Automated Meter Reading (AMR) technology revolutionizes utility management by enabling remote collection of consumption data through wireless communication systems. This infographic highlights key benefits of AMR, including improved accuracy, reduced labor costs, and real-time monitoring capabilities. Understanding how AMR works and its impact on efficiency can help utilities optimize resource management and enhance customer service.
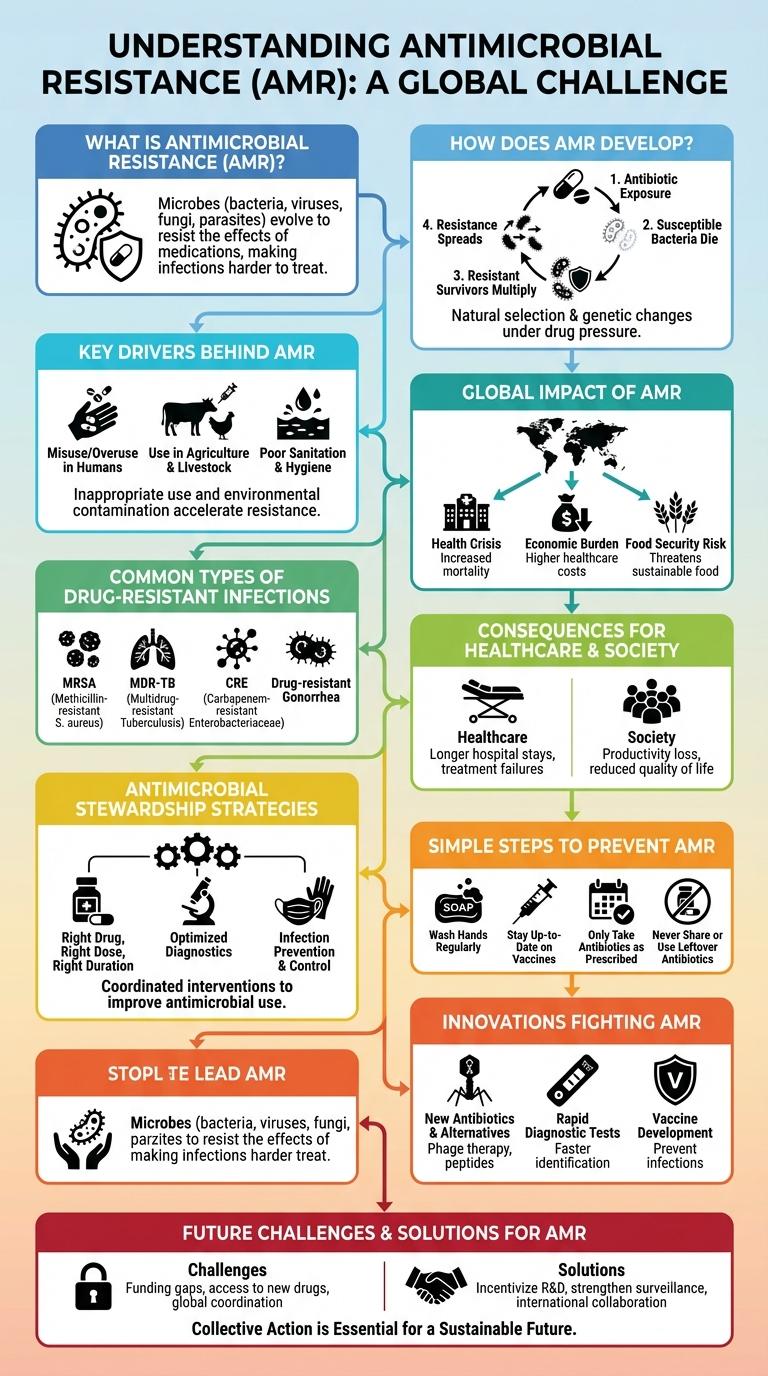
What is Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)?
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) occurs when bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve to resist the effects of medications, rendering treatments ineffective. AMR threatens the successful treatment of infections and increases the risk of disease spread, severe illness, and death. The misuse and overuse of antibiotics in humans, animals, and agriculture accelerate this global health challenge.
How Does AMR Develop?
How does antimicrobial resistance (AMR) develop?
AMR develops when bacteria mutate or acquire genes that enable them to survive exposure to antimicrobial drugs. This process is accelerated by the misuse and overuse of antibiotics in humans, animals, and agriculture.
Key Drivers Behind AMR
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) arises primarily from the overuse and misuse of antibiotics in both human medicine and agriculture. This leads to bacteria evolving mechanisms to survive and render treatments ineffective.
Poor infection control in healthcare settings accelerates the spread of resistant bacteria. Lack of new antibiotics development further compounds the challenge of combating resistant infections.
Global Impact of AMR
Common Types of Drug-Resistant Infections
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) leads to the rise of drug-resistant infections that challenge effective treatment. Common drug-resistant infections include Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), Multidrug-resistant Tuberculosis (MDR-TB), Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), Vancomycin-resistant Enterococci (VRE), and Drug-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae. These infections increase healthcare costs, cause longer hospital stays, and raise mortality rates globally.
Consequences for Healthcare and Society
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a severe threat to healthcare systems worldwide, reducing the effectiveness of treatments. It increases the burden on society through higher medical costs and prolonged illnesses.
- Increased Mortality Rates - AMR leads to infections that are harder to treat, causing more deaths globally each year.
- Longer Hospital Stays - Patients with resistant infections require extended hospital care, straining healthcare resources.
- Economic Burden - AMR drives up healthcare expenses due to expensive alternative treatments and additional medical interventions.
Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategies
Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) poses a significant threat to global health by rendering common infections harder to treat. Effective Antimicrobial Stewardship Strategies are essential to preserve the efficacy of existing antibiotics and reduce resistance.
- Optimized Antibiotic Use - Ensures antibiotics are prescribed only when necessary and appropriate to limit unnecessary exposure.
- Infection Prevention - Implements hygiene measures and vaccinations to reduce infection rates and antibiotic demand.
- Surveillance and Monitoring - Tracks antibiotic use and resistance patterns to inform targeted interventions.
Combining these strategies supports sustainable antibiotic effectiveness and combats the rise of resistant pathogens.
Simple Steps to Prevent AMR
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) occurs when microbes evolve to resist the effects of medications. Preventing AMR is crucial to maintaining the effectiveness of antibiotics and other antimicrobials.
Practice proper hand hygiene to reduce the spread of infections. Only use antibiotics when prescribed by a healthcare professional. Complete the full course of treatment even if symptoms improve to avoid resistant bacteria development.
Innovations Fighting AMR
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) poses a significant global health threat, challenging the effectiveness of existing antibiotics. Innovations in the fight against AMR are crucial to developing new treatments and preserving current therapies.
Cutting-edge technologies such as rapid diagnostic tools enable precise identification of resistant pathogens, allowing tailored treatments. Novel drug development including antimicrobial peptides and bacteriophage therapy offers alternative solutions to combat resistant bacteria.
