Occupational therapy enhances individuals' ability to perform daily activities through tailored interventions and adaptive techniques. It addresses physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges to promote independence and improve quality of life. This infographic highlights key aspects, benefits, and applications of occupational therapy in various settings.
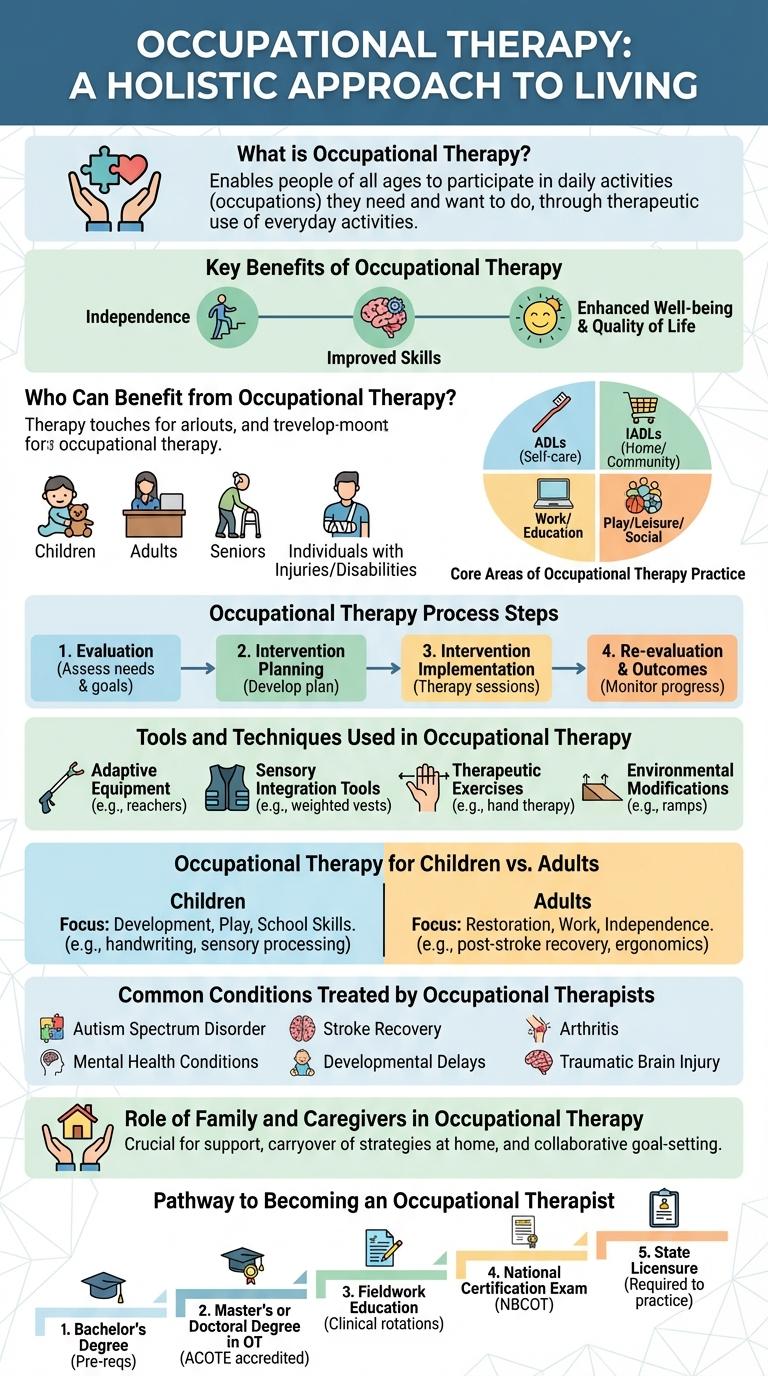
What is Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy is a healthcare profession that helps individuals regain or develop the skills needed for daily living and working. It focuses on improving physical, cognitive, and emotional abilities to enhance independence.
Therapists use personalized interventions to support recovery from injury, illness, or disability. This therapy benefits people of all ages, promoting active participation in meaningful activities.
Key Benefits of Occupational Therapy
What are the key benefits of occupational therapy? Occupational therapy helps individuals regain independence by improving daily living skills. It enhances physical, mental, and emotional well-being through personalized interventions.
