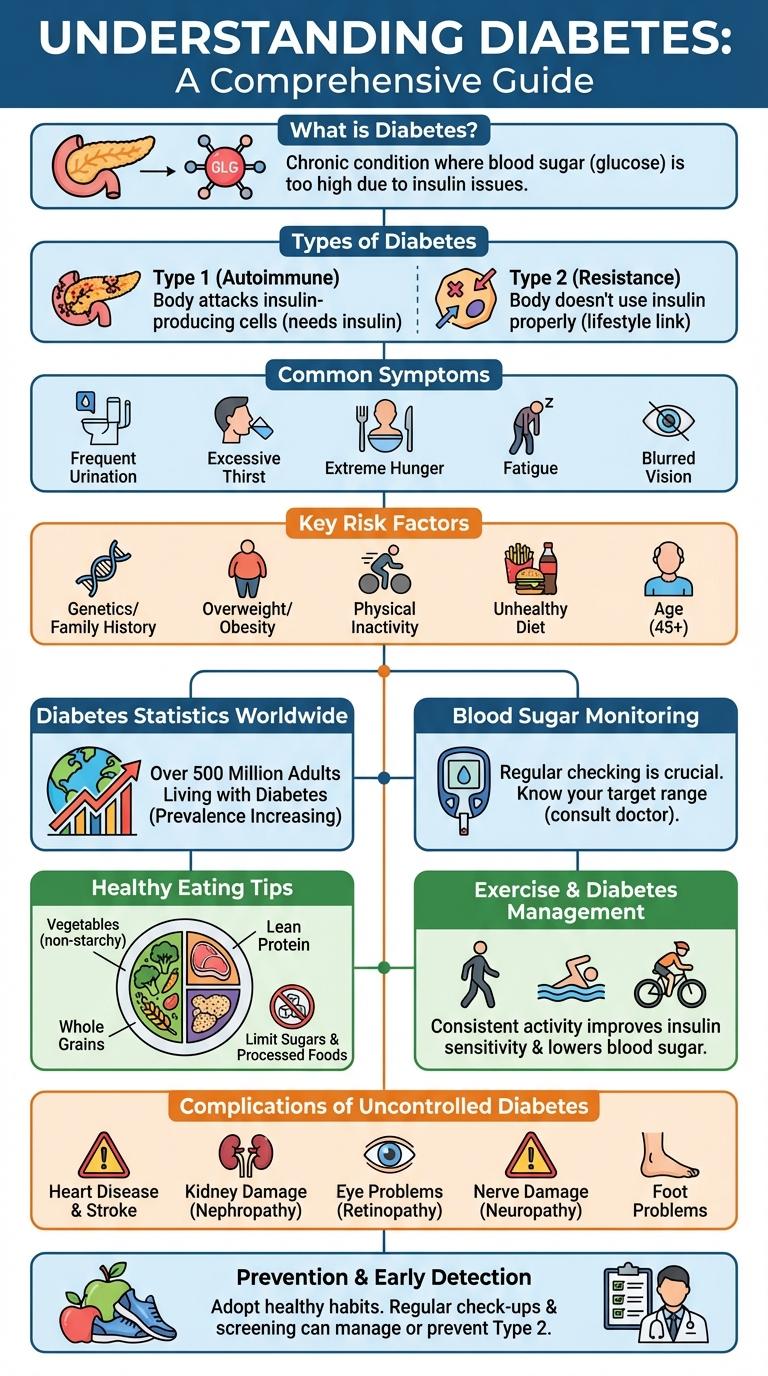
Diabetes is a chronic condition affecting millions worldwide, characterized by elevated blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or deficiency. Understanding its risk factors, symptoms, and management strategies is crucial for prevention and control. This infographic visually presents key information to raise awareness and support healthier lifestyle choices.
What is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition characterized by elevated blood glucose levels. It affects the body's ability to produce or properly use insulin, a hormone crucial for regulating blood sugar.
- Type 1 Diabetes - An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes - A metabolic disorder causing insulin resistance and impaired insulin production.
- Gestational Diabetes - A temporary form of diabetes occurring during pregnancy affecting blood sugar control.
Types of Diabetes
What are the main types of diabetes?
Diabetes is primarily classified into three types: Type 1, Type 2, and Gestational diabetes. Each type affects the body's ability to regulate blood sugar differently.
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Type 1 | An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin. |
| Type 2 | Characterized by insulin resistance and often associated with lifestyle factors. |
| Gestational | Develops during pregnancy and usually resolves after delivery. |
Common Symptoms
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Early detection of common symptoms is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
Common symptoms include frequent urination, excessive thirst, and unexplained weight loss. Other signs are increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores.
Key Risk Factors
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels due to insulin resistance or inadequate insulin production. Key risk factors include obesity, physical inactivity, and a family history of diabetes. Other critical factors are age over 45, hypertension, and poor dietary habits.
Diabetes Statistics Worldwide
Over 530 million adults globally are living with diabetes, according to the International Diabetes Federation. The prevalence has nearly doubled since 2000, with type 2 diabetes accounting for approximately 90% of cases. Diabetes is a leading cause of blindness, kidney failure, heart attacks, stroke, and lower limb amputation worldwide.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
Blood sugar monitoring is a crucial component in managing diabetes effectively. Regular tracking helps patients maintain optimal glucose levels and prevent complications.
Using devices like glucometers, individuals can check their blood sugar multiple times a day. Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) provide real-time data and trends, improving glucose control. Accurate monitoring supports informed decisions about diet, exercise, and medication adjustments.
Healthy Eating Tips
Healthy eating is crucial for managing diabetes effectively and maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Choosing the right foods can improve overall health and reduce the risk of complications.
- Choose whole grains - Whole grains like brown rice and oats provide fiber that helps control blood glucose.
- Include lean proteins - Lean meats, fish, and plant-based proteins support muscle health without raising blood sugar.
- Eat plenty of vegetables - Non-starchy vegetables are low in calories and high in nutrients beneficial for diabetes.
- Limit added sugars - Reducing sugary foods and drinks prevents spikes in blood glucose levels.
- Control portion sizes - Proper portioning helps manage calorie intake and stabilizes blood sugar.
Consistent healthy eating habits are key to long-term diabetes management and improved quality of life.
Exercise and Diabetes Management
Exercise plays a crucial role in diabetes management by improving blood glucose control and enhancing insulin sensitivity. Regular physical activity helps reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications such as cardiovascular disease and neuropathy.
Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise per week is recommended for people with diabetes. Strength training twice a week improves muscle mass, which assists in glucose metabolism and overall glycemic control.
Complications of Uncontrolled Diabetes
| Complication | Description |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | High blood sugar increases risk of heart attacks, stroke, and hypertension by damaging blood vessels. |
| Neuropathy | Nerve damage causes pain, tingling, or numbness, primarily in the extremities, increasing injury risk. |
| Kidney Damage (Nephropathy) | Excess glucose impairs kidney filtration, leading to chronic kidney disease or failure. |
| Eye Damage (Retinopathy) | High glucose levels harm retinal blood vessels, causing vision loss and potential blindness. |
| Foot Ulcers and Infections | Poor circulation and neuropathy increase risk of wounds, infections, and in severe cases, amputation. |
