Local issues in the Philippines reflect the diverse challenges faced by communities across the nation, including poverty, environmental degradation, and access to education. Visualizing these concerns through an infographic provides a clear and impactful way to understand their scope and urgency. Highlighting key data points helps drive awareness and encourages collective action to address these pressing problems.
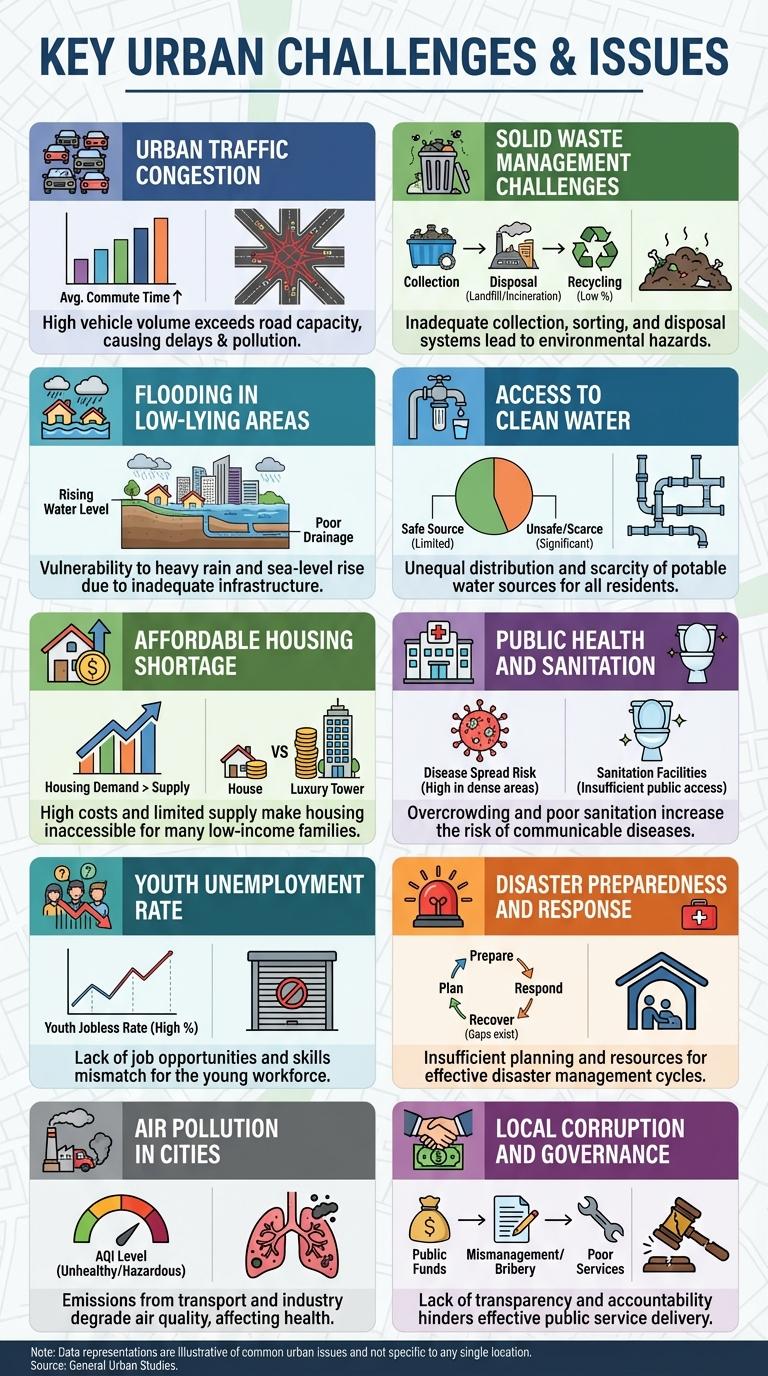
Urban Traffic Congestion
Urban traffic congestion in the Philippines, especially in Metro Manila, severely impacts daily commute times and economic productivity. The growing number of vehicles and insufficient infrastructure are key contributors to this persistent problem.
- High Vehicle Density - Metro Manila hosts over 4 million registered vehicles, causing frequent gridlocks during peak hours.
- Inadequate Public Transport - Limited and inefficient public transportation options push more commuters to use private vehicles.
