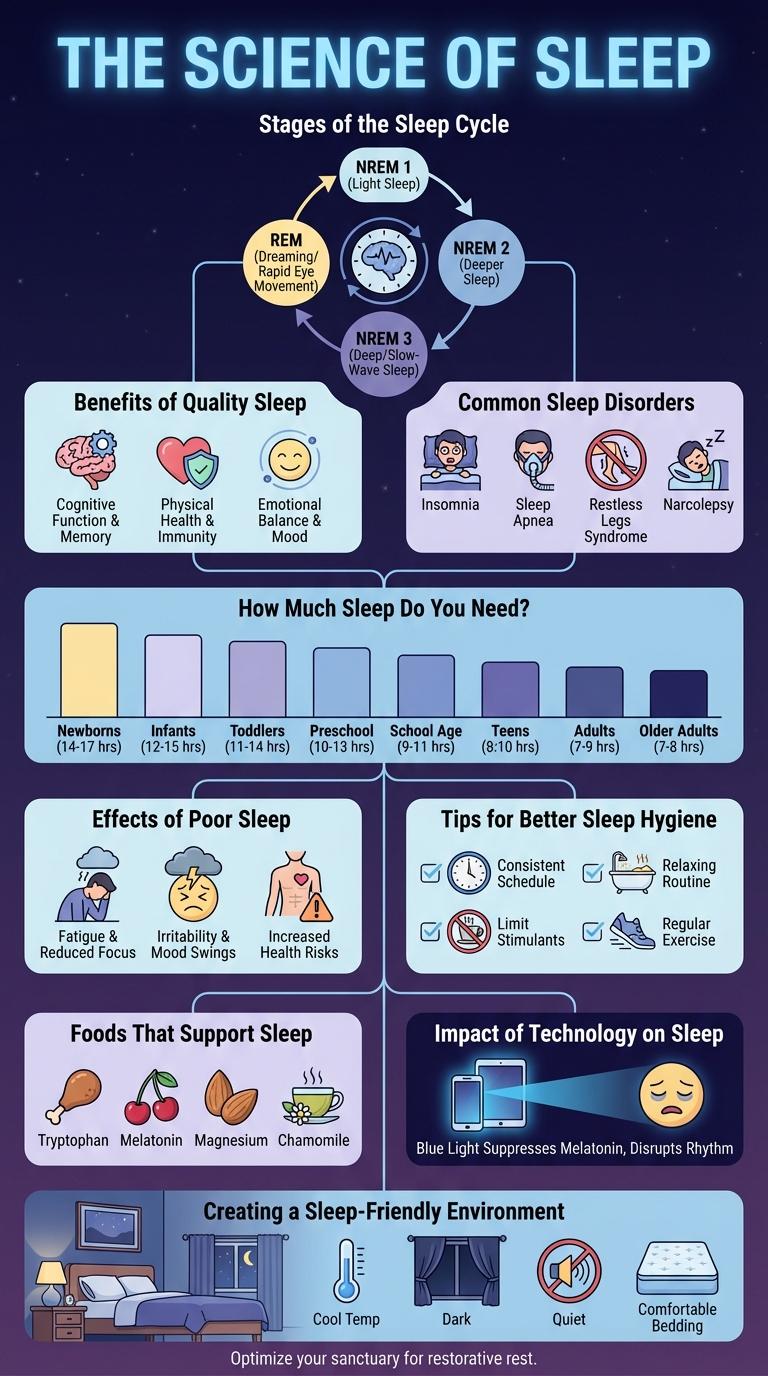
The Science of Sleep
What happens in the brain during sleep? Sleep involves complex processes that help restore brain function and consolidate memories. The brain cycles through different stages, including REM and non-REM sleep, each essential for health.
How does sleep affect physical health? Sleep supports immune function, tissue repair, and hormone regulation. Poor sleep can increase risks for heart disease, diabetes, and obesity.
