Occupational safety and health practices play a crucial role in preventing workplace injuries and illnesses. Effective safety programs reduce hazards and promote employee well-being across various industries. Visualizing key statistics and guidelines through an infographic enhances understanding and encourages proactive risk management.
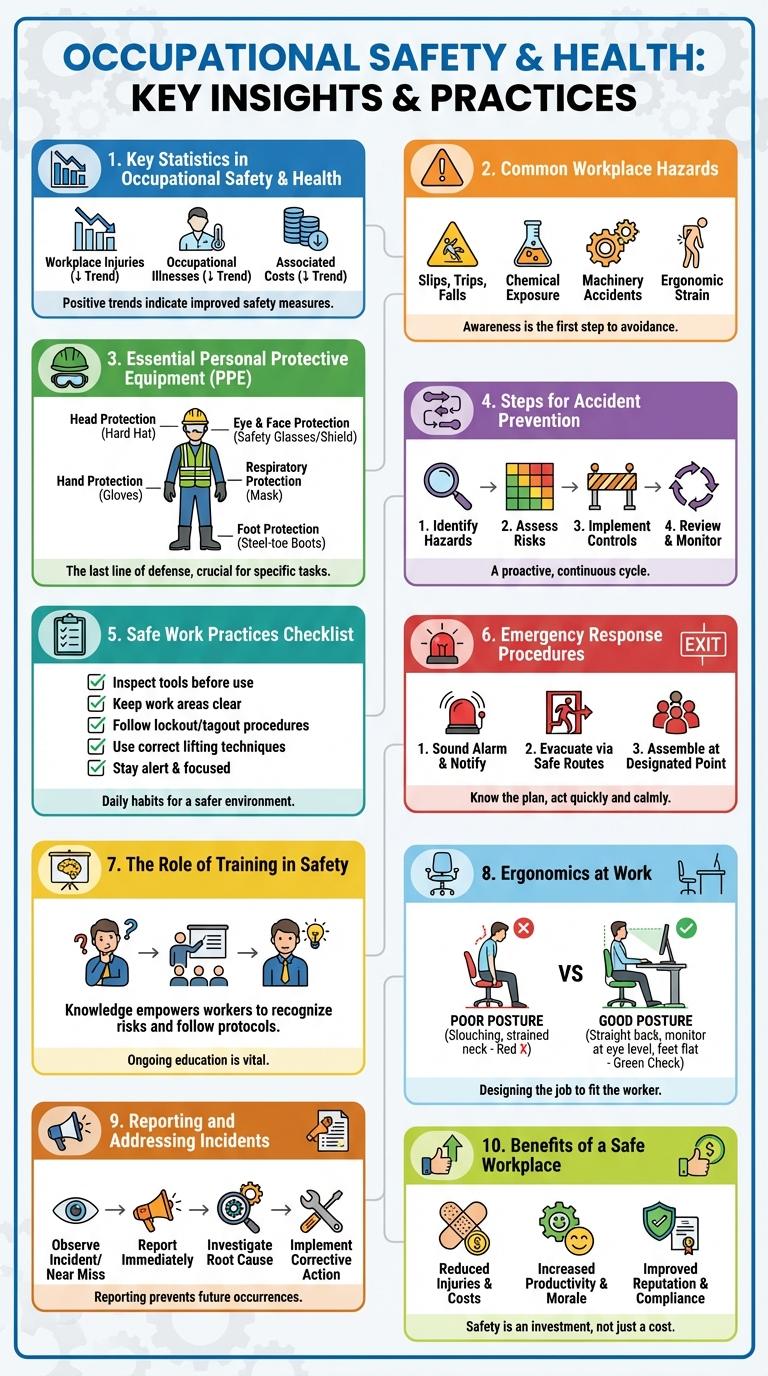
Key Statistics in Occupational Safety & Health
Occupational safety and health (OSH) is crucial for reducing workplace injuries and illnesses globally. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), over 2.3 million people die annually from work-related accidents or diseases.
Work-related injuries cost approximately 4% of the global GDP each year, highlighting the economic impact of unsafe working conditions. Implementing effective OSH measures can reduce workplace incidents by up to 40%, improving both employee well-being and productivity.
Common Workplace Hazards
Workplace safety is essential to prevent injuries and ensure a healthy work environment. Recognizing common occupational hazards helps in implementing effective safety measures.
- Slips, Trips, and Falls - These incidents are the leading cause of workplace injuries, often due to wet floors or uneven surfaces.
- Exposure to Hazardous Substances - Contact with chemicals, gases, or asbestos can cause acute or chronic health problems.
- Ergonomic Risks - Poor posture and repetitive motions contribute to musculoskeletal disorders in workers.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment
Occupational safety and health prioritize the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) to minimize workplace hazards. Proper PPE reduces injury risks and ensures compliance with safety regulations.
- Hard Hats - Protect the head from falling objects and impact injuries in construction and industrial settings.
- Safety Goggles - Shield eyes from dust, chemicals, and flying debris to prevent visual impairment.
- Respirators - Filter airborne contaminants and protect respiratory health in environments with hazardous particles or gases.
Steps for Accident Prevention
Effective accident prevention in occupational safety and health relies on structured steps that minimize hazards and promote a safe work environment. Understanding and implementing these steps reduces injury risks and enhances workplace productivity.
Identifying potential hazards is the first critical step, involving thorough workplace inspections and risk assessments. Training employees on safety protocols and proper use of equipment ensures they are prepared to avoid accidents.
Safe Work Practices Checklist
Occupational safety and health are essential for preventing workplace injuries and ensuring employee well-being. A Safe Work Practices Checklist helps maintain a secure and productive environment.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) - Confirm all workers wear appropriate PPE for their tasks, including helmets, gloves, and eye protection.
- Hazard Identification - Regularly inspect the workplace to identify and address potential safety hazards.
- Emergency Procedures - Ensure all employees are trained on emergency exits, fire drills, and first aid protocols.
Consistent use of a Safe Work Practices Checklist reduces risks and promotes a culture of safety at work.
Emergency Response Procedures
Emergency response procedures are critical protocols designed to protect employees and minimize hazards during workplace emergencies. Key components include clear evacuation routes, accessible emergency equipment, and immediate communication systems. Regular training and drills ensure quick, coordinated actions that reduce injuries and save lives.
The Role of Training in Safety
Training plays a crucial role in occupational safety and health by equipping employees with essential knowledge and skills to prevent workplace accidents. Effective training reduces injury rates and fosters a safety-conscious culture within organizations.
Workers trained in hazard recognition and safe work practices are better prepared to handle emergencies and avoid risks. Consistent training ensures compliance with regulatory standards such as OSHA guidelines. Employers who invest in safety training experience fewer incidents and lower workers' compensation costs.
Ergonomics at Work
| Ergonomics Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Study of designing workplace tasks to fit the worker's capabilities and limitations. |
| Common Risks | Repetitive strain injuries, poor posture, musculoskeletal disorders. |
| Workplace Solutions | Adjustable chairs, ergonomic keyboards and mice, proper lighting. |
| Benefits | Reduced injury rates, increased productivity, improved employee comfort. |
| Key Statistics | Ergonomic interventions can reduce musculoskeletal disorders by 50% (OSHA). |
Reporting and Addressing Incidents
Effective reporting and addressing incidents is crucial for maintaining occupational safety and health. Workers must promptly report any accidents, near misses, or hazardous conditions to ensure timely intervention. Implementing clear procedures and training enhances the organization's ability to prevent future incidents and promote a safer work environment.
