Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) affects millions worldwide, often resulting in severe emotional distress and impaired daily functioning. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for effective support and recovery. This infographic provides clear, concise information to help raise awareness and promote mental health education.
Understanding PTSD: Key Facts
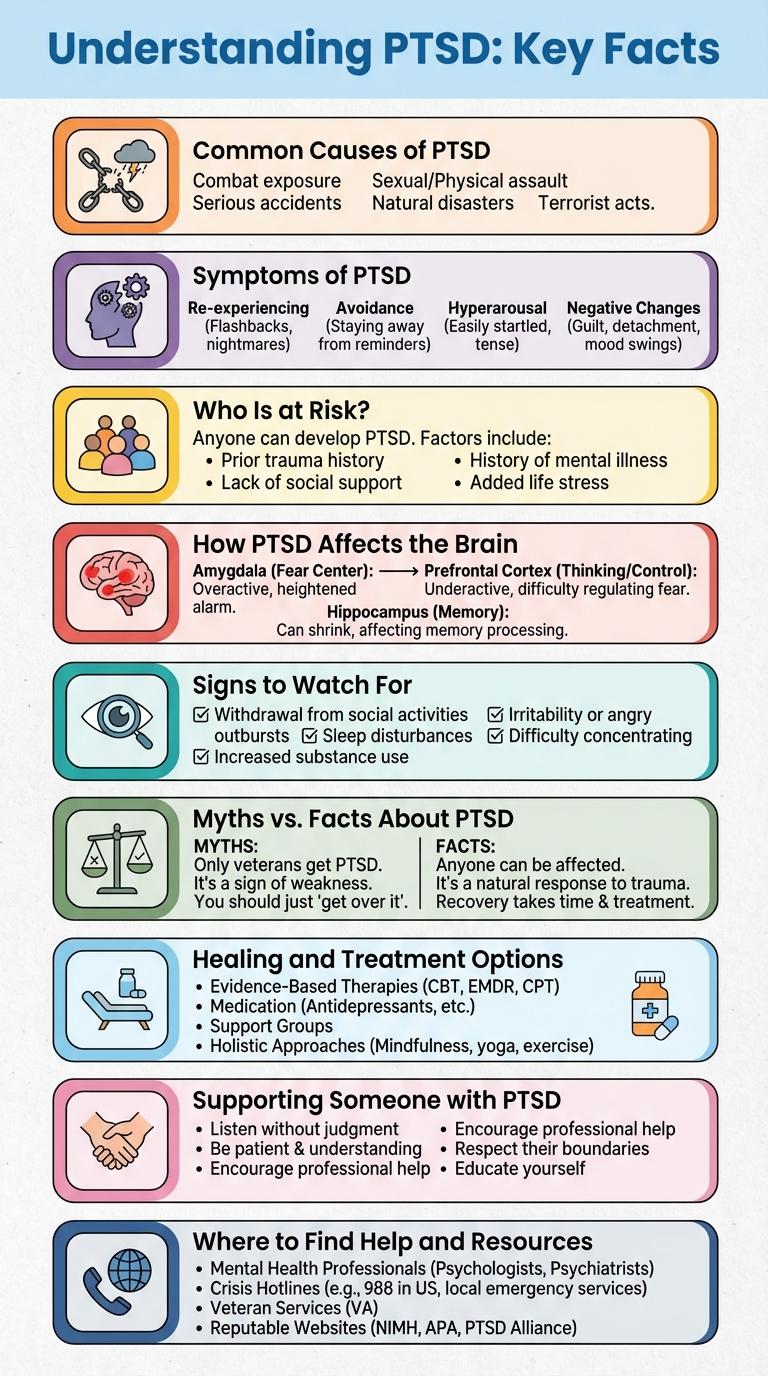
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) affects approximately 7-8% of the U.S. population at some point in their lives. It develops after exposure to traumatic events such as accidents, natural disasters, or combat. Symptoms include flashbacks, severe anxiety, and uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
Common Causes of PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) commonly arises after experiencing or witnessing traumatic events such as military combat, serious accidents, or natural disasters. Survivors of physical or sexual assault and childhood abuse frequently develop PTSD due to the intense psychological impact. Exposure to sudden, life-threatening situations or prolonged stressful environments significantly increases the risk of developing PTSD symptoms.
