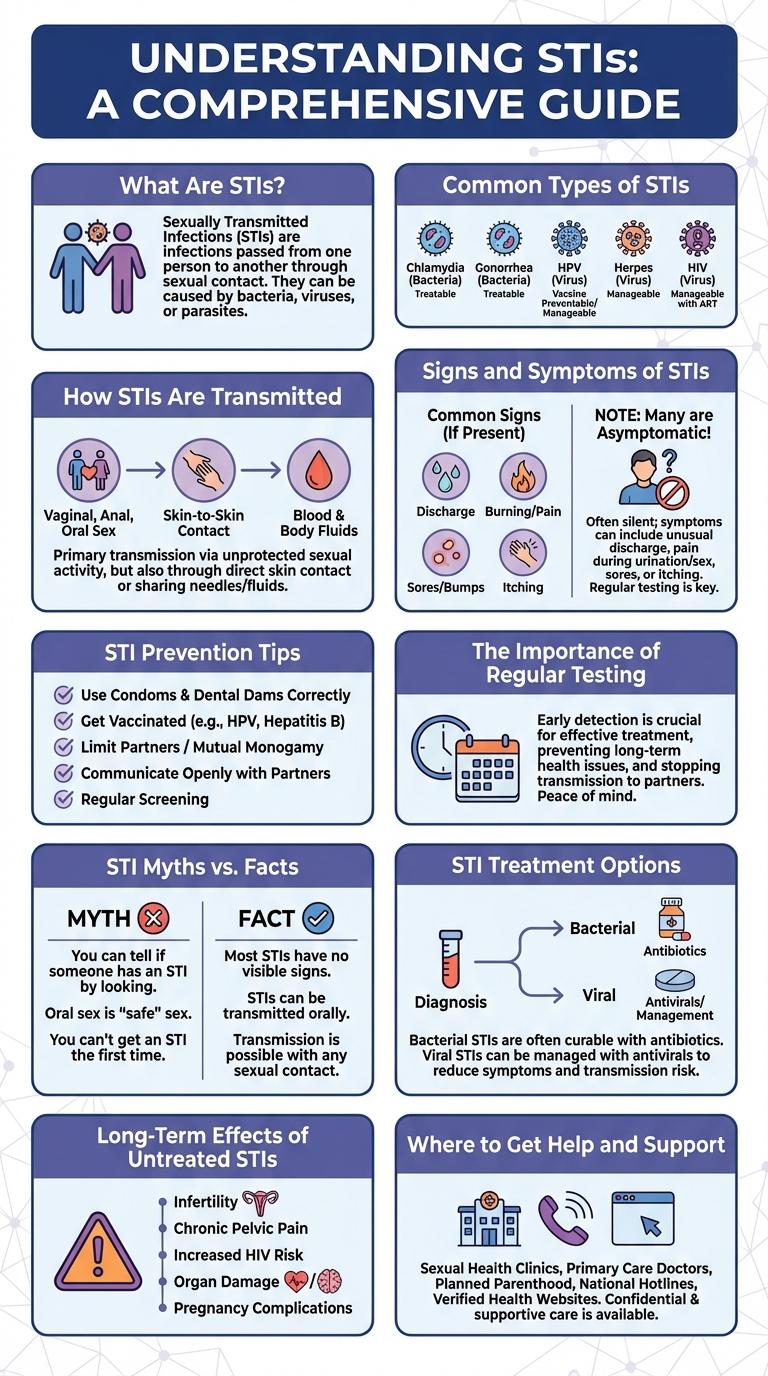
Understanding sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is crucial for maintaining sexual health and preventing their spread. Visual data representations in infographics offer clear insights into common STIs, their symptoms, transmission methods, and prevention strategies. This infographic serves as an essential tool for raising awareness and promoting informed decisions about sexual wellness.
What Are STIs?
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are infections transmitted primarily through sexual contact. They affect millions of people worldwide and can impact reproductive health if untreated.
