Violence against women remains a pervasive global issue that affects millions across all cultures and societies. This infographic highlights key statistics, types of abuse, and the urgent need for stronger protective measures. Understanding the scope and impact of this violence is essential for fostering awareness and driving meaningful change.
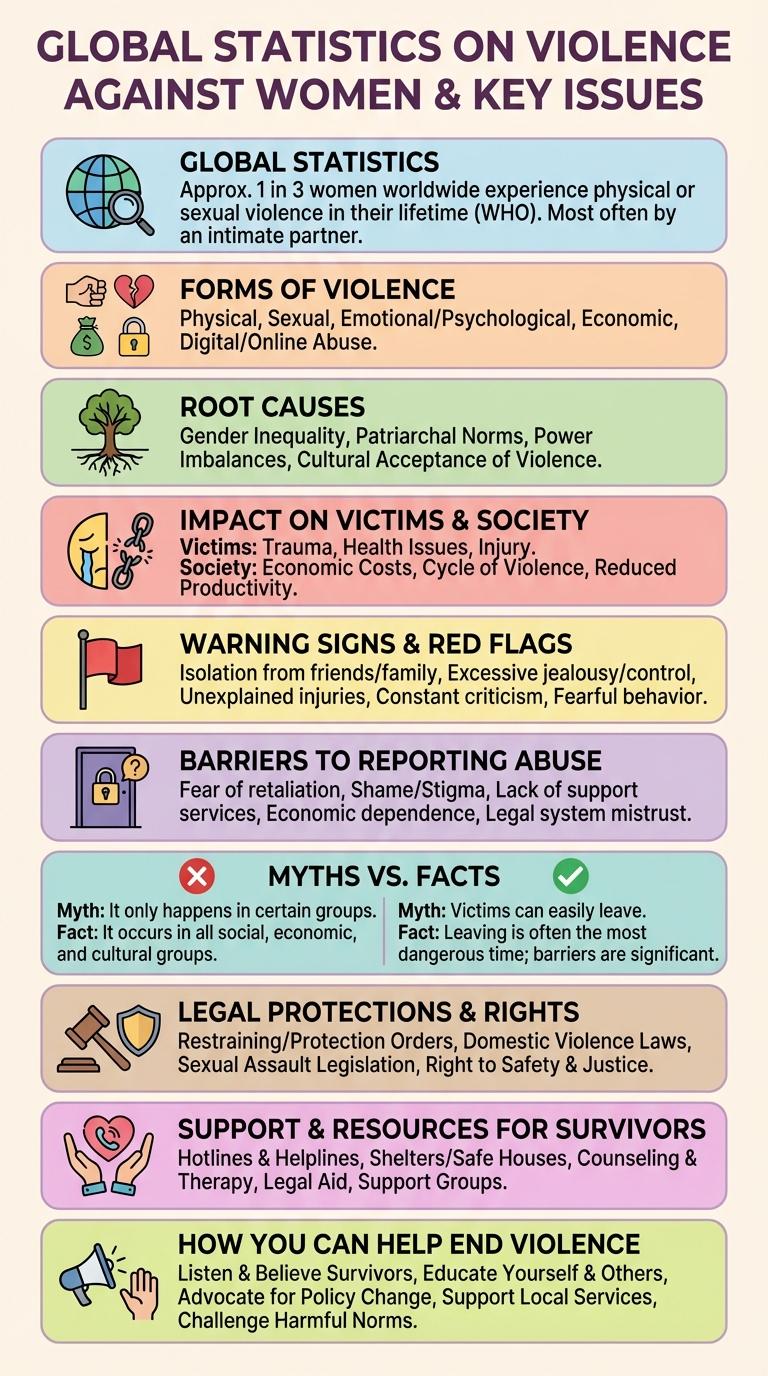
Global Statistics on Violence Against Women
Violence against women remains a critical global issue affecting millions across all regions. These statistics reveal the widespread nature and severity of the problem.
- 1 in 3 women worldwide - Experience physical or sexual violence, mostly by intimate partners.
- 35% of women - Have faced either physical or sexual intimate partner violence or non-partner sexual violence in their lifetime.
- Approximately 137 women daily - Are victims of femicide globally, murdered by a member of their own family or intimate partner.
Understanding these numbers is essential for driving policy changes and support programs to protect women everywhere.
Forms of Violence Women Experience
Violence against women encompasses various forms that affect their physical, emotional, and psychological well-being. Understanding these forms is crucial for addressing and preventing such abuse effectively.
- Physical Violence - Acts such as hitting, slapping, or any physical harm inflicted intentionally on women.
- Sexual Violence - Unwanted sexual acts, including assault or harassment, violating a woman's autonomy.
- Emotional Abuse - Psychological tactics like intimidation, manipulation, and constant criticism that undermine a woman's self-worth.
- Economic Abuse - Controlling a woman's financial resources to limit her independence and freedom.
- Stalking and Harassment - Persistent unwanted attention causing fear and distress to women in their daily lives.
Root Causes of Gender-Based Violence
Gender-based violence (GBV) stems from deep-rooted social, cultural, and economic inequalities that perpetuate power imbalances between men and women. These inequalities foster environments where abuse and discrimination become normalized and tolerated.
Key root causes include rigid gender norms and stereotypes that limit women's autonomy and justify control over their behavior. Economic dependency and lack of access to education increase vulnerability to violence. Cultural acceptance of violence as a conflict resolution method further entrenches GBV in many societies.
Impact on Victims and Society
Violence against women severely affects the physical and mental health of victims, often leading to chronic trauma and long-term psychological issues. It undermines their sense of security, negatively impacting their ability to participate fully in social and economic activities.
Society bears substantial costs from violence against women, including increased healthcare expenses and lost productivity. The perpetuation of gender inequality and social instability hinders overall community development and economic growth.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
Violence against women often begins with subtle warning signs that escalate over time. Awareness of these red flags can help in early intervention and prevention.
Common warning signs include controlling behavior, isolation from friends and family, and sudden changes in personality. Recognizing these red flags empowers individuals to seek help and support victims effectively.
Barriers to Reporting Abuse
Violence against women remains a critical global issue, with numerous victims unable to seek help. Barriers to reporting abuse prevent many women from accessing justice and support.
- Fear of Retaliation - Victims often fear further harm or threats from their abusers if they report the violence.
- Lack of Trust in Authorities - Many women doubt that law enforcement or judicial systems will provide protection or take their cases seriously.
- Social Stigma - Cultural norms and shame discourage women from disclosing abuse to avoid judgment or ostracism from their communities.
Myths vs. Facts About Violence Against Women
Violence against women is often surrounded by myths that distort the reality and hinder effective support and prevention. Common misconceptions include beliefs that victims provoke violence or that abuse only occurs in certain socioeconomic groups. Facts reveal that violence affects women of all backgrounds and the responsibility lies solely with the perpetrators, highlighting the need for informed awareness and action.
Legal Protections and Rights
Legal protections for women against violence vary globally, often including restraining orders, criminal penalties for offenders, and victim support services. International agreements like the Istanbul Convention set standards for combating violence against women and ensuring their rights. Effective enforcement of these laws remains crucial to protect women and uphold their human rights.
Support and Resources for Survivors
Where can survivors of violence against women find support and resources?
Various organizations provide confidential help, counseling, and legal assistance to survivors. Access to shelters and hotlines offers immediate safety and guidance for those in need.
