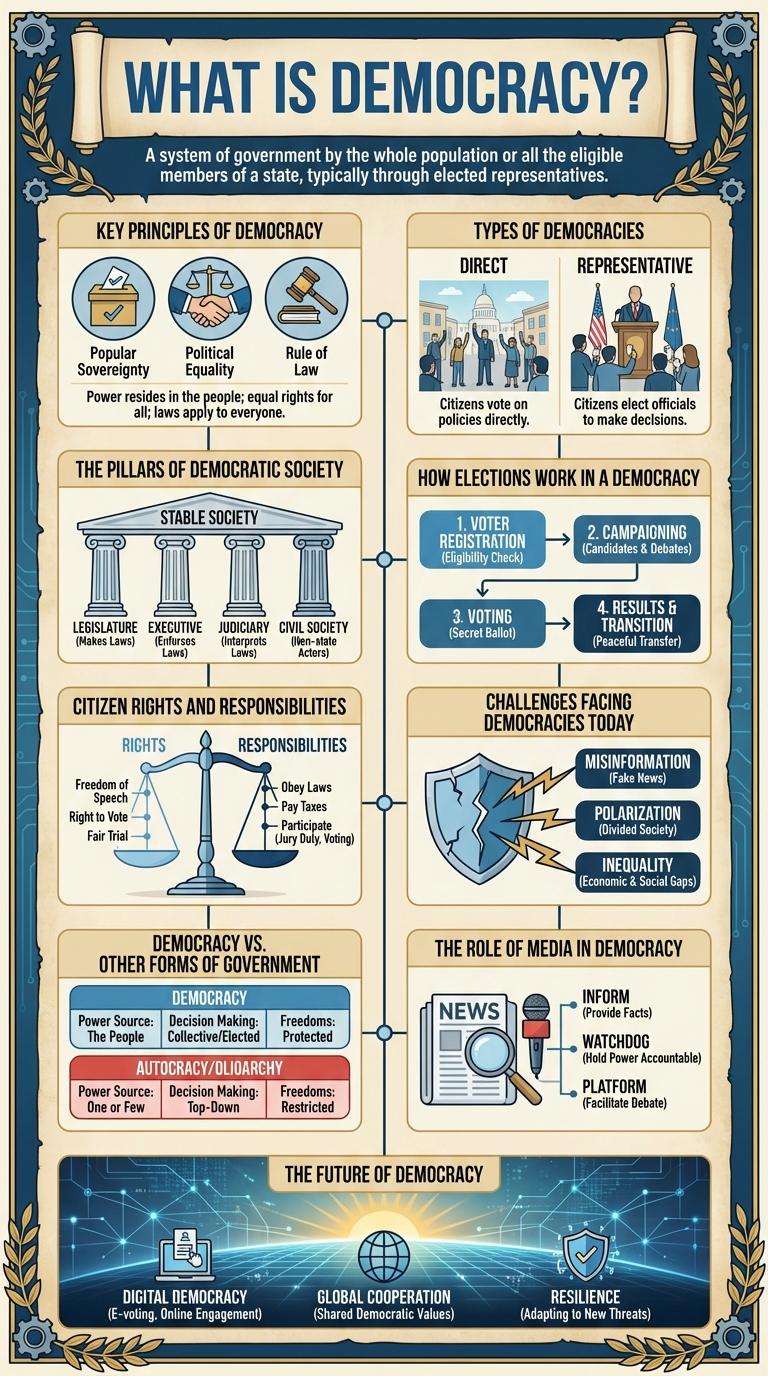
Democracy empowers citizens by ensuring equal participation in decision-making processes and safeguarding fundamental rights. This infographic visually breaks down key principles such as voting rights, freedom of speech, and the separation of powers. Understanding these elements highlights how democracy fosters transparency, accountability, and social inclusivity.
What Is Democracy?
Democracy is a form of government where power is vested in the people. Citizens have the right to participate in decision-making, typically through voting.