- Caused by various pathogens - STIs result from bacteria, viruses, parasites, or fungi entering the body during sexual activity.
- Range of symptoms - Some STIs show visible signs, while others remain asymptomatic and undetected for long periods.
- Treatable and preventable - Early diagnosis and consistent use of protection reduce transmission risk and improve health outcomes.
Common Types of STIs
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are caused by bacteria, viruses, or parasites that spread primarily through sexual contact. Common types of STIs include chlamydia, gonorrhea, syphilis, human papillomavirus (HPV), and herpes simplex virus (HSV). Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications and transmission.
| STI | Description |
|---|---|
| Chlamydia | Bacterial infection causing pain, discharge, and potential infertility if untreated. |
| Gonorrhea | Bacterial infection with symptoms similar to chlamydia; can cause severe reproductive damage. |
| Syphilis | Progresses in stages and can affect multiple organs if untreated. |
| HPV | Viral infection linked to genital warts and cervical cancer. |
| Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV) | Causes painful sores and remains dormant with periodic outbreaks. |
How STIs Are Transmitted
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) spread primarily through unprotected sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. Body fluids such as semen, vaginal fluids, and blood carry the infectious pathogens.
Skin-to-skin contact with infected areas can also transmit certain STIs like herpes and human papillomavirus (HPV). Sharing needles or from mother to child during childbirth are additional transmission routes.
Signs and Symptoms of STIs
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) often present with varied signs and symptoms. Recognizing these early symptoms is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
- Unusual Discharge - Abnormal discharge from the genital area can indicate infections like chlamydia or gonorrhea.
- Painful Urination - Experiencing pain or burning while urinating is a common symptom of several STIs.
- Sores or Bumps - The presence of sores, blisters, or bumps on genital or anal areas may signal herpes or syphilis.
Early detection through awareness of these symptoms helps prevent complications and transmission to others.
STI Prevention Tips
| STI Prevention Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Consistent Condom Use | Use condoms correctly during all types of sexual activity to reduce the risk of STI transmission. |
| Regular Testing | Get tested for STIs regularly, especially if you have multiple partners or a new partner. |
| Limit Sexual Partners | Reduce the number of sexual partners to lower exposure to potential infections. |
| Vaccination | Receive vaccines for preventable STIs such as HPV and Hepatitis B. |
| Open Communication | Discuss STI status and prevention methods openly with sexual partners to ensure mutual safety. |
The Importance of Regular Testing
Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) is crucial for maintaining sexual health and preventing transmission. Early detection through testing significantly improves treatment outcomes and reduces complications.
- Detects Infections Early - Identifying STIs early allows for timely medical intervention and reduces the risk of spreading infections to partners.
- Protects Sexual Partners - Regular testing helps prevent transmitting infections to others, supporting safer sexual relationships.
- Supports Overall Health - Early diagnosis and treatment of STIs prevent serious health issues such as infertility, organ damage, and chronic infections.
STI Myths vs. Facts
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) are common and affect millions of people worldwide each year. Misconceptions about STIs contribute to stigma and hinder prevention and treatment efforts.
Many people believe you can always tell if someone has an STI, but most STIs show no symptoms. Condoms are highly effective in reducing the risk of transmission, contradicting myths that they do not protect against STIs. Regular testing is crucial since early detection improves treatment outcomes and prevents spread.
STI Treatment Options
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) require targeted treatment based on the specific pathogen involved. Effective management reduces complications and prevents transmission to others.
Bacterial STIs like chlamydia and gonorrhea are typically treated with prescribed antibiotics. Viral infections such as HIV and herpes rely on antiviral medications to control symptoms and viral load.
Long-Term Effects of Untreated STIs
Untreated sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can lead to serious long-term health complications, including infertility and chronic pelvic pain. Certain STIs such as syphilis and HIV may cause damage to vital organs like the heart and nervous system if left untreated. Early detection and treatment are crucial to prevent these lasting effects and protect overall reproductive and general health.
