Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body, playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health. Composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, each component has specific functions essential for immunity, clotting, and oxygen delivery. Understanding the composition and functions of blood helps in recognizing its importance in medical diagnostics and treatment.
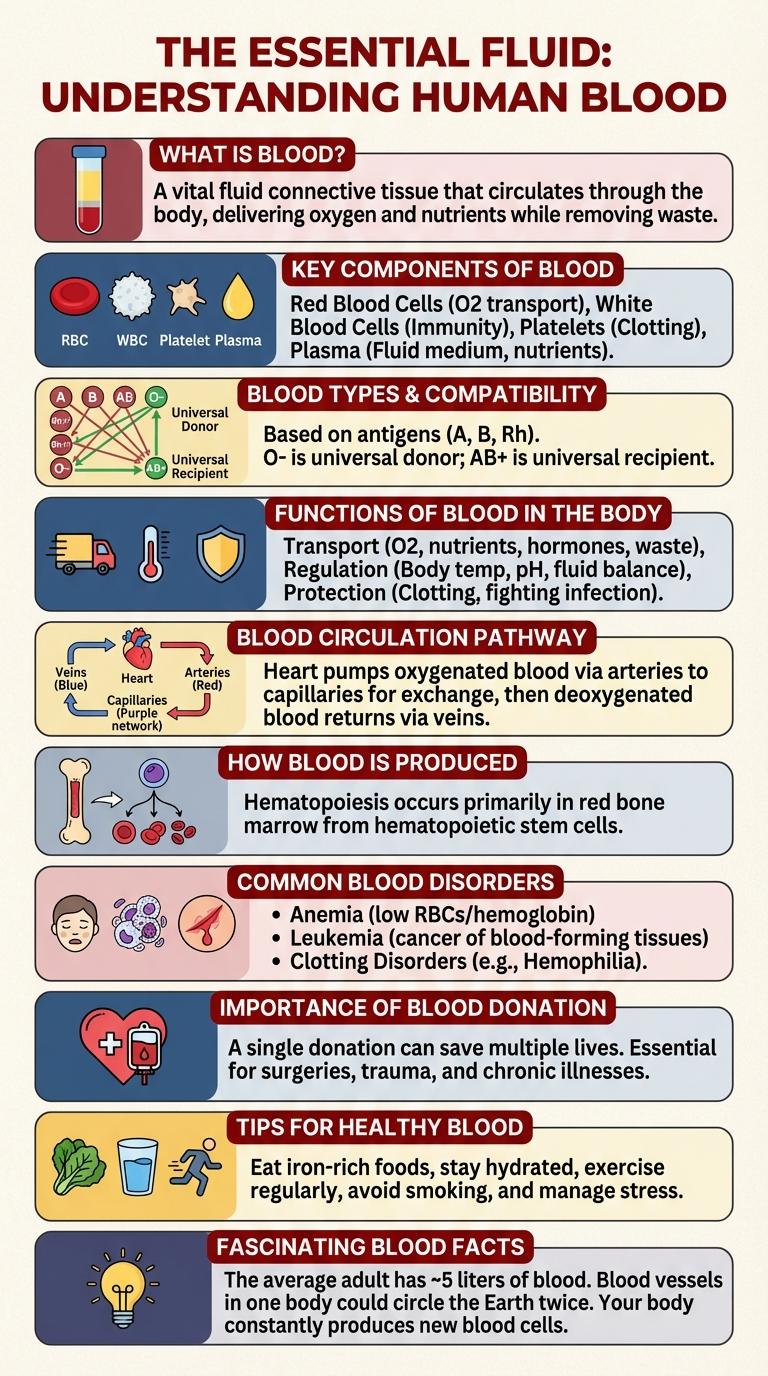
What is Blood?
Blood is a vital fluid that circulates through the human body, delivering oxygen and nutrients to cells. It also plays a key role in removing waste products and defending against infections.
Composed of red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma, blood maintains homeostasis and supports immune function.
- Oxygen Transport - Red blood cells carry oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body.
- Immune Defense - White blood cells protect the body by identifying and fighting pathogens.
- Clotting Mechanism - Platelets help form clots to stop bleeding and repair blood vessel injuries.
