ASEAN integration promotes economic growth, social progress, and cultural development across Southeast Asia. The infographic highlights key milestones, benefits, and challenges of fostering regional cooperation among member countries. Understanding ASEAN's integration process reveals its impact on trade, connectivity, and political stability in the region.
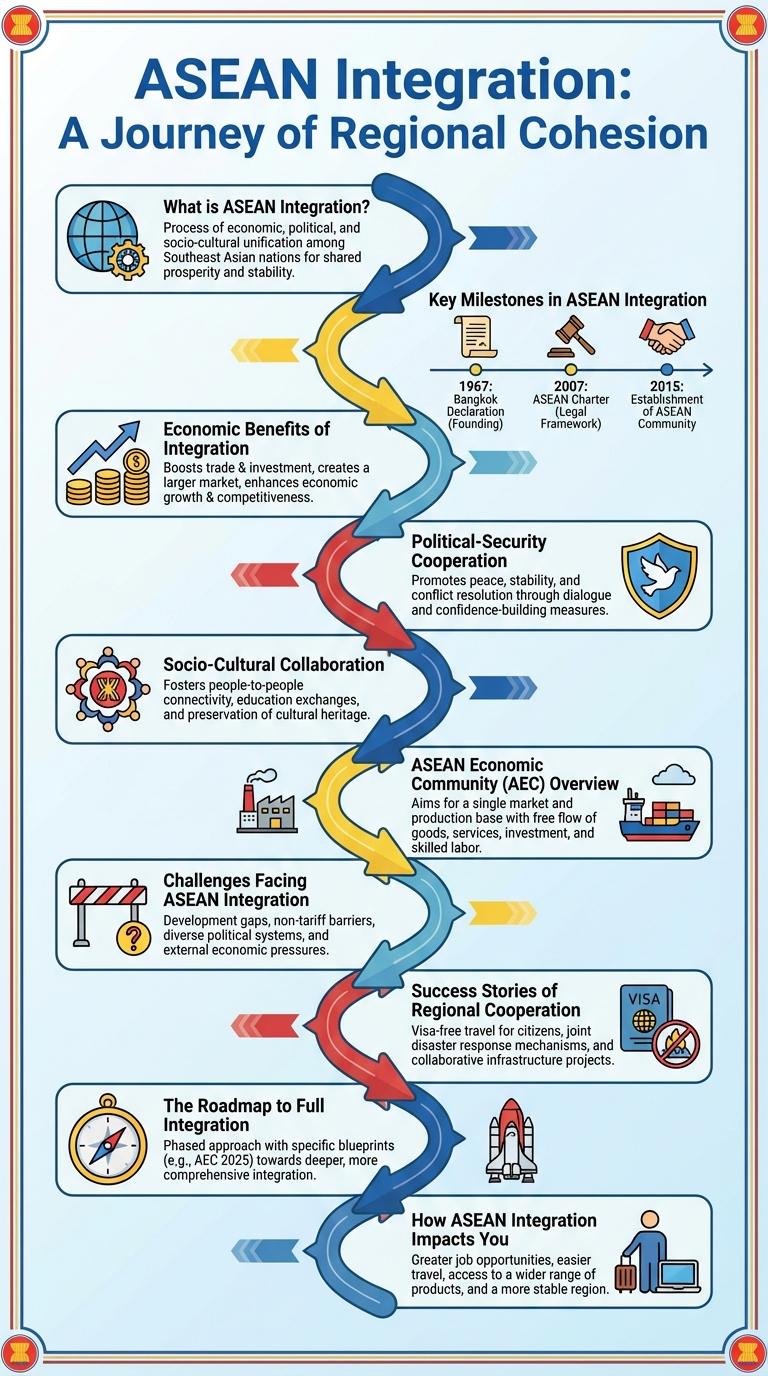
What is ASEAN Integration?
ASEAN Integration refers to the process of creating a single market and production base among the 10 Southeast Asian nations in the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN). It aims to enhance economic cooperation, reduce trade barriers, and promote regional stability.
This integration covers key sectors such as trade, investment, labor mobility, and regulatory alignment. By fostering closer ties, ASEAN Integration seeks to boost growth, competitiveness, and global connectivity for member countries.
