Migration shapes societies by influencing cultural diversity, economic development, and demographic shifts. Visual representations in infographics provide clear insights into migration patterns, causes, and impacts worldwide. Understanding these trends helps policymakers and communities address challenges and opportunities linked to human mobility.
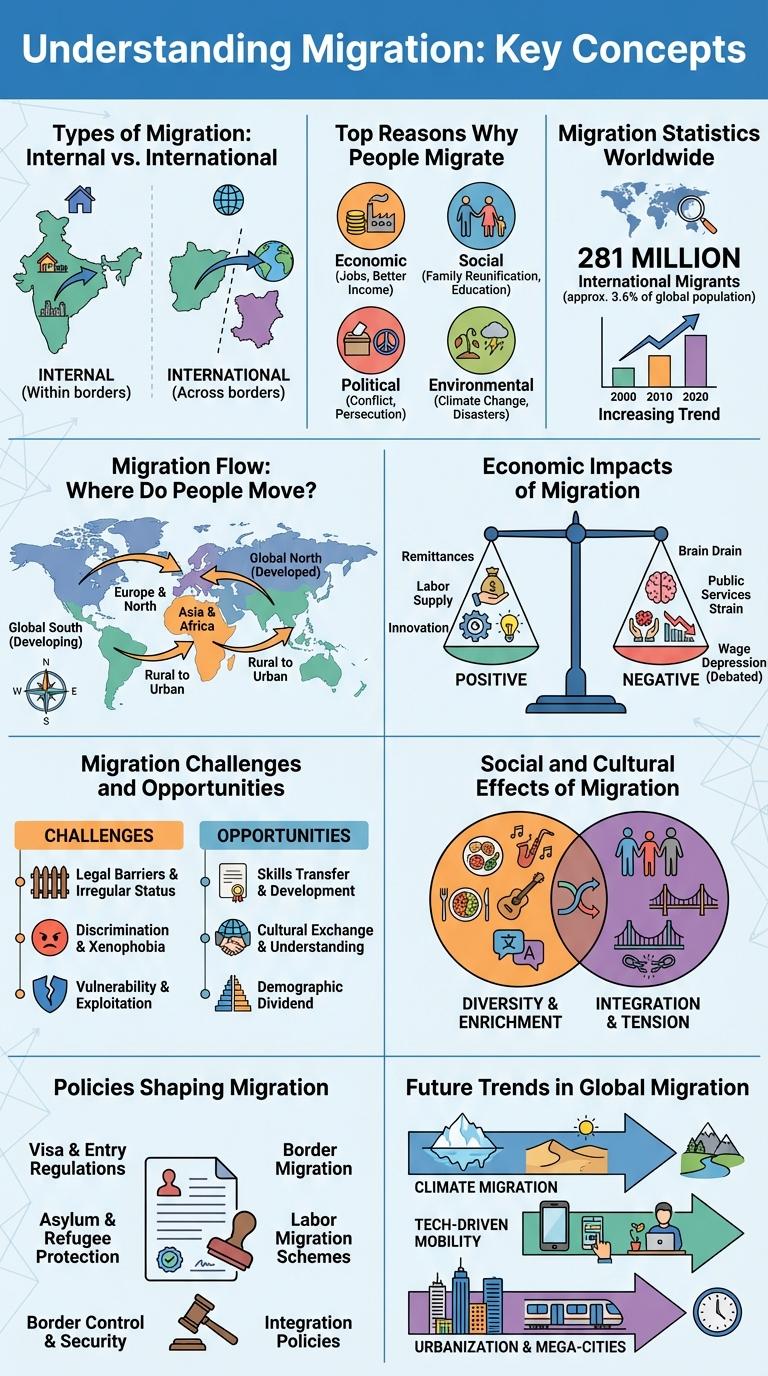
Understanding Migration: Key Concepts
Migration involves the movement of people from one place to another, driven by various social, economic, and environmental factors. Understanding migration requires exploring key concepts that define its causes, types, and impacts.
