Smoking and poor dietary habits significantly contribute to numerous health problems such as heart disease, respiratory issues, and obesity. Both behaviors increase the risk of chronic illnesses and reduce overall life expectancy. Addressing these factors is crucial for improving public health and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
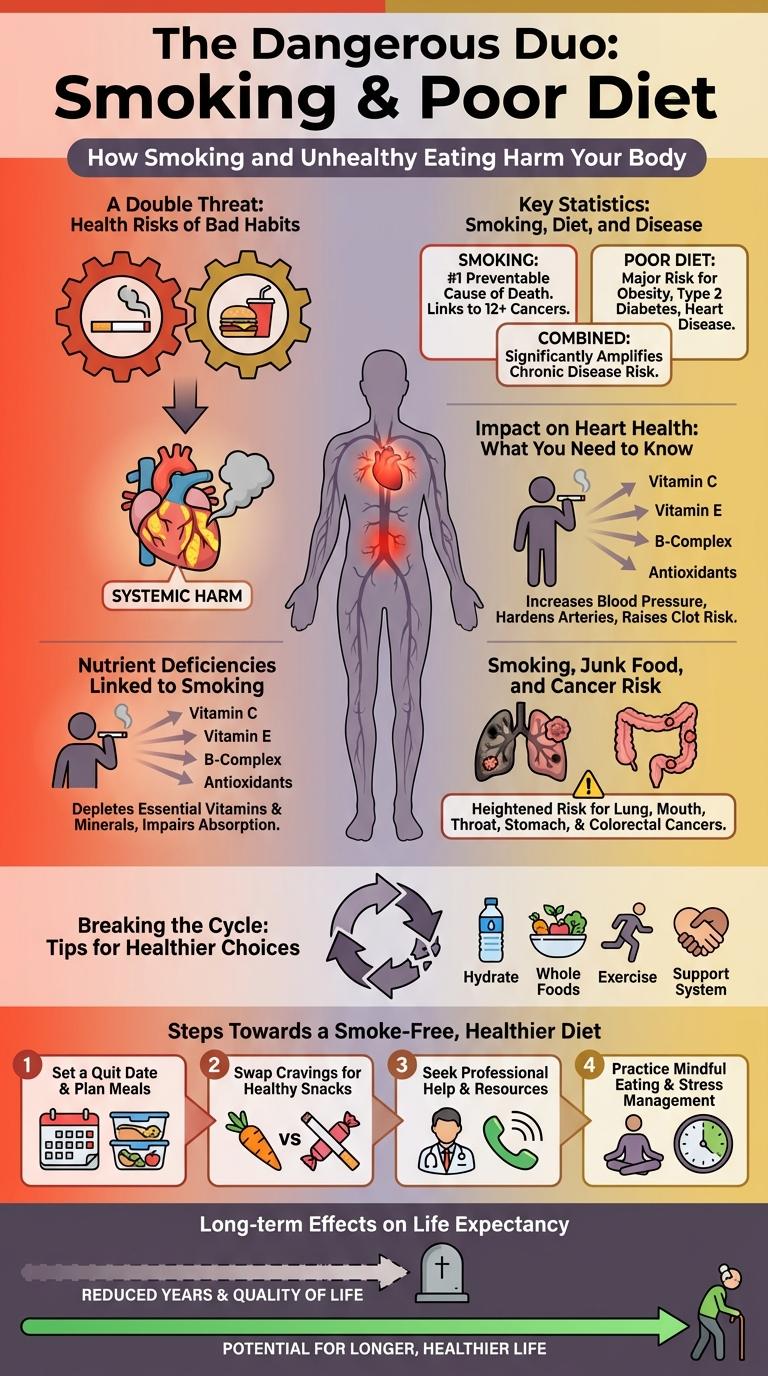
The Dangerous Duo: Smoking & Poor Diet
Smoking combined with poor dietary habits significantly elevates the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, stroke, and cancer. This dangerous duo exacerbates oxidative stress and inflammation, leading to accelerated cellular damage.
Poor nutrition weakens the body's ability to repair damage caused by toxins in cigarette smoke, impairing immune function. Together, they create a harmful cycle that severely compromises overall health and longevity.
How Smoking and Unhealthy Eating Harm Your Body
Smoking introduces harmful chemicals into the body that damage the lungs, heart, and blood vessels, significantly increasing the risk of cancer, respiratory diseases, and cardiovascular problems. Poor dietary habits, such as high consumption of processed foods and sugars, contribute to obesity, diabetes, and nutrient deficiencies.
The combination of smoking and unhealthy eating accelerates inflammation and oxidative stress, weakening the immune system and impairing organ function. Together, these habits drastically increase the risk of chronic diseases and reduce overall life expectancy.
