Corruption in the Philippines significantly impacts governance, economic development, and public trust. This infographic highlights key statistics, sectors most affected, and the consequences of corrupt practices on society. Understanding these insights is essential for promoting transparency and accountability across the nation.
The Cost of Corruption in the Philippines
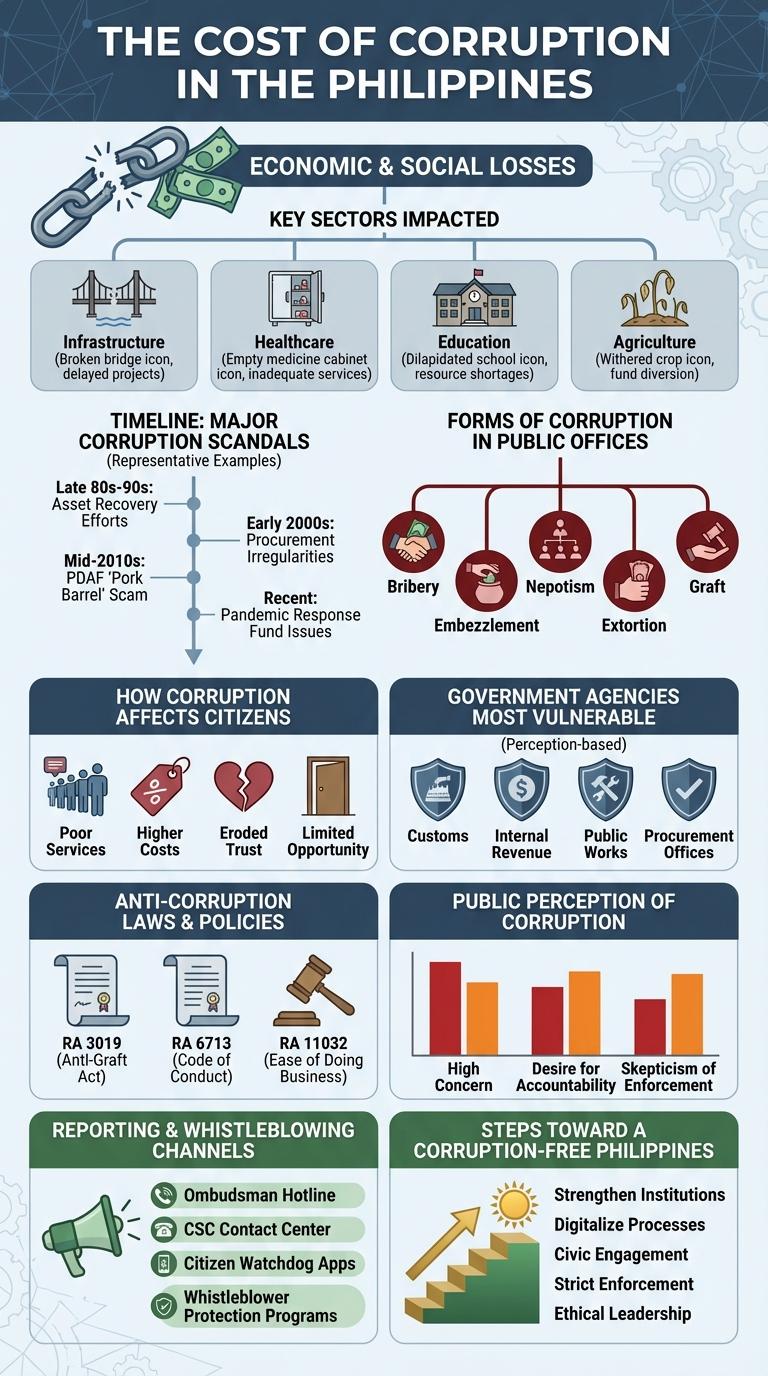
Corruption in the Philippines significantly hampers economic growth and undermines public trust in government institutions. The financial and social costs of corruption affect various sectors, from infrastructure to healthcare.
- Economic Loss - Corruption is estimated to cost the Philippine economy up to PHP 240 billion annually, reducing funds available for development.
- Public Services Impact - Corruption leads to poor quality in education, healthcare, and infrastructure, limiting access for vulnerable populations.
- Foreign Investment - High corruption levels deter foreign investors, slowing down job creation and economic expansion.