Key Components of Blood
Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. It consists of several key components, each with specific functions essential for maintaining health.
The main components of blood include red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, and plasma. Red blood cells carry oxygen, white blood cells fight infections, platelets aid in clotting, and plasma serves as the liquid medium transporting these elements.
Blood Types and Compatibility
Blood types determine how blood transfusions are safely administered. Understanding compatibility between different blood groups is crucial for medical treatments and emergencies.
- Blood Groups - The main blood types are A, B, AB, and O, classified by the presence or absence of antigens on red blood cells.
- Rh Factor - Blood is further categorized by Rh factor, either positive (+) or negative (-), influencing compatibility.
- Compatibility - Type O negative blood is the universal donor, while AB positive is the universal recipient.
Accurate matching of blood types prevents adverse reactions during transfusions and ensures patient safety.
Functions of Blood in the Body
Blood plays a vital role in maintaining homeostasis and supporting life functions. It serves as a transport medium for essential substances throughout the body.
- Transportation of Oxygen and Nutrients - Blood carries oxygen from the lungs and nutrients from the digestive tract to the body's cells.
- Removal of Waste Products - Blood transports carbon dioxide and metabolic wastes to the lungs and kidneys for elimination.
- Immune System Support - Blood contains white blood cells and antibodies that defend the body against infections and foreign invaders.
- Regulation of Body Temperature - Blood absorbs and distributes heat to maintain a stable internal temperature.
- Clotting and Healing - Blood platelets and proteins work together to form clots that stop bleeding and initiate tissue repair.
Blood Circulation Pathway
Blood circulation is the continuous movement of blood through the heart, arteries, veins, and capillaries. It delivers oxygen and nutrients to tissues while removing waste products like carbon dioxide.
The pathway begins in the heart's right atrium, moves to the right ventricle, and then flows to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygen-rich blood returns to the left atrium, proceeds to the left ventricle, and is pumped through the arteries to the body.
How Blood is Produced
Blood is produced primarily in the bone marrow through a process called hematopoiesis. Stem cells within the marrow differentiate into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, each serving vital functions in oxygen transport, immunity, and clotting. This continuous production ensures the maintenance of healthy blood cell levels essential for overall body function.
Common Blood Disorders
Blood is a vital fluid that transports oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. Common blood disorders include anemia, which reduces red blood cells or hemoglobin, and leukemia, a type of cancer affecting white blood cells. Other frequent conditions are hemophilia, a bleeding disorder, and thrombocytopenia, characterized by low platelet counts affecting blood clotting.
Importance of Blood Donation
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Life-saving Resource | Blood donation provides critical supplies for surgeries, trauma care, and chronic illnesses like anemia and cancer. |
| Blood Types Compatibility | Donated blood is matched by types: A, B, AB, and O, each positive or negative, ensuring safe transfusions. |
| Emergency Preparedness | Regular donations maintain adequate blood stocks for emergencies, natural disasters, and accidents. |
| Health Benefits for Donors | Donating blood can improve cardiovascular health and stimulate healthy blood cell production. |
| Community Support | Blood donation fosters social solidarity by supporting vulnerable populations and saving lives. |
Tips for Healthy Blood
What are effective ways to maintain healthy blood? Consuming a balanced diet rich in iron and vitamins supports optimal blood health. Staying hydrated and regular exercise help improve circulation and prevent blood-related issues.
How does diet influence blood quality? Iron-rich foods like spinach and red meat boost hemoglobin production, essential for oxygen transport. Vitamins B6, B12, and folate aid in red blood cell formation and reduce anemia risk.
Why is hydration important for blood health? Proper hydration maintains blood volume and viscosity, ensuring smooth blood flow. Drinking at least 8 glasses of water daily helps prevent blood thickening and clot formation.
What role does exercise play in blood maintenance? Regular physical activity enhances blood circulation and oxygen delivery to tissues. Exercise supports healthy cholesterol levels, reducing the risk of blood vessel damage.
How can lifestyle choices impact blood? Avoiding smoking reduces the risk of blood vessel constriction and clotting. Limiting alcohol intake and managing stress contribute to overall cardiovascular and blood health.