A Double Threat: Health Risks of Bad Habits
Smoking and poor dietary habits pose significant health risks that often compound each other, leading to more severe medical conditions. Both behaviors contribute to chronic diseases that reduce quality of life and increase mortality rates.
Smoking introduces harmful toxins that damage the lungs and cardiovascular system, while poor dietary choices contribute to obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The combination of these habits accelerates the development of chronic illnesses, including cancer and stroke. Addressing both smoking and diet simultaneously is crucial for improving overall health outcomes and preventing life-threatening conditions.
Key Statistics: Smoking, Diet, and Disease
Smoking and poor dietary habits are leading risk factors contributing to chronic diseases worldwide. Approximately 1.3 billion people smoke globally, increasing their risk of cardiovascular disease, cancer, and respiratory conditions. Diets high in processed foods and low in fruits and vegetables contribute to obesity, diabetes, and hypertension, exacerbating the global burden of non-communicable diseases.
| Key Statistic | Data |
|---|---|
| Global smokers | 1.3 billion people |
| Annual smoking-related deaths | 8 million |
| Adults with poor diet | 88% globally consume inadequate fruits and vegetables |
| Obesity prevalence | 13% of adults worldwide |
| Non-communicable diseases linked | 70% of global deaths |
Impact on Heart Health: What You Need to Know
Smoking and poor dietary habits significantly increase the risk of heart disease by contributing to arterial damage and elevated cholesterol levels. Understanding their impact helps in making informed lifestyle choices to protect heart health.
Heart disease remains the leading cause of death globally, with smoking and unhealthy diets as major contributors.
- Smoking damages blood vessels - Chemicals in tobacco lead to inflammation and narrowing of arteries, increasing heart attack risk.
- Poor diet raises cholesterol - High intake of saturated fats and trans fats elevates LDL cholesterol, promoting plaque buildup in arteries.
- Combined effects amplify risk - Smoking and unhealthy eating together accelerate heart disease development and complications.
Nutrient Deficiencies Linked to Smoking
Smoking significantly depletes essential nutrients such as vitamin C, vitamin E, and folate, leading to increased oxidative stress and impaired immune function. Poor dietary habits exacerbate these deficiencies, resulting in heightened risks of cardiovascular diseases, weakened bone health, and delayed wound healing. Addressing nutrient gaps through diet or supplementation is crucial for smokers to mitigate adverse health effects and improve overall wellness.
Smoking, Junk Food, and Cancer Risk
Smoking and poor dietary habits significantly increase the risk of cancer. Both factors contribute to the development of unhealthy cells and weaken the body's defense mechanisms.
- Smoking - Tobacco smoke contains over 70 carcinogens that damage DNA and promote tumor growth.
- Junk Food - Diets high in processed foods, sugars, and unhealthy fats lead to chronic inflammation linked to cancer.
- Cancer Risk - Combined exposure to smoking and poor nutrition multiplies the chances of developing lung, colorectal, and pancreatic cancers.
Maintaining a balanced diet and avoiding smoking are essential strategies for reducing cancer risk and promoting long-term health.
Breaking the Cycle: Tips for Healthier Choices
How can you break the cycle of smoking and poor dietary habits for better health? Quitting smoking lowers the risk of heart disease and cancer significantly. Adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables boosts your immune system and energy levels.
What are practical tips to improve eating habits while quitting smoking? Plan meals ahead to avoid unhealthy snacking triggered by nicotine cravings. Replace sugary drinks with water or herbal teas to reduce sugar intake and improve hydration.
How does physical activity support healthier lifestyle changes? Regular exercise helps reduce withdrawal symptoms and stress caused by quitting smoking. It also encourages better appetite control and promotes weight management.
Which foods help reduce nicotine cravings and improve mood? Foods high in antioxidants like berries and nuts stabilize blood sugar and fight inflammation. Omega-3 rich foods such as salmon contribute to brain health and mood regulation.
Why is professional support important when breaking unhealthy habits? Healthcare providers can offer personalized quitting plans and nutritional advice. Support groups increase motivation and provide accountability during lifestyle changes.
Long-term Effects on Life Expectancy
| Risk Factor | Impact on Life Expectancy |
|---|---|
| Smoking | Reduces average life expectancy by approximately 10 years due to increased risk of lung cancer, heart disease, and stroke. |
| Poor Dietary Habits | Can shorten lifespan by up to 5 years through factors like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. |
| Combined Effect | Smoking combined with poor diet synergistically increases mortality risk, potentially reducing life expectancy by 15 years or more. |
| Chronic Disease Risk | Both smoking and poor nutrition contribute to chronic conditions such as COPD, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome. |
| Preventative Impact | Quitting smoking and adopting a balanced diet significantly improve longevity and quality of life. |