It ensures equal rights and freedoms for all individuals within a society. Democratic systems promote accountability, transparency, and the rule of law.
Key Principles of Democracy
What are the fundamental principles that define democracy? Democracy revolves around the core values of participation, equality, and accountability. These principles ensure that every citizen has a voice in governance and that leaders are responsible to the people.
How does participation shape a democratic society? Active involvement of citizens in voting and policy-making fosters representative leadership. This participatory process strengthens the legitimacy of government decisions.
Why is equality a crucial principle in democracy? Equality guarantees that all individuals have the same rights and opportunities under the law. It prevents discrimination and promotes fairness across diverse populations.
What role does accountability play in maintaining democracy? Leaders in a democracy must answer to the electorate and adhere to established laws. Accountability mechanisms help prevent abuses of power and protect citizens' interests.
How do transparency and rule of law support democratic values? Transparency allows citizens access to information about government actions and decisions. The rule of law ensures that laws apply equally, safeguarding freedoms and justice within the democratic system.
Types of Democracies
Democracy is a system of government where citizens exercise power by voting. Different types of democracies provide various frameworks for political participation and decision-making.
- Direct Democracy - Citizens vote directly on laws and policies without intermediaries.
- Representative Democracy - Elected officials make decisions on behalf of the people.
- Constitutional Democracy - Government powers are limited by a constitution protecting individual rights.
- Participatory Democracy - Emphasizes broad participation beyond voting in decision-making processes.
- Deliberative Democracy - Focuses on reasoned debate and discussion before making decisions.
The Pillars of Democratic Society
Democracy rests on key pillars that uphold its foundation: participation, transparency, and rule of law. Active citizen engagement ensures voices are heard in decision-making processes. Transparent governance and adherence to legal frameworks protect rights and maintain accountability.
How Elections Work in a Democracy
In a democracy, elections are a fundamental process that allows citizens to choose their leaders and influence government policies. Eligible voters cast ballots to select representatives who reflect their preferences and values.
Election systems can vary, including direct voting for candidates or parties and proportional representation. Transparency and fairness in voting procedures ensure the legitimacy and accountability of elected officials.
Citizen Rights and Responsibilities
Democracy empowers citizens by granting them fundamental rights such as freedom of speech, voting, and equality before the law. These rights ensure active participation in governance and protection from discrimination.
Alongside rights, citizens hold responsibilities including obeying laws, paying taxes, and engaging in community service. Voting in elections is a key duty that shapes government policies. Responsible citizenship sustains a healthy democratic system by promoting accountability and social cohesion.
Challenges Facing Democracies Today
Democracies worldwide face challenges such as declining trust in institutions, misinformation, and political polarization. These issues undermine effective governance and citizen participation. Addressing these challenges requires transparent communication, education, and reforms to strengthen democratic processes.
Democracy vs. Other Forms of Government
| Democracy | Other Forms of Government |
|---|---|
| Power rests with the people through free and fair elections. | Power may rest with a single ruler, elite group, or ruling party. |
| Guarantees civil liberties such as freedom of speech and press. | Civil liberties often restricted or controlled to maintain authority. |
| Leaders are accountable and can be removed by voters. | Leadership often hereditary, appointed, or maintained by force. |
| Laws reflect the will of the majority while protecting minority rights. | Laws may serve the interests of rulers over the population. |
| Political pluralism and multiple parties encourage participation. | Limited or no political parties; opposition suppressed or banned. |
The Role of Media in Democracy
Media plays a crucial role in shaping democratic societies by providing information, fostering public debate, and holding power accountable. The influence of media ensures transparency and promotes citizen engagement in democratic processes.
- Information Dissemination - Media delivers timely and accurate news to the public, empowering voters with knowledge about political issues and candidates.
- Watchdog Function - Investigative journalism uncovers corruption and abuses of power, ensuring government accountability.
- Public Forum - Media platforms enable diverse voices to participate in discussions, supporting pluralism and democratic dialogue.
Robust media systems are essential for sustaining healthy democracies and enabling informed citizen participation.
