Graft and corruption undermine the integrity of institutions and hinder economic development worldwide. This infographic highlights the key forms of corruption, their impact on society, and the measures taken to combat these unethical practices. Understanding these elements is crucial for promoting transparency and accountability.
Understanding Graft and Corruption
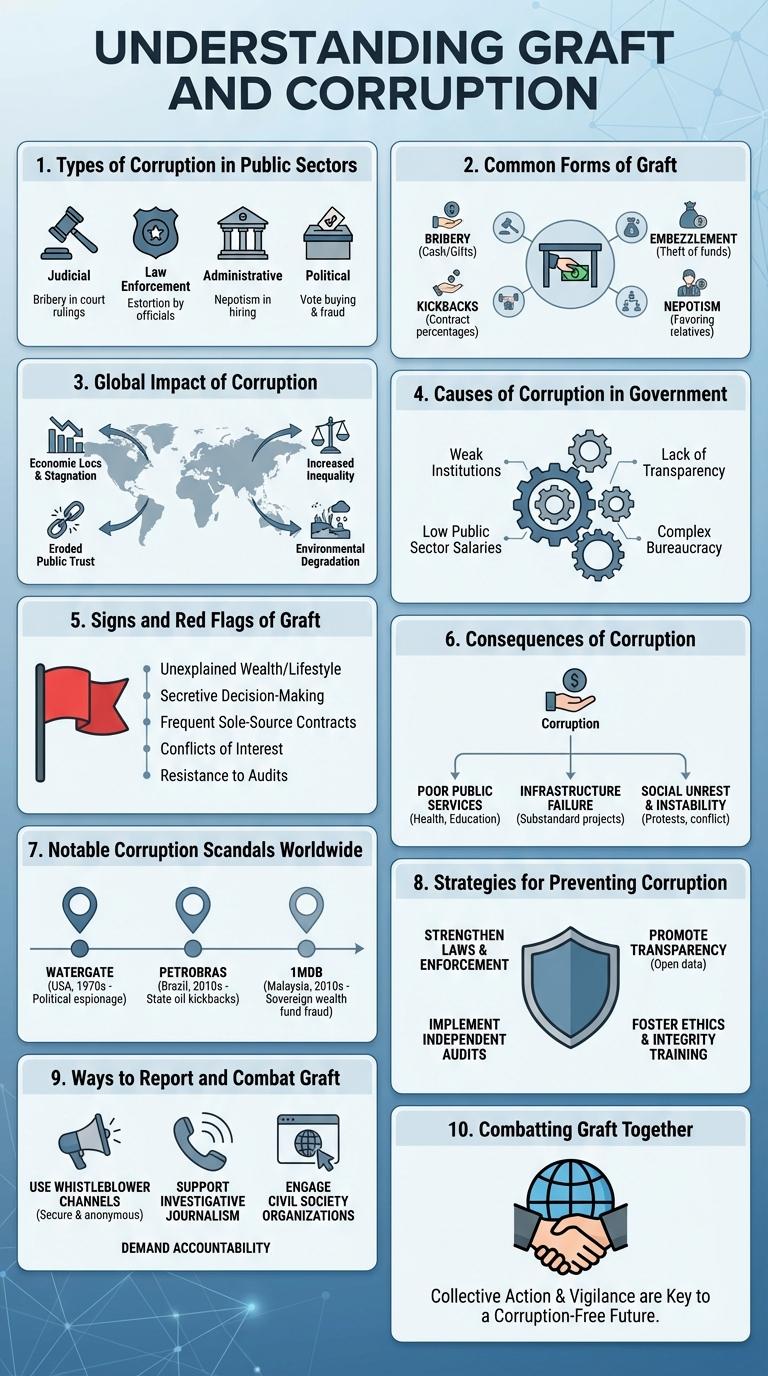
Graft and corruption involve the abuse of power for personal gain, undermining trust in institutions. These practices distort economic and social systems, leading to unfair resource distribution. Understanding the mechanisms behind graft is essential to fostering transparency and accountability.
