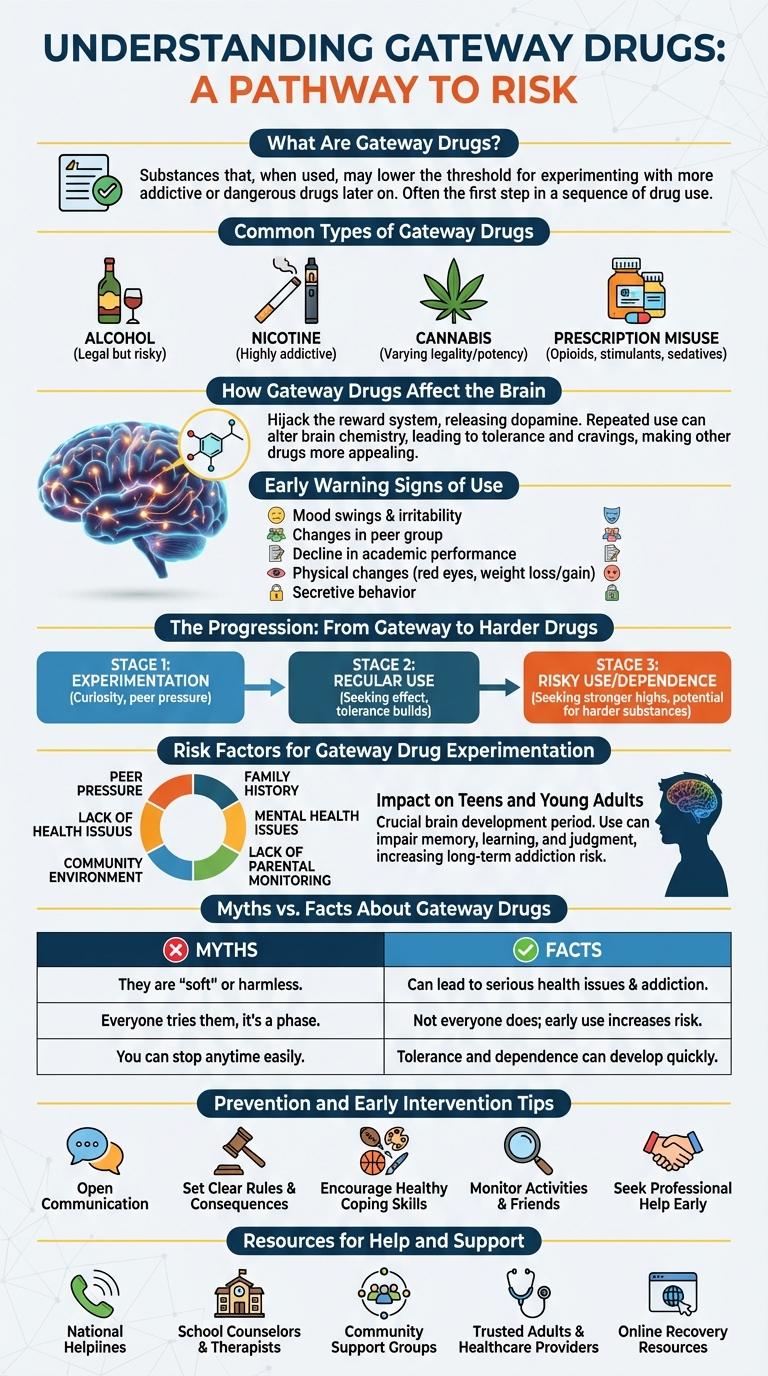
Gateway drugs are substances that may lead individuals to experiment with more harmful drugs over time. Understanding the role of these initial substances helps in identifying risk patterns and preventing further substance abuse. This infographic highlights key information about common gateway drugs, their effects, and the pathway to addiction.
What Are Gateway Drugs?
Gateway drugs are substances that may lead individuals to try more harmful and addictive drugs. Understanding these drugs helps in preventing drug abuse and promoting healthier choices.
- Definition of Gateway Drugs - These are typically less addictive substances used before trying stronger drugs.
- Common Examples - Tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana are often identified as gateway drugs.
- Impact on Behavior - Use of gateway drugs can increase the likelihood of future substance abuse and addiction.
Common Types of Gateway Drugs
Gateway drugs are substances that may lead to the use of more harmful and addictive drugs. Common types of gateway drugs include tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana. These substances are often the first drugs tried, increasing the risk of progressing to stronger drugs.
How Gateway Drugs Affect the Brain
Gateway drugs such as tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana introduce the brain to substances that alter its chemistry. These drugs impact brain regions responsible for reward, decision-making, and impulse control.
The use of gateway drugs triggers the release of dopamine, creating pleasurable sensations that reinforce the behavior. Over time, this can lead to changes in the brain's reward system, reducing sensitivity to natural rewards. This neural adaptation increases the likelihood of experimenting with stronger, more harmful substances.
Early Warning Signs of Use
Gateway drugs such as tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana often introduce individuals to more harmful substance use. Early warning signs include sudden changes in behavior, declining academic performance, and withdrawal from family or friends. Recognizing these indicators promptly can help prevent progression to more serious drug use.
The Progression: From Gateway to Harder Drugs
Gateway drugs such as tobacco, alcohol, and marijuana often serve as the initial substances experimented with by individuals. These drugs can alter brain chemistry, increasing the likelihood of trying more potent and addictive substances.
Research shows that early use of gateway drugs correlates with a higher risk of progressing to harder drugs like cocaine, heroin, or methamphetamine. This progression is influenced by environmental, genetic, and psychological factors that reinforce substance dependence.
Risk Factors for Gateway Drug Experimentation
Impact on Teens and Young Adults
Gateway drugs are substances that often lead teens and young adults to try more harmful and addictive drugs. Early use of these substances increases the risk of long-term mental and physical health problems.
- Increased Risk of Addiction - Teens using gateway drugs have a higher chance of developing substance dependence later in life.
- Impaired Brain Development - Exposure to these drugs during adolescence affects brain areas responsible for decision-making and impulse control.
- Decline in Academic Performance - Use of gateway drugs often correlates with lower grades and decreased school attendance.
Preventive education and early intervention are critical to reducing the impact of gateway drugs on young populations.
Myths vs. Facts About Gateway Drugs
Are gateway drugs truly a direct path to harder substance abuse? Many believe using gateway drugs inevitably leads to serious addiction. Research shows that while gateway drugs can increase risk, multiple factors influence substance abuse progression.
Do all teens who try gateway drugs develop addiction? Experimentation does not guarantee addiction or progression. Most teens who try substances like marijuana or alcohol do not become addicted or move on to harder drugs.
Is marijuana always considered a gateway drug? Marijuana is often labeled as a gateway drug, but evidence varies. The likelihood of it leading to harder drug use depends on genetic, social, and environmental factors.
Does using tobacco or alcohol as gateway drugs increase addiction risk? Early use of tobacco and alcohol is linked to higher chances of future substance use. These substances can affect brain development, influencing risk-taking behaviors and addiction predisposition.
Can education and prevention reduce the impact of gateway drugs? Comprehensive prevention programs targeting youth reduce initiation and misuse. Educating about risks and promoting healthy coping skills lowers chances of progressing from gateway drugs to harder substances.
Prevention and Early Intervention Tips
Gateway drugs often serve as an introduction to more addictive substances, highlighting the importance of prevention and early intervention. Educating youth about the risks of these substances reduces the likelihood of progression to harder drugs.
Parents and educators play a crucial role by creating open communication and monitoring behavior changes early. Providing support and resources during the initial stages can prevent long-term addiction and promote healthier choices.
