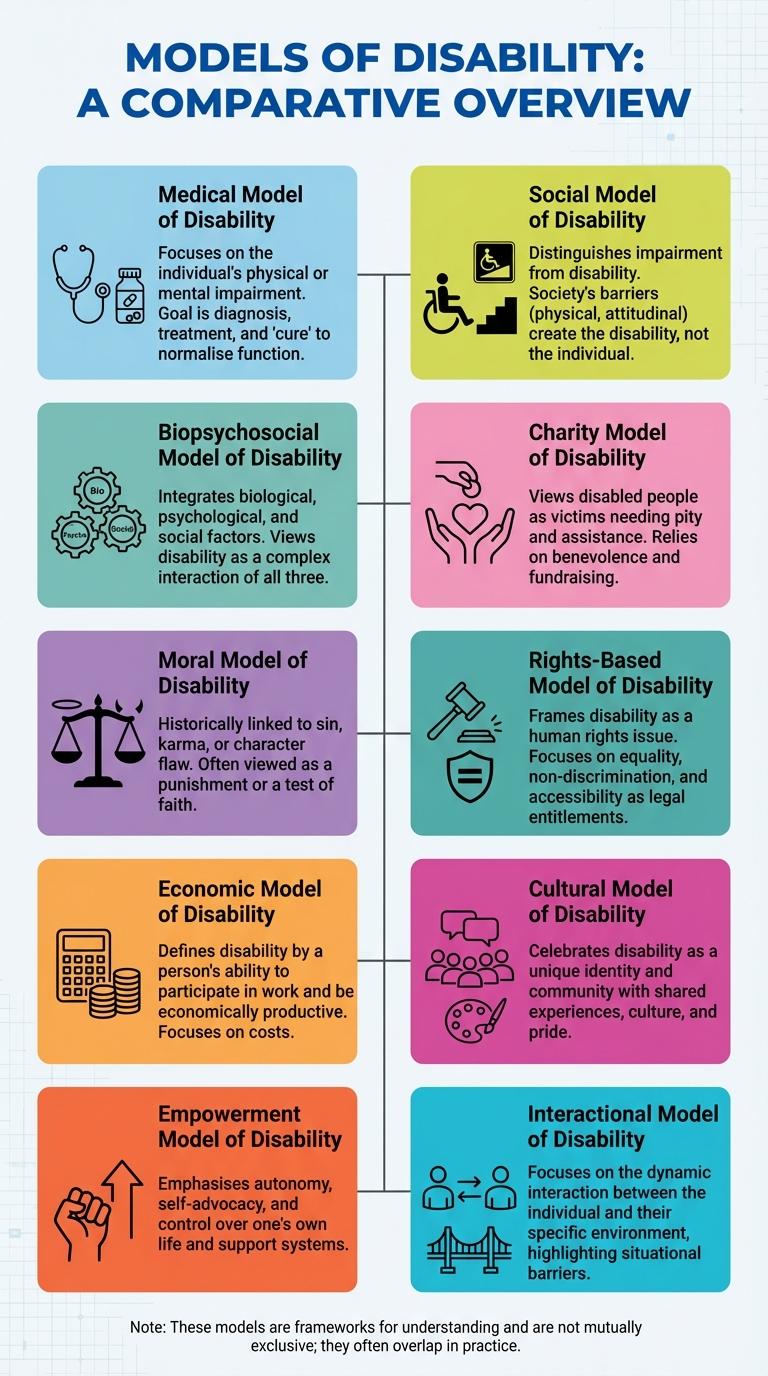
Disability models provide different perspectives on how society understands and responds to disability. These frameworks highlight the contrast between viewing disability as an individual impairment versus a result of social barriers. Understanding these models is key to promoting inclusivity and shaping effective policies.
Medical Model of Disability
The Medical Model of Disability views disability primarily as a physical or mental impairment that needs to be cured or managed by medical intervention. It emphasizes diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation within healthcare settings.
This model often focuses on the individual's limitations rather than societal barriers. It shapes policies by prioritizing medical solutions over social inclusion and accessibility improvements.
Social Model of Disability
The Social Model of Disability emphasizes that disability arises from societal barriers rather than an individual's impairments. It advocates for removing physical, attitudinal, and systemic obstacles to promote inclusion and equality. This model shifts the focus from "fixing" the person to transforming society.
Biopsychosocial Model of Disability
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | The Biopsychosocial Model of Disability integrates biological, psychological, and social factors to understand disability comprehensively. |
| Biological Component | Focuses on physical or mental impairments affecting body functions and structures. |
| Psychological Component | Considers emotional and cognitive aspects that influence individual's experience of disability. |
| Social Component | Examines societal attitudes, environmental barriers, and social support impacting participation and inclusion. |
| Significance | Offers a holistic approach to disability, encouraging personalized support and inclusive policies. |
Charity Model of Disability
The Charity Model of Disability views disabled individuals as passive recipients of charity and pity. This model often emphasizes dependence and portrays disability as a personal tragedy requiring help. Critics argue it reinforces stereotypes and limits the empowerment of disabled people.
Moral Model of Disability
The Moral Model of Disability views disability as a consequence of an individual's moral failing or sin. This model often leads to stigmatization and social exclusion of people with disabilities.
- Cause - Disability is seen as a punishment or result of immoral behavior.
- Focus - Emphasizes personal responsibility rather than social or environmental factors.
- Impact - Leads to shame, guilt, and discrimination against individuals with disabilities.
Rights-Based Model of Disability
The Rights-Based Model of Disability emphasizes that societal barriers and discrimination are the primary factors limiting the participation of disabled individuals. This model advocates for equal rights, accessibility, and inclusion as fundamental human rights.
This model shifts the focus from an individual's impairment to the social and legal structures that create disadvantage. It highlights the importance of anti-discrimination laws, accessibility standards, and inclusive policies. Empowerment and respect for autonomy are core principles driving the rights-based approach.
Economic Model of Disability
What is the Economic Model of Disability?
The Economic Model of Disability views disability primarily in terms of economic productivity and costs. It emphasizes how impairments limit individuals' ability to work and contribute financially to society.
Cultural Model of Disability
The Cultural Model of Disability views disability through the lens of cultural beliefs, values, and practices. This model emphasizes how societies shape the meaning and experience of disability.
It challenges dominant medical perspectives by highlighting diverse cultural understandings and representations of disability. The model promotes inclusion by valuing different ways of being and knowing.
Empowerment Model of Disability
The Empowerment Model of Disability emphasizes the importance of self-advocacy and personal agency for individuals with disabilities. This model promotes equality by recognizing the strengths and rights of disabled people within society.
- Focus on Strengths - Encourages viewing disability through the lens of individual abilities and potential rather than limitations.
- Self-Advocacy - Highlights the role of disabled individuals in making decisions that affect their lives and promoting their own rights.
- Social Inclusion - Aims to remove societal barriers and foster environments where people with disabilities can fully participate.
