Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones and increased fracture risk, affecting millions worldwide. This infographic visually presents key facts, risk factors, and prevention tips to help readers understand and combat bone loss effectively. Clear data and actionable advice empower individuals to take proactive steps toward maintaining strong bone health.
Understanding Osteoporosis: The Silent Disease
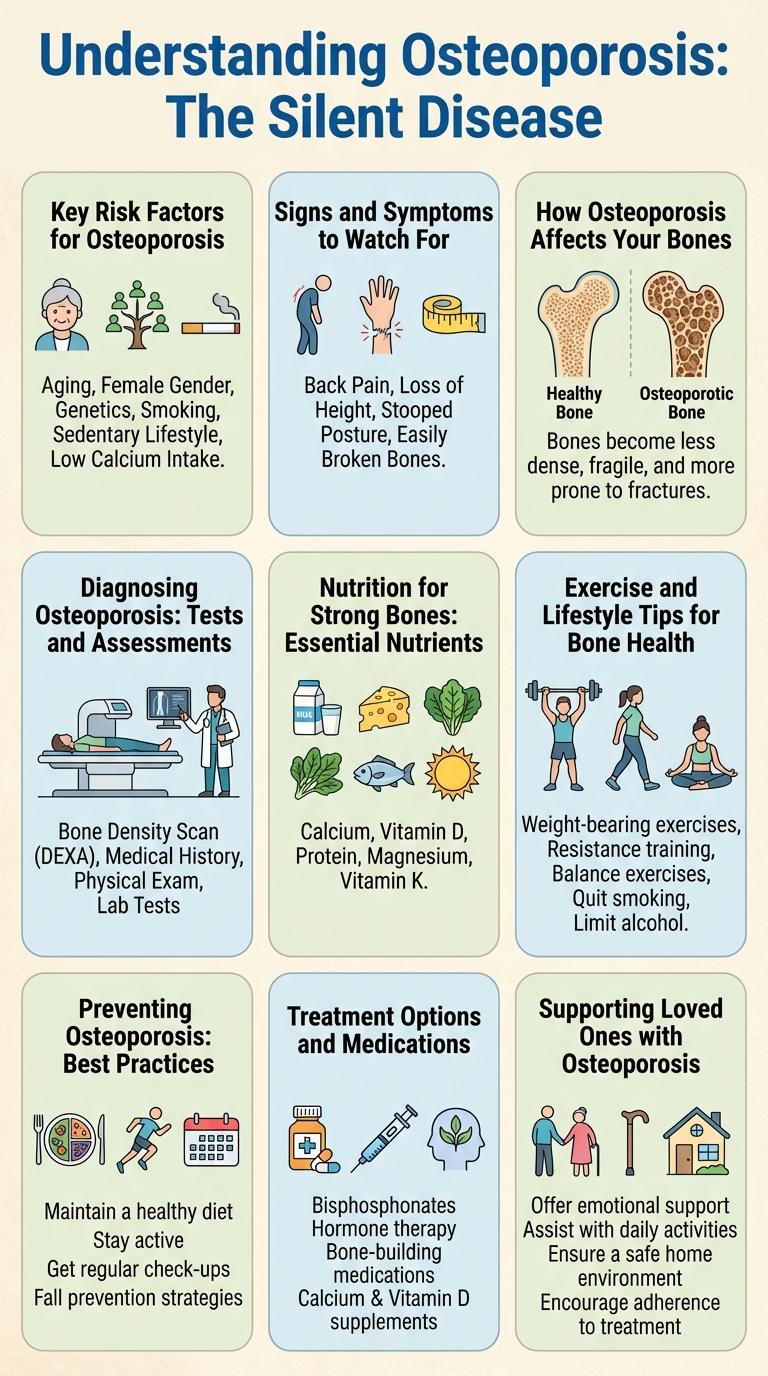
Osteoporosis is a progressive bone disease characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk. Often called the "silent disease," it develops without noticeable symptoms until a fracture occurs.
Bone mass peaks by early adulthood and gradually declines with age, especially in postmenopausal women. Risk factors include calcium deficiency, vitamin D insufficiency, sedentary lifestyle, and certain medications. Early detection through bone density tests can prevent serious fractures and improve quality of life.
Key Risk Factors for Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a common bone disease characterized by decreased bone density and increased fracture risk. Understanding key risk factors helps in early detection and prevention of bone loss.
