Malnutrition affects millions worldwide, impacting physical growth, cognitive development, and overall health. This infographic highlights key statistics, causes, and consequences of malnutrition to raise awareness and promote effective interventions. Understanding these factors is essential for addressing this critical global health issue.
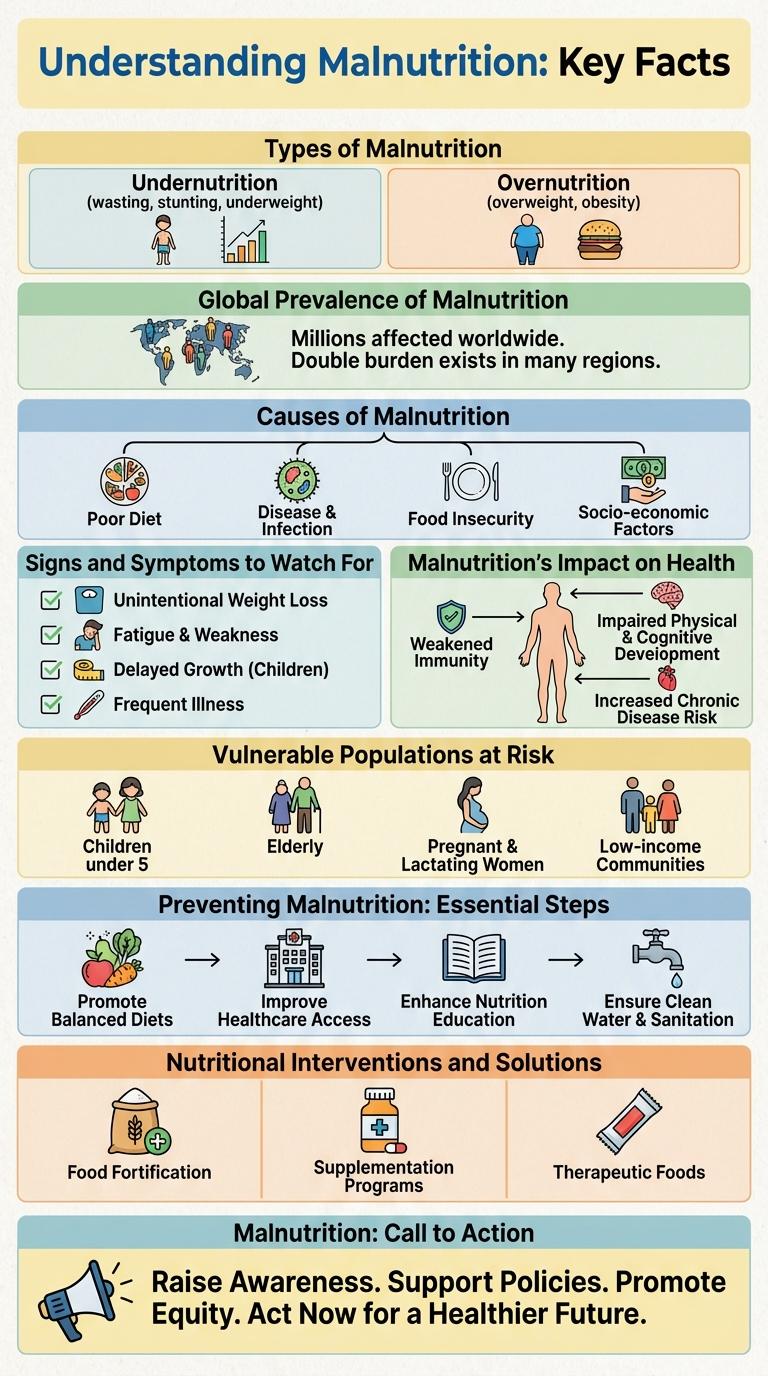
Understanding Malnutrition: Key Facts
Malnutrition affects over 820 million people worldwide, impacting physical health and cognitive development. It includes both undernutrition, such as stunting and wasting, and overnutrition, leading to obesity and diet-related diseases. Early detection and balanced nutrition are critical for preventing long-term health complications.
Types of Malnutrition
Malnutrition encompasses a range of conditions caused by insufficient, excessive, or imbalanced nutrient intake. Recognizing the different types is essential for effective diagnosis and treatment.
- Undernutrition - Occurs when the intake of calories or essential nutrients is insufficient to meet the body's needs, leading to weight loss and stunted growth.
- Overnutrition - Results from excessive consumption of calories or nutrients, often causing obesity and related chronic diseases.
- Micronutrient Deficiency - Involves a shortage of vital vitamins and minerals like iron, iodine, or vitamin A, impairing vital bodily functions and immune response.
Global Prevalence of Malnutrition
Malnutrition affects millions of people worldwide, impacting health and development across all ages. It includes undernutrition, micronutrient deficiencies, and overweight/obesity, posing serious global health challenges.
- Undernutrition in Children - Approximately 45 million children under 5 suffer from wasting, indicating severe weight loss and acute malnutrition.
- Micronutrient Deficiencies - Over 2 billion individuals face deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, leading to impaired immune function and growth.
- Global Overnutrition - More than 1.9 billion adults are overweight or obese, increasing risks for chronic diseases worldwide.
Causes of Malnutrition
Malnutrition arises when the body does not receive adequate nutrients, affecting growth and overall health. Key causes include insufficient food intake, poor nutrient absorption, and increased nutrient requirements due to illness.
Chronic diseases, infections, and inadequate breastfeeding contribute significantly to malnutrition. Socioeconomic factors such as poverty, food insecurity, and lack of education also play crucial roles in its prevalence.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Malnutrition manifests through various signs and symptoms that indicate nutrient deficiencies or excesses. Common indicators include unintended weight loss, persistent fatigue, and weakened immune function. Early recognition of these symptoms is crucial for timely intervention and effective treatment.
Malnutrition's Impact on Health
Malnutrition significantly impairs physical and mental health across all age groups. It weakens the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections and diseases.
Malnourished individuals experience stunted growth, muscle wasting, and delayed cognitive development. Chronic malnutrition leads to long-term health complications such as anemia and osteoporosis. Children and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to these severe health impacts.
Vulnerable Populations at Risk
Who are the most vulnerable populations at risk of malnutrition? Children under five years, pregnant and lactating women, and the elderly face increased malnutrition risks due to higher nutritional needs and limited access to food. Populations in low-income regions and those affected by conflict or natural disasters experience heightened vulnerability to nutrient deficiencies and related health complications.
Preventing Malnutrition: Essential Steps
Malnutrition affects millions worldwide, leading to weakened immunity and increased vulnerability to diseases. Preventing malnutrition is crucial for maintaining overall health and enhancing life quality.
Key steps include ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients and promoting regular health screenings. Access to clean water, sanitation, and education on proper feeding practices also play vital roles in prevention.
Nutritional Interventions and Solutions
Malnutrition affects millions worldwide, demanding effective nutritional interventions for improved health outcomes. Targeted solutions address deficiencies and promote balanced diets.
- Supplementation Programs - Provide essential vitamins and minerals to vulnerable populations to prevent nutrient deficiencies.
- Fortification of Foods - Enrich commonly consumed foods with micronutrients to improve dietary quality at the population level.
- Nutrition Education - Enhance awareness and knowledge to encourage healthier food choices and practices.
- Community-Based Approaches - Engage local populations in identifying needs and delivering tailored nutritional support.
- Breastfeeding Promotion - Support exclusive breastfeeding to ensure infants receive optimal nutrition during critical growth periods.
Implementing multifaceted nutritional interventions significantly reduces malnutrition and fosters sustainable health improvements.