Why is REM sleep important? REM sleep enhances learning, problem-solving, and emotional processing. This stage is characterized by rapid eye movement and vivid dreaming.
How much sleep is optimal for adults? Most adults need 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night for optimal cognitive and physical performance. Consistent sleep schedules promote better rest.
Can sleep deprivation impact mental health? Lack of sleep increases stress, anxiety, and depression risks. Chronic sleep deprivation impairs attention, memory, and decision-making abilities.
Stages of the Sleep Cycle
The sleep cycle consists of multiple stages that repeat throughout the night, each essential for restorative rest. These stages include Non-REM and REM sleep, which contribute to physical and mental recovery.
Non-REM sleep is divided into three stages: N1, N2, and N3, progressing from light to deep sleep. REM sleep is characterized by rapid eye movement and vivid dreaming, playing a crucial role in memory consolidation.
Benefits of Quality Sleep
Quality sleep enhances cognitive function, improving memory, attention, and problem-solving skills. It supports physical health by boosting the immune system and reducing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes and heart disease. Consistent good sleep also promotes emotional well-being, lowering stress levels and improving mood regulation.
Common Sleep Disorders
Sleep disorders affect millions worldwide, disrupting rest and overall health. Recognizing common conditions can lead to better diagnosis and treatment.
- Insomnia - Difficulty falling or staying asleep causes significant daytime fatigue and impaired function.
- Sleep Apnea - Breathing repeatedly stops during sleep, leading to poor oxygen flow and fragmented rest.
- Restless Legs Syndrome - Uncomfortable sensations in the legs provoke an uncontrollable urge to move them.
- Narcolepsy - Sudden sleep attacks and excessive daytime sleepiness impair alertness and safety.
- Parasomnias - Abnormal behaviors like sleepwalking and night terrors disrupt normal sleep cycles.
How Much Sleep Do You Need?
Sleep requirements vary by age, influencing overall health and daily performance. Understanding how much sleep you need helps optimize well-being and cognitive function.
The National Sleep Foundation recommends 7-9 hours for adults aged 18-64, while teenagers need 8-10 hours for proper development. Younger children and infants require even more sleep to support growth and brain development. Inadequate sleep negatively affects memory, mood, and immune system strength.
Effects of Poor Sleep
Poor sleep negatively impacts cognitive functions, leading to reduced concentration and memory problems. It increases the risk of chronic health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Emotional stability also suffers, causing higher levels of stress, anxiety, and depression.
Tips for Better Sleep Hygiene
Quality sleep is essential for physical and mental health. Practicing good sleep hygiene can significantly improve sleep quality and duration.
- Maintain a Consistent Sleep Schedule - Going to bed and waking up at the same time daily helps regulate your body's internal clock.
- Create a Relaxing Bedtime Routine - Engage in calming activities like reading or meditation to signal your body it's time to wind down.
- Limit Exposure to Screens Before Bed - Reducing blue light from phones and computers prevents disruption of melatonin production, aiding sleep onset.
Implementing these tips fosters restorative sleep and enhances overall well-being.
Foods That Support Sleep
| Food | Sleep Support Benefits |
|---|---|
| Cherries | Natural source of melatonin, helps regulate sleep cycles |
| Almonds | Rich in magnesium, promotes muscle relaxation and improves sleep quality |
| Kiwi | Contains antioxidants and serotonin, supports sleep onset and duration |
| Chamomile Tea | Contains apigenin, an antioxidant that binds to brain receptors promoting calmness |
| Turkey | High in tryptophan, an amino acid that increases melatonin production |
Impact of Technology on Sleep
Technology significantly affects sleep quality and patterns. Exposure to screens before bedtime disrupts the body's natural sleep cycle.
- Blue Light Exposure - Blue light emitted from devices suppresses melatonin production, delaying sleep onset.
- Increased Alertness - Interactive technology use stimulates the brain, making it harder to relax and fall asleep.
- Sleep Duration Reduction - Excessive screen time correlates with shorter total sleep duration and fragmented sleep.
