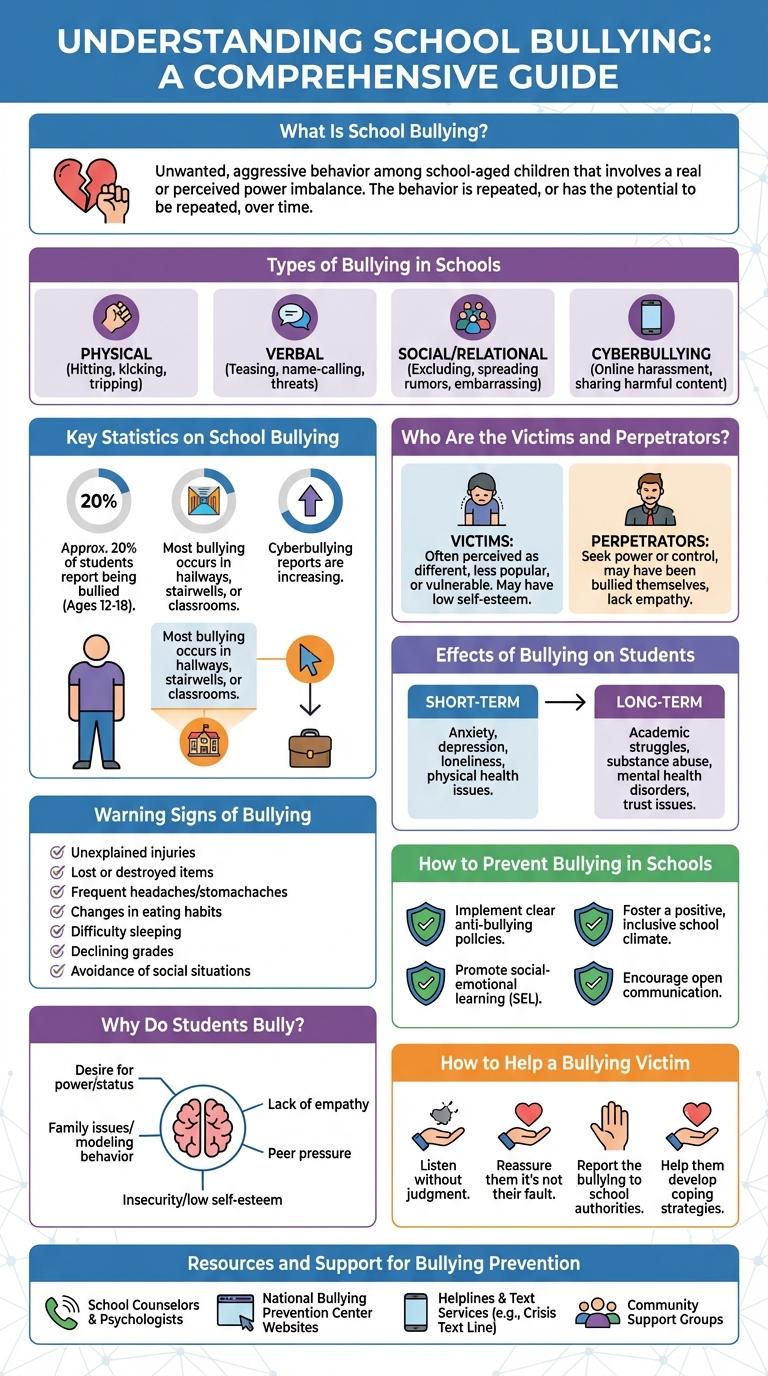
Bullying in school remains a critical issue affecting students' mental health and academic performance. This infographic highlights key statistics, the common forms of bullying, and effective prevention strategies. Understanding these elements is essential for creating safer and more supportive educational environments.
What Is School Bullying?
What is school bullying?
School bullying involves repeated aggressive behavior intended to hurt or intimidate another student physically, verbally, or socially. It creates a hostile environment that affects a student's emotional and academic well-being.
Types of Bullying in Schools
| Type of Bullying | Description |
|---|---|
| Physical Bullying | Involves hitting, pushing, or other forms of physical aggression towards a student. |
| Verbal Bullying | Includes name-calling, teasing, threats, and verbal abuse targeting an individual. |
| Social Bullying | Excludes someone, spreading rumors, embarrassing a student in public, or damaging social relationships. |
| Cyberbullying | Using digital devices to send hurtful messages, post harmful content, or harass peers online. |
| Relational Bullying | Manipulating friendships or social groups to isolate or harm an individual emotionally. |
Key Statistics on School Bullying
Bullying in schools affects approximately 1 in 3 students globally, leading to significant emotional and academic consequences. Around 20% of students report being bullied regularly, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue.
Verbal bullying is the most common form, followed by social and physical bullying. Schools with effective anti-bullying policies see up to a 50% reduction in bullying incidents.
Who Are the Victims and Perpetrators?
Bullying in school primarily affects students aged 12 to 15, with victims often exhibiting lower self-esteem and increased absenteeism. Perpetrators are frequently students seeking control or social dominance, with boys more likely to engage in physical bullying and girls in relational aggression. Understanding the distinct profiles of victims and perpetrators is crucial for developing targeted anti-bullying interventions.
Warning Signs of Bullying
Bullying in school affects millions of students worldwide, creating a toxic environment that hinders learning and emotional well-being. Recognizing the warning signs early can help prevent long-term psychological damage and promote a safer educational space.
- Unexplained Injuries - Frequent bruises, cuts, or scratched skin may indicate physical bullying or harassment.
- Change in Eating Habits - Skipping meals or binge eating can be a response to stress caused by bullying.
- Declining Academic Performance - A sudden drop in grades or loss of interest in schoolwork often signals emotional distress linked to bullying.
Effects of Bullying on Students
Bullying in school significantly impacts students' mental health, leading to increased anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem. Victims often experience difficulty concentrating, which hinders academic performance and overall school engagement.
Long-term effects include chronic stress and social withdrawal, which can persist into adulthood. Schools that address bullying effectively see improved student well-being and a safer learning environment.
Why Do Students Bully?
Bullying in schools stems from a complex mix of psychological and social factors. Understanding why students bully helps in creating effective prevention strategies.
- Desire for Power - Some students bully to assert dominance and control over peers.
- Seeking Attention - Bullying can be a way for students to gain recognition from friends or social groups.
- Emotional Instability - Students experiencing stress or insecurity may bully to cope with their feelings.
How to Prevent Bullying in Schools
Preventing bullying in schools requires creating a positive and inclusive environment where students feel safe and respected. Implementing clear anti-bullying policies and providing regular training for staff and students can help identify and address bullying behavior early. Encouraging open communication between students, parents, and teachers promotes awareness and collective responsibility in stopping bullying.
How to Help a Bullying Victim
Bullying in school affects millions of students worldwide, causing emotional and psychological harm. Helping a victim requires awareness, empathy, and proactive intervention.
First, listen carefully to the victim without judgment to provide emotional support. Encourage them to speak to a trusted adult, such as a teacher or school counselor. Report the bullying incidents to ensure the school takes appropriate action to protect the student.