- Infrastructure Limitations - Narrow roads and lack of proper traffic management systems worsen congestion in urban areas.
Solid Waste Management Challenges
Solid waste management in the Philippines faces significant challenges due to rapid urbanization and population growth. Inefficient waste segregation and limited recycling facilities contribute to increasing landfill overflow and environmental pollution. Community education and stricter enforcement of waste disposal laws are essential to improve sustainable waste management practices.
Flooding in Low-Lying Areas
Flooding in low-lying areas of the Philippines poses a significant threat to communities and infrastructure. Seasonal heavy rains and typhoons exacerbate water accumulation, leading to frequent flood events.
- Urban Drainage Systems - Insufficient and clogged drainage systems contribute to the severity of floods in many low-lying neighborhoods.
- Population Density - High population density in coastal and inland flood-prone areas increases vulnerability and impacts more residents.
- Climate Change Effects - Rising sea levels and increased rainfall intensity linked to climate change heighten flooding risks in these regions.
Effective flood management strategies and community awareness are essential to mitigate risks and protect vulnerable populations.
Access to Clean Water
How many Filipinos lack access to clean water? Approximately 3.3 million people in the Philippines do not have access to safe and potable water sources. This issue affects health, hygiene, and overall quality of life in many communities.
What are the main causes of limited clean water access? Contamination of water sources, inadequate infrastructure, and frequent natural disasters like typhoons contribute significantly to the problem. Urban and rural areas both face unique challenges in maintaining water quality.
Which regions in the Philippines have the poorest access to clean water? Regions such as the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) and some parts of Mindoro and Palawan report the lowest access rates. Rural barangays often experience the most severe shortages and water contamination.
How does lack of clean water impact public health? Waterborne diseases such as diarrhea, cholera, and typhoid fever are prevalent due to unsafe water supplies. Children and vulnerable populations suffer the highest rates of illness and mortality linked to poor water quality.
What initiatives are underway to improve water access? Government programs, NGOs, and international partners are implementing water supply projects, sanitation improvements, and community education. Investments in water infrastructure and watershed protection are priorities to ensure sustainable clean water access.
Affordable Housing Shortage
The Philippines faces a significant shortage of affordable housing, impacting millions of low-income families. Rapid urbanization and population growth have intensified the demand for affordable homes.
- High Population Density - Urban centers like Metro Manila experience overcrowding, driving up housing demand and prices.
- Limited Government Housing Programs - Insufficient funding and resources hamper large-scale affordable housing development.
- Rising Construction Costs - Increasing prices of materials and labor result in fewer affordable housing projects being completed.
Public Health and Sanitation
Public health and sanitation remain critical challenges in the Philippines, with many rural areas lacking access to clean water and proper waste disposal systems. Waterborne diseases such as cholera and dengue fever continue to affect thousands annually due to inadequate sanitation infrastructure. Government initiatives focus on improving water quality, promoting hygiene education, and expanding healthcare access to reduce the disease burden nationwide.
Youth Unemployment Rate
| Year | Youth Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| 2019 | 16.9 |
| 2020 | 19.8 |
| 2021 | 17.2 |
| 2022 | 15.5 |
| 2023 | 14.0 |
The youth unemployment rate in the Philippines remains a significant local issue. High rates reflect challenges in job matching, skills development, and economic conditions. Efforts to improve vocational training, entrepreneurship programs, and policy reforms target lowering these rates. Monitoring these statistics helps inform stakeholders for better youth employment strategies and policies.
Disaster Preparedness and Response
Disaster preparedness and response are vital in the Philippines due to its location in the Pacific Ring of Fire, making it prone to typhoons, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions. Effective local strategies help minimize damage and save lives during these natural events.
The government and communities collaborate to strengthen early warning systems, evacuation plans, and emergency supplies. Public education campaigns increase awareness and readiness across vulnerable areas. Continuous investment in infrastructure resilience enhances response capabilities and recovery speed.
Air Pollution in Cities
Air pollution in Philippine cities, especially Metro Manila, poses serious health risks to millions of residents. Major sources include vehicular emissions, industrial activities, and open burning of waste.
Particulate matter (PM2.5) levels frequently exceed World Health Organization standards, contributing to respiratory diseases and cardiovascular problems. Efforts to reduce pollution focus on improving public transportation, enforcing emission standards, and promoting green spaces.
