Smoking poses serious health risks, contributing to diseases like lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory problems. This infographic highlights key statistics on smoking prevalence, its impact on public health, and benefits of quitting. Understanding these facts empowers individuals to make informed decisions about tobacco use.
The Shocking Facts About Smoking
| Fact | Data |
|---|---|
| Annual Deaths Worldwide | Over 8 million |
| Nicotine Addiction Rate | 70-90% of smokers |
| Increased Lung Cancer Risk | 25 times higher than non-smokers |
| Secondhand Smoke Deaths | Approx. 1.2 million per year |
| Average Lifespan Reduction | 10 years for smokers |
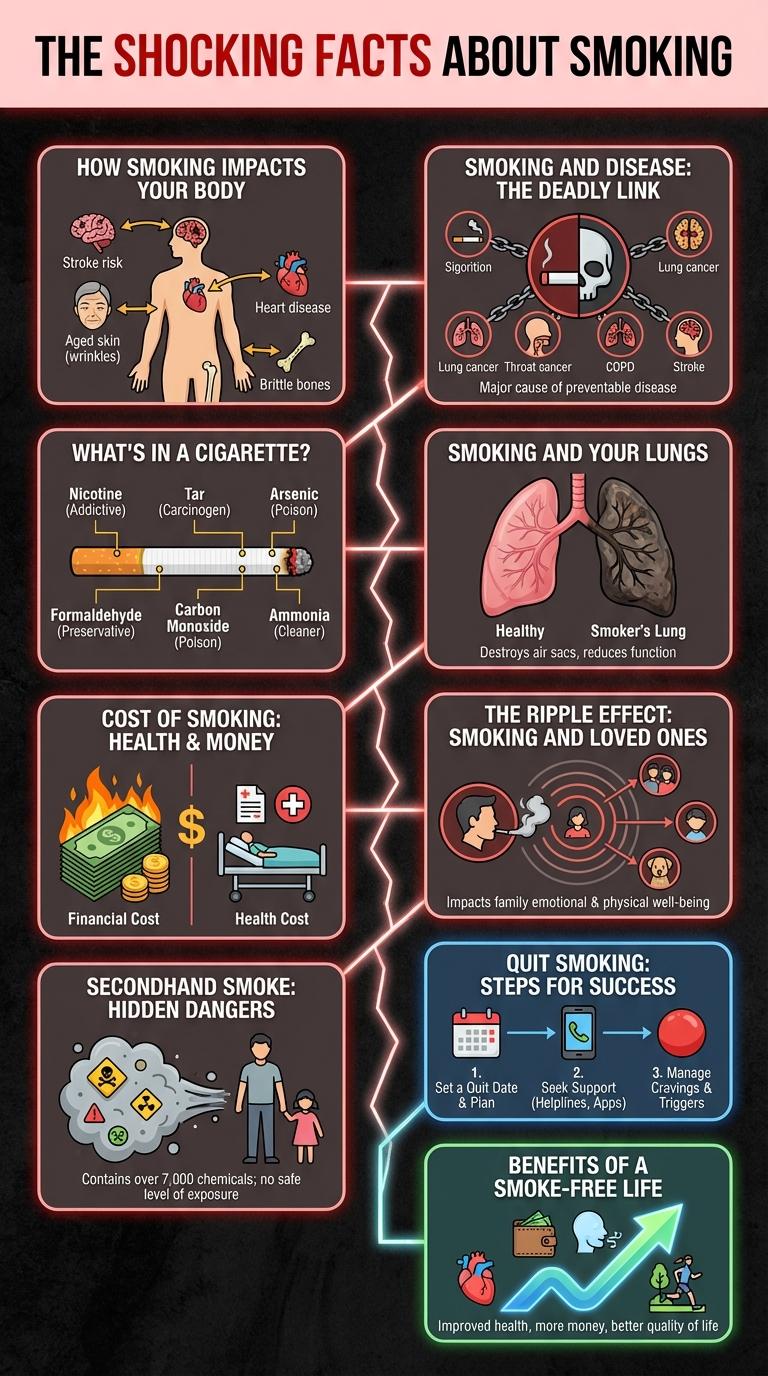
How Smoking Impacts Your Body
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals such as nicotine, tar, and carbon monoxide into the body, damaging organs and tissues. It significantly increases the risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory infections by impairing lung function and blood circulation. Chronic exposure to these toxins accelerates aging, weakens the immune system, and reduces oxygen delivery throughout the body.
Smoking and Disease: The Deadly Link
Smoking is a leading cause of numerous deadly diseases worldwide. It significantly increases the risk of developing chronic conditions such as lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke.
Every year, smoking contributes to over 8 million deaths globally. Chemicals in tobacco smoke damage the lungs and blood vessels, promoting cancer and cardiovascular issues. Quitting smoking reduces disease risk and improves life expectancy dramatically.
What's in a Cigarette?
Cigarettes contain over 7,000 chemicals, with at least 70 known to cause cancer. Key harmful substances include nicotine, tar, carbon monoxide, formaldehyde, and ammonia. These toxic ingredients contribute to addiction, lung damage, and severe health risks.
Smoking and Your Lungs
How does smoking affect your lungs?
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals that damage lung tissue and reduce lung function. This increases the risk of lung diseases such as chronic bronchitis, emphysema, and lung cancer.
Cost of Smoking: Health & Money
Smoking causes severe damage to health and imposes substantial financial burdens on individuals and healthcare systems. Understanding the cost of smoking highlights the need for effective prevention and cessation efforts.
- Health risks of smoking - Smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses, significantly reducing life expectancy.
- Medical expenses - Smokers incur higher healthcare costs due to frequent hospital visits, treatments for chronic diseases, and medication needs.
- Financial loss - The average smoker spends thousands of dollars annually on cigarettes, resulting in a significant personal economic impact.
The Ripple Effect: Smoking and Loved Ones
Smoking not only harms the smoker but also significantly impacts the health of their loved ones through secondhand smoke exposure. Family members, especially children, face increased risks of respiratory infections, asthma, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS).
The emotional and financial burden of smoking-related illnesses affects entire households, reducing quality of life and increasing medical expenses. Quitting smoking benefits both the smoker and those around them, promoting a healthier environment for everyone.
Secondhand Smoke: Hidden Dangers
Secondhand smoke poses serious health risks to non-smokers exposed regularly. It contains toxic chemicals that can cause various diseases even without direct smoking.
- Contains harmful chemicals - Secondhand smoke includes over 7,000 chemicals, hundreds are toxic and about 70 can cause cancer.
- Increases heart disease risk - Exposure raises the risk of coronary heart disease by 25-30% in non-smokers.
- Harms children's health - Children exposed to secondhand smoke have higher rates of asthma, respiratory infections, and sudden infant death syndrome.
Minimizing exposure to secondhand smoke protects lung health and reduces preventable illnesses.
Quit Smoking: Steps for Success
Quitting smoking significantly improves health and reduces the risk of serious diseases such as lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. Success requires a clear plan, determination, and support from resources like counseling and medication.
Step 1: Set a quit date within two weeks to prepare mentally and physically. Step 2: Identify triggers and develop strategies to avoid or cope with cravings to maintain focus on quitting.
Step 3: Seek professional help through support groups, quitlines, or healthcare providers for guidance and encouragement. Step 4: Use FDA-approved cessation aids like nicotine patches, gum, or prescription medications to ease withdrawal symptoms.
Step 5: Monitor progress regularly and celebrate milestones to stay motivated. Step 6: Build a healthy lifestyle with exercise, balanced diet, and stress management to support lasting tobacco-free living.