- Types of Migration - Migration can be internal or international, temporary or permanent, voluntary or forced.
- Push and Pull Factors - Push factors such as conflict and poverty drive people away, while pull factors like job opportunities attract migrants.
- Impact on Societies - Migration shapes cultural diversity, economic development, and demographic changes in both origin and destination areas.
Grasping these concepts helps frame migration as a complex, multifaceted phenomenon influencing global populations.
Types of Migration: Internal vs. International
| Type of Migration | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| Internal Migration |
Movement of people within the same country. Includes rural to urban, urban to rural, and intercity migration. Often driven by employment, education, or family reasons. Does not involve border crossing or changes in citizenship. Examples: moving from a village to a metropolitan area. |
| International Migration |
Movement across country borders. Often involves changes in legal status or citizenship. Motivated by factors like economic opportunity, conflict, or environmental conditions. Can be temporary (seasonal work) or permanent relocation. Examples: migrant workers moving from Mexico to the USA. |
Top Reasons Why People Migrate
Migration is the movement of people from one place to another in search of better opportunities. Understanding the key reasons behind migration helps reveal social, economic, and environmental challenges worldwide.
- Economic Opportunities - Many individuals migrate to improve their living standards through better jobs and income prospects.
- Conflict and Safety - People flee regions affected by war, violence, or persecution to find secure environments.
- Education Access - Migration occurs as students seek quality education and professional development abroad.
Migration Statistics Worldwide
Migration continues to shape global demographics with over 280 million international migrants recorded in 2023. This number represents approximately 3.6% of the world population, reflecting significant movement driven by economic, social, and environmental factors.
Asia hosts the largest share of international migrants, followed by Europe and North America. Top destination countries include the United States, Germany, and Saudi Arabia, each attracting millions of migrants annually due to job opportunities and political stability.
Migration Flow: Where Do People Move?
Migration flow illustrates the movement of people across regions and countries, driven by factors such as economic opportunities, conflicts, and environmental changes. Major migration corridors include movements from Latin America to North America, South Asia to the Middle East, and Africa to Europe. Understanding these patterns helps policymakers address challenges related to integration, resource allocation, and human rights protection.
Economic Impacts of Migration
Migration significantly influences global and local economies by altering labor markets and consumer demand. Understanding these economic impacts helps policymakers design effective migration frameworks.
- Labor Market Dynamics - Migration increases workforce diversity, filling critical skill gaps and supporting economic growth.
- Remittance Flows - Migrants send financial support back home, boosting household incomes and stimulating development in origin countries.
- Entrepreneurship and Innovation - Migrants often create new businesses, driving innovation and job creation in host economies.
Social and Cultural Effects of Migration
How does migration influence social structures in host communities? Migration often leads to increased cultural diversity, enriching societies with new traditions and perspectives. It can also challenge existing social norms, prompting adaptation and change.
What cultural effects arise from the integration of migrants? Migrants contribute to the blending of languages, cuisines, and festivals, creating dynamic multicultural environments. This fusion fosters greater cultural understanding and innovation.
| Social Effects | Cultural Effects |
|---|---|
| Population diversity | New cultural traditions |
| Community adaptation | Language variation |
| Changes in social norms | Culinary fusion |
| Expansion of social networks | Cultural festivals |
| Potential social tensions | Intercultural dialogue |
Migration Challenges and Opportunities
Migration presents significant challenges such as cultural integration, employment barriers, and access to essential services. Migrants often face difficulties adapting to new environments while contributing valuable skills and diversity to host communities. Addressing these challenges unlocks opportunities for economic growth, innovation, and enhanced social cohesion.
Policies Shaping Migration
Migration is influenced by a complex web of policies that determine how people move across borders. Governments create regulations that impact migrant rights, entry requirements, and labor market access.
Policies shaping migration include visa rules, asylum procedures, and integration programs. These frameworks balance border security with humanitarian commitments and economic needs. Changing political landscapes and international agreements continuously redefine migration flows.
