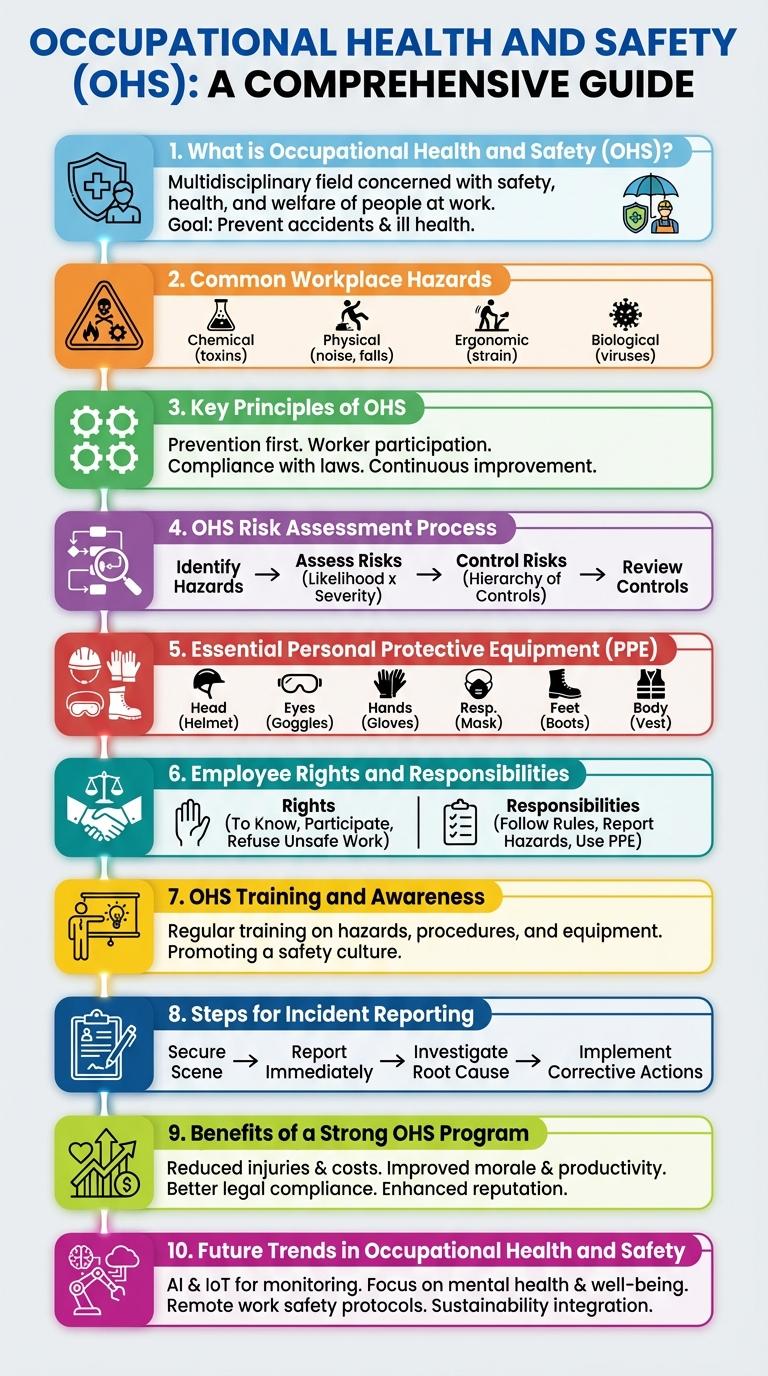
Workplace safety is a critical priority that protects employees from hazards and reduces the risk of accidents and injuries. Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) programs establish standards and practices to ensure a safe work environment through training, hazard identification, and compliance with regulations. Visualizing key OHS concepts through an infographic simplifies complex information, making it easier to understand and implement safety measures effectively.
What is Occupational Health and Safety (OHS)?
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) is a discipline focused on ensuring the safety, health, and welfare of people at work. OHS involves implementing policies, procedures, and practices to prevent workplace accidents, injuries, and illnesses. Effective OHS programs contribute to safer work environments, improved employee well-being, and compliance with legal regulations.