- Age - Bone density naturally decreases as people age, increasing osteoporosis risk.
- Gender - Women are more prone due to hormonal changes after menopause affecting bone strength.
- Calcium and Vitamin D Deficiency - Low intake of these nutrients weakens bones over time.
- Physical Inactivity - Lack of weight-bearing exercise leads to weaker bones.
- Family History - A genetic predisposition raises the likelihood of developing osteoporosis.
Addressing these risk factors is essential for maintaining healthy bones throughout life.
Signs and Symptoms to Watch For
Osteoporosis is a condition that weakens bones, making them fragile and more likely to break. Recognizing early signs and symptoms is essential for timely intervention and treatment.
- Frequent Bone Fractures - Experiencing fractures from minor falls or injuries may indicate decreased bone density due to osteoporosis.
- Loss of Height - A noticeable decrease in height over time can result from vertebral compression fractures.
- Back Pain - Persistent or sudden back pain might be caused by fractured or collapsed vertebrae linked to osteoporosis.
- Stooped Posture - Developing a hunched or stooped posture is often a sign of spinal bone weakening.
- Bone Density Loss - Low bone mineral density detected through medical scans is a key indicator of osteoporosis.
How Osteoporosis Affects Your Bones
Osteoporosis weakens bones by reducing their density and quality, making them fragile. This condition causes bones to become porous and more prone to fractures, especially in the hip, spine, and wrist. Loss of bone mass disrupts the bone structure, compromising strength and increasing the risk of breaks from minor falls or stresses.
Diagnosing Osteoporosis: Tests and Assessments
Osteoporosis is diagnosed through specific tests that measure bone density and assess fracture risk. Early detection allows for timely intervention to prevent bone loss and fractures.
- Bone Mineral Density (BMD) Test - Uses DEXA scans to measure bone strength, identifying osteoporosis or low bone mass.
- FRAX Assessment Tool - Estimates a 10-year probability of fractures by evaluating clinical risk factors combined with BMD results.
- Vertebral Fracture Assessment (VFA) - Detects existing spinal fractures using low-dose X-rays during a DEXA scan.
Nutrition for Strong Bones: Essential Nutrients
| Essential Nutrient | Role in Bone Health |
|---|---|
| Calcium | Builds and maintains bone density, preventing bone loss |
| Vitamin D | Enhances calcium absorption and promotes bone growth |
| Magnesium | Supports bone structure and influences calcium metabolism |
| Vitamin K | Activates bone-building proteins and supports bone mineralization |
| Protein | Provides amino acids necessary for bone repair and health |
Exercise and Lifestyle Tips for Bone Health
How can exercise improve bone health in individuals with osteoporosis? Weight-bearing and resistance exercises stimulate bone formation and slow down bone loss. Regular physical activity enhances muscle strength, balance, and coordination, reducing the risk of falls and fractures.
What lifestyle habits support stronger bones? Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake are essential for bone mineralization and overall bone density. Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption helps maintain healthy bone remodeling processes.
Which exercises are most effective for preventing osteoporosis-related fractures? Activities like walking, jogging, dancing, and lifting weights apply mechanical stress that promotes bone growth. Balance exercises such as tai chi and yoga improve stability, decreasing fall risk.
How frequent and intense should bone-strengthening exercises be? Experts recommend at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. Incorporating strength training 2 to 3 times weekly supports continuous bone reinforcement.
What role does posture and ergonomics play in osteoporosis management? Maintaining good posture reduces spinal stress and risk of vertebral fractures. Using supportive furniture and practicing safe movement techniques protect bones during daily activities.
Preventing Osteoporosis: Best Practices
Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Preventing osteoporosis involves maintaining a diet rich in calcium and vitamin D to support bone density. Regular weight-bearing exercise, avoiding smoking, and limiting alcohol intake are essential practices for maintaining strong bones and reducing osteoporosis risk.
Treatment Options and Medications
Osteoporosis treatment aims to strengthen bones and prevent fractures through lifestyle changes and medication. Effective treatment options include bisphosphonates, hormone therapy, and calcium plus vitamin D supplements.
Bisphosphonates like alendronate reduce bone loss by inhibiting osteoclast activity. Hormone therapy, including selective estrogen receptor modulators, helps maintain bone density in postmenopausal women.
