An infographic about elections visually presents key information such as voter turnout, candidate statistics, and electoral processes. It simplifies complex data, making it easier to understand voting patterns and the impact of elections on society. This visual tool enhances civic awareness and encourages informed participation in democratic systems.
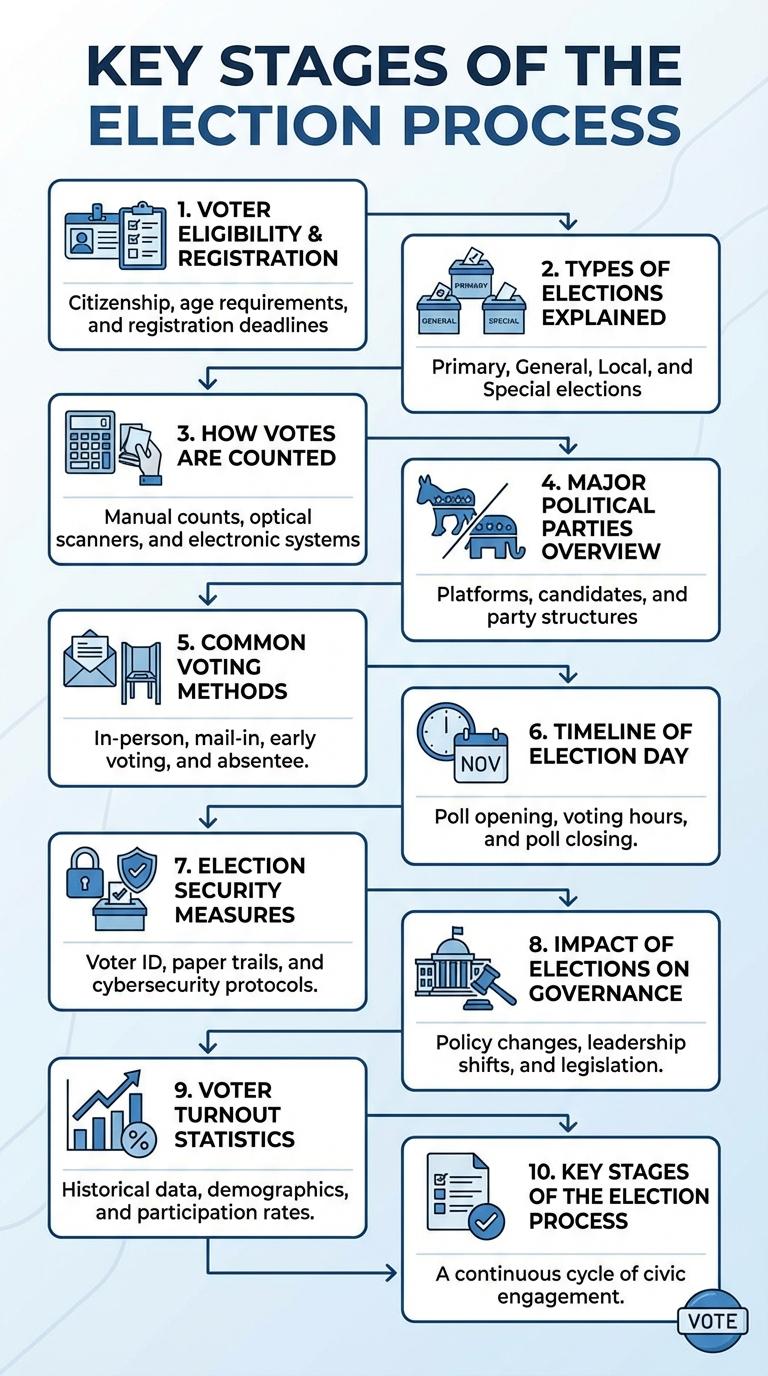
Key Stages of the Election Process
What are the key stages of the election process? The election process includes voter registration, candidate nomination, campaigning, voting, and vote counting. Each stage ensures a free and fair election that reflects the will of the people.
Voter Eligibility and Registration
Voter eligibility is determined by specific criteria including age, citizenship, and residency requirements. Eligible voters must typically be 18 years or older and registered within their jurisdiction.
Registration processes vary by region but commonly involve filling out a form online or in person before a set deadline. Accurate registration ensures access to polling locations and helps maintain the integrity of elections.
Types of Elections Explained
Types of elections vary based on the positions being filled and the governing system. Common types include general, primary, local, and special elections.
General elections decide officeholders like presidents, governors, and legislators. Primary elections select party candidates for the general election. Local elections cover city councils, mayors, and school boards, while special elections address specific issues or vacancies.
How Votes Are Counted
Votes in an election are typically counted through a systematic process involving electronic machines or manual tallying. Each ballot is verified for validity before being added to the total count. The results are then aggregated at local and national levels to determine the final outcome.
Major Political Parties Overview
| Political Party | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Democratic Party | Center-left ideology, supports social equity, environmental protection, and expanded healthcare access. |
| Republican Party | Center-right ideology, emphasizes limited government, free-market principles, and strong national defense. |
| Libertarian Party | Advocates for individual liberty, minimal government intervention, and free-market economics. |
| Green Party | Focuses on environmental sustainability, social justice, and grassroots democracy. |
| Independent | Candidates not affiliated with major parties, often emphasizing issue-based platforms and voter reform. |
Common Voting Methods
Voting methods vary worldwide but commonly include paper ballots, electronic voting, and mail-in ballots. Each method aims to ensure voter accessibility, security, and accurate results.
Paper ballots are traditional and favored for their simplicity and auditability. Electronic voting offers speed and convenience but requires robust cybersecurity measures to maintain trust.
Timeline of Election Day
Election Day follows a structured timeline to ensure an organized voting process. Key events mark the day from early morning setups to the closing of polls and vote counting.
- Polling Stations Open - Polling stations typically open between 6 AM and 8 AM to start receiving voters.
- Midday Voter Turnout - By midday, a significant portion of registered voters will have cast their ballots.
- Polls Close and Vote Counting Begins - Polls usually close between 7 PM and 9 PM, immediately followed by the counting of votes.
Election Security Measures
Election security measures are essential to protect the integrity of democratic processes. Key strategies include voter ID verification, secure ballot handling, and robust cybersecurity defenses to prevent tampering. These efforts ensure transparent and trustworthy elections worldwide.
Impact of Elections on Governance
Elections serve as a critical mechanism for shaping government policies and leadership. They directly influence the accountability and transparency of governing bodies.
- Enhances Representative Leadership - Elections enable citizens to choose leaders who reflect their priorities and values.
- Promotes Accountability - Regular elections hold officials responsible for their performance and decisions.
- Drives Policy Change - Election outcomes often lead to shifts in governmental policies aligned with voter demands.
Effective governance depends on the active participation and informed choices of the electorate in elections.