Symptoms of PTSD
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) manifests through a variety of symptoms that impact daily life. Key symptoms include intrusive memories, flashbacks, and nightmares related to traumatic events.
Other common symptoms involve emotional numbness, heightened anxiety, difficulty sleeping, and irritability. Recognizing these symptoms early can lead to effective treatment and improved outcomes.
Who Is at Risk?
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) can affect anyone exposed to traumatic events, but certain groups have a higher likelihood of developing symptoms. Understanding who is at risk helps in providing targeted support and early intervention.
- Military Personnel - Exposure to combat and life-threatening situations increases the risk of PTSD among soldiers and veterans.
- First Responders - Police officers, firefighters, and emergency medical workers frequently encounter traumatic scenarios, heightening their vulnerability to PTSD.
- Survivors of Violence - Victims of assault, abuse, or domestic violence face a greater chance of developing PTSD due to the nature of their traumatic experiences.
How PTSD Affects the Brain
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) significantly alters brain function, impacting areas responsible for memory, emotion, and stress regulation. The amygdala becomes hyperactive, heightening fear responses and emotional reactions.
The hippocampus, critical for memory formation, often shrinks, resulting in difficulties distinguishing past trauma from the present. The prefrontal cortex experiences reduced activity, impairing decision-making and emotional control.
Signs to Watch For
What are the common signs to watch for in PTSD? PTSD often manifests through intense, disturbing thoughts and feelings related to a traumatic experience. Recognizing these signs early can lead to effective treatment and support.
How does PTSD affect emotional responses? Individuals with PTSD may experience severe anxiety, depression, or emotional numbness. These symptoms interfere with daily functioning and relationships.
What behavioral changes indicate PTSD? Avoidance of places, people, or activities that remind someone of trauma is a key behavioral sign. Hypervigilance and irritability are also common indicators.
Are physical symptoms linked to PTSD? Yes, symptoms can include headaches, dizziness, or gastrointestinal problems without clear medical causes. Sleep disturbances like nightmares and insomnia frequently occur.
How important is professional evaluation for PTSD? Early diagnosis by a mental health professional is crucial for managing PTSD effectively. Comprehensive assessment ensures tailored therapy and support plans.
Myths vs. Facts About PTSD
| Myths About PTSD | Facts About PTSD |
|---|---|
| PTSD only affects combat veterans. | PTSD can affect anyone who experienced trauma, including accidents, abuse, or disasters. |
| People with PTSD are violent or dangerous. | Most individuals with PTSD are not violent and seek help for their symptoms. |
| PTSD is a sign of weakness or personal failure. | PTSD is a mental health condition caused by traumatic events, not a weakness. |
| PTSD symptoms appear immediately after trauma. | Symptoms can appear weeks, months, or even years after the traumatic event. |
| PTSD cannot be treated effectively. | Evidence-based therapies and medication can significantly reduce PTSD symptoms. |
Healing and Treatment Options
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) affects millions worldwide, but effective healing and treatment options exist. Early intervention can significantly improve recovery outcomes for those suffering from PTSD.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) - CBT helps patients reframe negative thought patterns and develop coping strategies to manage PTSD symptoms.
- Exposure Therapy - This therapy gradually exposes patients to trauma-related triggers in a controlled environment to reduce fear and anxiety.
- Medication - Antidepressants and anti-anxiety medications can alleviate symptoms and support other forms of therapy for PTSD patients.
Supporting Someone with PTSD
Supporting someone with PTSD requires understanding, patience, and empathy. Recognizing symptoms and offering a safe, non-judgmental space is crucial for their healing journey.
Encourage professional help from therapists specializing in trauma. Avoid pressuring them to talk before they're ready and listen actively when they do. Maintain consistent support and educate yourself about PTSD to foster a compassionate environment.