Types of Corruption in Public Sectors
| Type of Corruption | Description |
|---|---|
| Bribery | Offering, giving, receiving, or soliciting something of value to influence the actions of a public official. |
| Embezzlement | Illegal taking of public funds or assets entrusted to public officials for personal use. |
| Nepotism | Favoring relatives or friends in public sector recruitment or contracts regardless of merit. |
| Extortion | Coercing individuals or companies to give money or favors under threats or pressure by public servants. |
| Kickbacks | Receiving a portion of profits from contracts or public projects as a reward for preferential treatment. |
Common Forms of Graft
Graft and corruption undermine trust in public institutions and hinder economic growth. These illegal activities involve the misuse of power for personal gain.
- Bribery - Offering or receiving money or gifts to influence a decision or action illegally.
- Embezzlement - Misappropriation of funds entrusted to an official or employee.
- Kickbacks - Payments made to someone who has facilitated a transaction or appointment.
- Favoritism - Granting unfair advantages to friends or relatives in business or government.
- Extortion - Obtaining money or favors through coercion or threats.
Global Impact of Corruption
Corruption undermines economic development and erodes public trust worldwide. Graft distorts resource allocation, leading to inefficiencies and increased inequality.
The global cost of corruption exceeds $2.6 trillion annually, representing more than 5% of global GDP. Developing countries suffer disproportionately, losing billions in foreign investment and aid. Strong anti-corruption measures are essential for sustainable growth and social stability across nations.
Causes of Corruption in Government
Corruption in government undermines public trust and hampers economic development. Understanding its root causes helps implement effective anti-corruption strategies.
- Poor Governance - Lack of transparency and weak institutional checks create opportunities for corrupt practices.
- Low Salaries - Insufficient compensation drives officials to accept bribes to supplement income.
- Concentration of Power - Excessive authority without accountability encourages misuse of public resources.
Signs and Red Flags of Graft
Graft and corruption undermine trust in institutions and drain public resources. Recognizing signs and red flags is crucial for early detection and prevention.
Common indicators include unusual financial transactions and unexplained wealth among officials. Frequent conflicts of interest and lack of transparency in decision-making processes also raise concerns.
Consequences of Corruption
What are the main consequences of corruption on society?
Corruption undermines trust in government and weakens institutions. It leads to increased poverty and slows economic growth.
How does corruption impact public services?
Corruption diverts resources away from essential services like healthcare and education. This results in lower quality and accessibility for citizens.
What effect does corruption have on economic development?
Corruption increases costs for businesses and creates unfair competitive advantages. Investors are discouraged, reducing overall investment in the economy.
How does corruption affect social equality?
Corruption exacerbates inequality by benefiting a privileged few at the expense of the majority. It reduces opportunities for marginalized groups to improve their living standards.
Can corruption influence political stability?
Corruption erodes public confidence in leadership and governance. This can lead to political unrest and reduced democratic participation.
Notable Corruption Scandals Worldwide
Corruption and graft have caused significant economic and social damage across the globe. Numerous high-profile scandals illuminate the widespread impact of unethical practices in governance and business.
- Enron Scandal (2001) - Corporate fraud exposed massive accounting deception leading to bankruptcy and regulatory reforms in the United States.
- Siemens Bribery Case (2008) - German multinational fined over $1.6 billion for systematic bribery to secure government contracts worldwide.
- Operation Car Wash (2014) - Brazilian investigation uncovered corruption at Petrobras involving politicians and executives with billions in kickbacks.
- 1MDB Scandal (2015) - Malaysia's state fund was looted of billions, implicating high-ranking officials and international financial institutions.
- FIFA Corruption Case (2015) - Global soccer governing body officials were arrested for bribery and money laundering related to tournament hosting rights.
These scandals highlight the critical need for transparency, accountability, and legal reforms to combat graft and support ethical governance worldwide.
Strategies for Preventing Corruption
Corruption undermines trust and hampers economic development in societies worldwide. Effective strategies to prevent graft are essential for transparent governance and sustainable growth.
Implementing strict anti-corruption laws and ensuring their enforcement deters corrupt practices. Promoting transparency through open access to public records enhances accountability among officials.