How does occupational therapy support physical recovery? It promotes mobility and strength, reducing pain and preventing further injury. Patients achieve better coordination and motor skills tailored to their specific needs.
In what ways does occupational therapy improve mental health? Therapy sessions focus on coping strategies and stress management. It supports cognitive functions like memory, attention, and problem-solving.
Can occupational therapy aid children with developmental challenges? Yes, it fosters skill development in areas such as sensory processing and fine motor coordination. Early intervention improves academic performance and social participation.
Why is occupational therapy important for elderly individuals? It helps maintain independence in daily activities and delays the progression of chronic conditions. Therapy enhances quality of life by addressing physical limitations and cognitive decline.
Who Can Benefit from Occupational Therapy?
Occupational therapy supports individuals across all ages who face physical, developmental, or cognitive challenges. It aims to enhance daily living skills and promote independence in personal and professional environments.
Children with sensory processing issues, adults recovering from injuries, and seniors managing chronic conditions can benefit significantly. Therapists customize interventions to improve mobility, coordination, and mental health, fostering better quality of life.
Core Areas of Occupational Therapy Practice
Occupational therapy supports individuals in achieving independence across various life activities. Core areas of practice address physical, cognitive, and social challenges to enhance daily functioning.
- Activities of Daily Living (ADL) - Focuses on helping clients perform essential self-care tasks such as dressing, bathing, and eating.
- Instrumental Activities of Daily Living (IADL) - Addresses activities related to independent living like cooking, shopping, and managing finances.
- Work and Productivity - Supports clients in developing skills and adaptations needed for employment and productive participation in society.
Occupational therapy combines assessment and intervention tailored to individual needs, promoting overall health and quality of life.
Occupational Therapy Process Steps
Occupational therapy is a client-centered health profession that helps individuals of all ages develop, recover, or maintain meaningful daily activities. The therapy addresses physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges to improve quality of life.
The occupational therapy process follows structured steps to ensure effective intervention. It begins with an initial evaluation to understand the client's needs and goals. Next, the therapist develops a personalized intervention plan. During the intervention phase, specific therapeutic activities are applied to enhance functioning. Finally, progress is regularly reassessed to adjust the treatment plan and achieve optimal outcomes.
Tools and Techniques Used in Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy employs various tools and techniques to help individuals regain, develop, or maintain daily living skills. These interventions are tailored to support physical, cognitive, and emotional functioning.
- Adaptive Equipment - Devices like grabbers, specialized utensils, and dressing aids enhance independence in daily activities.
- Sensory Integration Therapy - Techniques designed to improve sensory processing and motor responses in patients.
- Assistive Technology - Use of software and hardware, such as communication boards and mobility aids, to aid clients.
- Therapeutic Exercises - Customized physical activities target strength, coordination, and range of motion improvements.
- Environmental Modifications - Adjustments in home or work settings to promote safer and more functional living spaces.
Occupational Therapy for Children vs. Adults
Occupational therapy (OT) helps individuals develop, recover, or maintain daily living and work skills. In children, OT focuses on improving fine motor skills, sensory processing, and cognitive development to support learning and play activities. For adults, OT addresses rehabilitation after injury or illness, enhancing mobility, independence, and job-related tasks through tailored interventions.
Common Conditions Treated by Occupational Therapists
Occupational therapists help individuals regain independence by addressing a variety of physical, cognitive, and emotional challenges. Common conditions treated include stroke, arthritis, traumatic brain injury, autism spectrum disorder, and developmental delays. Customized therapy plans focus on improving daily living skills, enhancing motor functions, and promoting mental health well-being.
Role of Family and Caregivers in Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy supports individuals in recovering and enhancing their ability to perform daily tasks. The role of family and caregivers is crucial in reinforcing therapy goals and promoting functional independence.
Family members and caregivers provide emotional support and encouragement throughout the therapy process. They also assist in practicing therapeutic activities outside clinical settings to improve outcomes.
- Emotional Support - Families offer motivation and reassurance that help patients stay engaged in their therapy routines.
- Practical Assistance - Caregivers help implement treatment plans by facilitating exercises and adaptive techniques at home.
- Communication Link - Family members communicate patient preferences and progress to therapists, enhancing personalized care.