Combating corruption is crucial for sustainable development and restoring confidence in the Philippines' governance.
Key Sectors Impacted by Corruption
Corruption in the Philippines significantly affects several key sectors, undermining economic growth and public trust. These sectors include government services, infrastructure, health, education, and law enforcement.
In government services, bribery and favoritism delay project implementation and reduce service quality. Infrastructure projects often suffer from inflated costs and substandard materials due to corrupt practices. The health sector faces fund misallocation, impacting medical supplies and patient care, while education experiences resource diversion that lowers school facility standards. Law enforcement corruption erodes justice, allowing criminal activities to flourish unchecked.
Timeline: Major Corruption Scandals
Corruption in the Philippines has been a persistent issue, marked by several major scandals that shaped the nation's political landscape. These scandals often involved high-ranking officials and significant public fund misappropriation.
One of the earliest major cases was the 1990s' Alabang Boys scandal, exposing police and military involvement in corrupt activities. The 2000s saw the controversial ZTE broadband deal, where government officials were accused of graft and kickbacks.
In 2013, the Priority Development Assistance Fund (PDAF) scam revealed misuse of lawmakers' discretionary funds, causing public outrage and legislative reforms. More recent cases include the 2015 pork barrel scam and the 2016 Mamasapano clash investigation linked to corruption allegations.
These incidents highlight recurring challenges in governance and transparency within the Philippines. Continuous reforms and vigilant civil society efforts remain crucial to combat corruption effectively.
Forms of Corruption in Public Offices
What are the common forms of corruption in public offices in the Philippines?
Corruption in the Philippines manifests in various forms within public offices. These include bribery, nepotism, embezzlement, favoritism, and kickbacks.
| Form of Corruption | Description |
|---|---|
| Bribery | Offering or receiving money or favors in exchange for preferential treatment. |
| Nepotism | Hiring or promoting relatives regardless of merit. |
| Embezzlement | Misappropriating public funds for personal use. |
| Favoritism | Giving undue advantage to friends or allies in government projects. |
| Kickbacks | Receiving a portion of payments from contractors or suppliers. |
How Corruption Affects Citizens
Corruption in the Philippines undermines trust in public institutions and hampers economic growth. Citizens often face increased costs for basic services due to bribery and misallocation of resources.
Essential public services like healthcare and education suffer from inadequate funding and poor implementation. As a result, poverty and inequality deepen, limiting opportunities for many Filipinos.
Government Agencies Most Vulnerable
Corruption in the Philippines significantly affects key government agencies, undermining public trust and service delivery. The most vulnerable agencies include the Bureau of Customs, the Department of Public Works and Highways, and the Philippine National Police, where corruption risks are high due to large budgets and discretionary powers. Strengthening transparency and accountability in these sectors is crucial to curbing corruption and promoting good governance.
Anti-Corruption Laws & Policies
The Philippines enforces various anti-corruption laws such as the Anti-Graft and Corrupt Practices Act (Republic Act No. 3019) aimed at preventing public officials from engaging in corrupt activities. The Sandiganbayan, a special court, handles corruption cases to ensure accountability and transparency in government. Recent policies emphasize the implementation of the Anti-Red Tape Act, which streamlines government processes to reduce opportunities for bribery and corruption.
Public Perception of Corruption
| Survey Aspect | Results / Insights |
|---|---|
| Percentage of Filipinos Who Believe Corruption is Widespread | Approximately 70% to 80% (Source: Transparency International - Global Corruption Barometer) |
| Public Sector Most Associated with Corruption | Police and Government Officials (over 50% perception rate) |
| Impact on Trust in Government | Less than 30% express high confidence in government institutions |
| Commonly Reported Forms of Corruption | Bribery, Nepotism, and Embezzlement |
| Public Demand for Anti-Corruption Measures | Over 85% support stronger transparency and accountability laws |
Reporting & Whistleblowing Channels
Corruption remains a significant challenge in the Philippines, with various channels established to encourage reporting and whistleblowing. These mechanisms aim to increase transparency and accountability in both public and private sectors.
- Integrity Hotline - A government-operated channel providing anonymous reporting options for corruption cases.
- Ombudsman's Complaint System - Enables citizens to file formal complaints against public officials suspected of corruption.
- Anti-Red Tape Authority (ARTA) Helpline - Facilitates reporting of bureaucratic corruption and inefficiency in government services.