Common Workplace Hazards
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) identifies common workplace hazards to prevent injuries and illnesses. These hazards include physical risks like slips, trips, and falls, as well as chemical exposure and ergonomic challenges. Understanding these dangers helps employers implement effective safety measures and protect workers.
Key Principles of OHS
| Key Principles of OHS | Description |
|---|---|
| Hazard Identification | Systematic detection of potential sources of harm in the workplace. |
| Risk Assessment | Evaluation of the likelihood and impact of hazards causing injury or illness. |
| Control Measures | Implementation of strategies to eliminate or reduce workplace hazards. |
| Employee Training | Providing workers with knowledge and skills on safe work practices and hazard control. |
| Continuous Improvement | Ongoing review and enhancement of occupational health and safety policies and procedures. |
OHS Risk Assessment Process
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) Risk Assessment is a systematic process to identify, evaluate, and control hazards in the workplace. It ensures a safer environment by minimizing potential risks to employees and assets.
The process begins with hazard identification, followed by risk analysis, and concludes with implementing control measures. Regular reviews and monitoring help maintain effective risk management and compliance with safety regulations.
Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) standards emphasize the importance of Essential Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) to safeguard workers in various industries. Proper PPE use reduces the risk of injury and exposure to hazardous conditions.
- Safety Helmets - Protect the head from impact, falling objects, and electrical hazards.
- Protective Eyewear - Shields eyes from dust, chemical splashes, and flying debris.
- High-Visibility Clothing - Enhances worker visibility in low-light or busy environments.
- Gloves - Provides hand protection against cuts, abrasions, chemicals, and heat.
- Respirators - Filters airborne contaminants to protect respiratory health.
Consistent use and proper maintenance of PPE are critical for effective workplace safety and health compliance.
Employee Rights and Responsibilities
What are the key employee rights in Occupational Health and Safety (OHS)? Employees have the right to a safe and healthy work environment free from recognized hazards. They are entitled to receive proper training and information about workplace risks.
What responsibilities do employees have under OHS regulations? Employees must follow all safety protocols and use protective equipment provided. Reporting unsafe conditions and participating in safety training sessions are essential duties.
How can employees exercise their right to refuse unsafe work? Workers can refuse work they believe is dangerous without fear of retaliation. They must promptly report the hazard to their employer or health and safety representative.
What role does employee participation play in workplace safety? Active involvement in safety committees and hazard assessments improves overall work conditions. Employees contribute valuable insights that prevent accidents and injuries.
How do communication and cooperation affect OHS outcomes? Open dialogue between employees and management fosters a culture of safety. Collaboration ensures hazards are identified and controlled efficiently.
OHS Training and Awareness
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) training is essential for creating a safe and compliant workplace. It equips employees with the knowledge to identify and mitigate potential hazards effectively.
OHS training improves awareness about workplace risks and safety procedures. Regular sessions ensure that all staff stay up-to-date with legal requirements and best practices. Effective training reduces workplace accidents and promotes a culture of safety across all levels.
Steps for Incident Reporting
Effective incident reporting is essential for maintaining workplace safety and preventing future accidents. Following clear steps ensures accurate documentation and timely response.
- Identify the Incident - Recognize and classify the type of incident that has occurred immediately after it happens.
- Report to Supervisor - Notify the designated authority or supervisor promptly to initiate the response process.
- Document Details - Complete an incident report form with precise details including date, time, location, and persons involved.
- Investigate the Incident - Conduct a thorough investigation to determine causes and contributing factors.
- Implement Corrective Actions - Apply measures to rectify hazards and prevent recurrence of similar incidents.
Benefits of a Strong OHS Program
Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) programs play a critical role in maintaining a secure work environment. A robust OHS program reduces risks and enhances employee well-being.
- Reduced Workplace Accidents - Effective OHS strategies significantly lower the incidence of work-related injuries and illnesses.
- Increased Productivity - Safe working conditions contribute to higher employee morale and efficiency.
- Legal Compliance - A strong OHS program ensures adherence to safety regulations, avoiding fines and legal issues.
- Cost Savings - Fewer accidents lead to reduced compensation claims and operational disruptions.
- Enhanced Reputation - Commitment to safety builds trust with clients, employees, and stakeholders.