Key Milestones in ASEAN Integration
ASEAN integration represents the collaboration of Southeast Asian nations to promote economic, political, and socio-cultural cooperation. Key milestones mark the significant steps towards creating a more unified and resilient ASEAN Community.
- ASEAN Declaration (1967) - Founding document signed by five countries to establish the Association of Southeast Asian Nations.
- ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) Agreement (1992) - Initiated tariff reduction to boost trade among member states.
- ASEAN Charter (2007) - Legal framework formalizing the organization's structure and goals.
- ASEAN Community Established (2015) - Creation of the ASEAN Economic, Political-Security, and Socio-Cultural Communities.
- RCEP Agreement Signing (2020) - Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership signed, involving ASEAN and partner countries for expanded trade integration.
Economic Benefits of Integration
The ASEAN integration fosters stronger economic growth by promoting a unified market of over 650 million people. It eliminates trade barriers, facilitating smoother transactions and boosting exports among member states. Businesses benefit from increased investment opportunities and enhanced regional competitiveness.
Political-Security Cooperation
ASEAN Political-Security Cooperation aims to promote regional peace and stability through dialogue and collaboration among member states. It focuses on preventing conflicts, addressing security challenges, and fostering mutual trust within Southeast Asia.
The ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC) framework supports efforts in conflict resolution, counterterrorism, and maritime security. ASEAN members engage in joint exercises, intelligence sharing, and diplomatic initiatives to strengthen collective security. These measures enhance regional resilience against non-traditional security threats and reinforce ASEAN's centrality in Asia-Pacific stability.
Socio-Cultural Collaboration
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Objective | Promote unity and understanding among ASEAN member states through cultural exchanges and social initiatives. |
| Key Programs | ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC), ASEAN Youth Volunteer Programme, ASEAN Festival of Arts. |
| Benefits | Enhanced regional identity, preservation of cultural heritage, stronger social ties across nations. |
| Member Participation | 10 ASEAN countries actively engage in joint activities, educational exchanges, and collaborative social projects. |
| Outcomes | Improved social cohesion, cultural diversity appreciation, and collaborative problem-solving for community development. |
ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) Overview
The ASEAN Economic Community (AEC) aims to create a single market and production base among the 10 ASEAN member states. It promotes the free flow of goods, services, investment, and skilled labor across the region.
The AEC enhances regional competitiveness, economic integration, and equitable economic development. It supports ASEAN's vision of being a dynamic and resilient economic region by 2025.
Challenges Facing ASEAN Integration
What are the key challenges facing ASEAN integration today? ASEAN integration encounters obstacles such as economic disparities among member states and varying levels of development. These differences hinder the creation of a fully cohesive economic community.
How do political and security issues impact ASEAN integration? Conflicting national interests and territorial disputes create tension within the region, slowing political cooperation and unity efforts. This affects ASEAN's goal of establishing a stable and peaceful environment.
Why is infrastructure development a barrier to ASEAN integration? Inadequate cross-border infrastructure limits efficient trade and connectivity between countries. Improving transportation and digital networks is essential for seamless integration.
What role do regulatory differences play in ASEAN integration challenges? Diverse regulations and standards complicate the harmonization of policies across member countries. Addressing these inconsistencies is vital for creating a single market and production base.
How do cultural and social diversity affect ASEAN integration? Varied languages, cultures, and social norms can slow down consensus-building and cooperation. Promoting mutual understanding is important to strengthen regional solidarity.
Success Stories of Regional Cooperation
ASEAN integration has significantly enhanced economic collaboration and political stability among Southeast Asian nations. Successful regional cooperation projects demonstrate the tangible benefits of unity in ASEAN.
- ASEAN Free Trade Area (AFTA) - AFTA has reduced tariffs, boosting intra-ASEAN trade by over 20% in the last decade.
- Disaster Response Coordination - ASEAN's coordinated approach to natural disasters has improved regional resilience and emergency response times.
- Trans-ASEAN Railway Network - This infrastructure project connects member countries, facilitating smoother trade and mobility.
These success stories exemplify ASEAN's progress toward deeper integration and sustainable regional development.
The Roadmap to Full Integration
The Roadmap to Full ASEAN Integration outlines key milestones for economic, political, and socio-cultural collaboration among member states. Target goals include establishing the ASEAN Economic Community, enhancing connectivity, and promoting sustainable development by 2025. This roadmap supports unified market access, regulatory harmonization, and improved regional stability.
