Infographics about bias visually represent how unconscious preferences influence decisions and behavior. They highlight common types of bias, such as confirmation bias and stereotyping, using clear statistics and examples. Understanding these patterns enhances awareness and promotes more objective thinking.
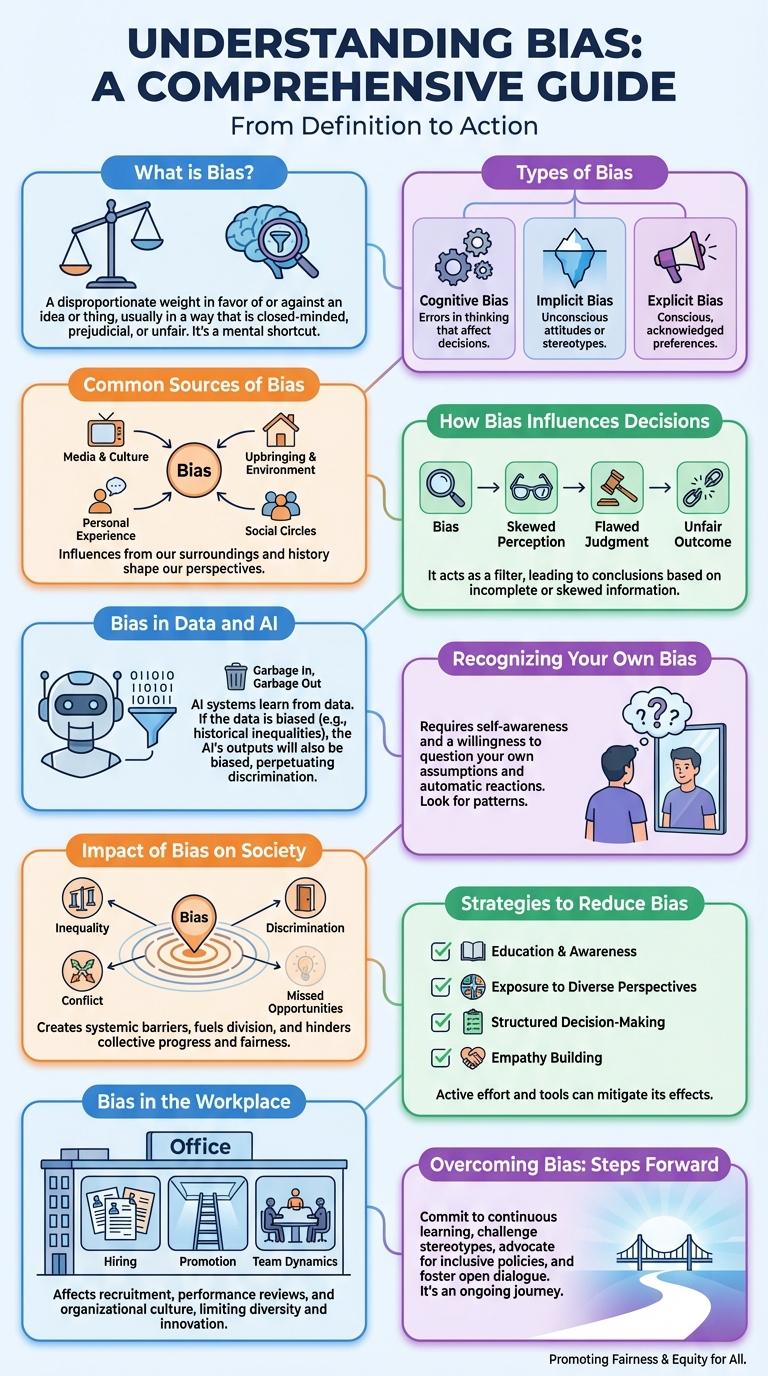
What is Bias?
Bias refers to a systematic inclination or prejudice towards or against something, often resulting in unfair outcomes. It affects how information is perceived, interpreted, and acted upon in various contexts.
- Cognitive Bias - Mental shortcuts or patterns that influence decision-making and judgment.
- Confirmation Bias - The tendency to favor information that confirms existing beliefs while ignoring contradictory evidence.
- Stereotyping - Assigning generalized attributes to individuals or groups, leading to oversimplified perceptions.
Types of Bias
Bias affects decision-making and perceptions across multiple contexts. Recognizing types of bias is essential for fostering fairness and accuracy.
Common types of bias include confirmation bias, where individuals favor information that supports their existing beliefs. Another type is selection bias, which occurs when samples are not representative of the population. Anchoring bias involves relying heavily on the first piece of information encountered.
Common Sources of Bias
Bias originates from various sources that influence perception and decision-making. Common sources include cognitive biases, cultural influences, and data sampling errors. Understanding these sources helps in identifying and mitigating bias in research and everyday judgments.
How Bias Influences Decisions
| Bias Type | Influence on Decisions |
|---|---|
| Confirmation Bias | Leads to favoring information that confirms existing beliefs, ignoring contradictory evidence. |
| Anchoring Bias | Causes overreliance on the first piece of information encountered, impacting judgment severity. |
| Availability Heuristic | Results in decisions based on readily available memories or examples, not all relevant information. |
| Implicit Bias | Unconscious attitudes influence actions and decisions, often without awareness of prejudice. |
| Hindsight Bias | Distorts memory of past events, leading to overestimating predictive abilities. |
Bias in Data and AI
Bias in data can lead to inaccurate AI predictions and unfair outcomes, affecting decision-making in sectors like healthcare, finance, and law enforcement. Biased datasets may reflect existing social prejudices, skewing AI models and perpetuating inequality. Addressing bias involves careful data collection, diverse training samples, and ongoing algorithm audits to ensure transparency and fairness.
Recognizing Your Own Bias
Recognizing your own bias is essential for clear thinking and fair decision-making. Biases influence perceptions and can distort reality without conscious awareness.
- Self-reflection - Regularly evaluate your thoughts and feelings to uncover hidden prejudices.
- Seek diverse perspectives - Exposure to different viewpoints challenges personal assumptions and broadens understanding.
- Understand cognitive biases - Learn about common mental shortcuts like confirmation bias to identify when they affect your judgment.
Awareness of personal bias leads to more objective and inclusive choices.
Impact of Bias on Society
Bias influences societal decisions, shaping public opinion and policy in ways that often reinforce inequality. It affects areas such as education, employment, and criminal justice, leading to unequal opportunities and treatment.
Understanding bias is crucial to promoting fairness and inclusivity within communities. Reducing bias can improve social cohesion and ensure equitable access to resources and rights for all individuals.
Strategies to Reduce Bias
How can individuals effectively reduce bias in decision-making? Awareness is the first step; recognizing personal biases helps in addressing them. Practicing perspective-taking and seeking diverse viewpoints strengthens objective understanding.
What role do organizations play in minimizing bias? Implementing structured decision-making processes limits subjective judgments. Training programs focused on unconscious bias increase employee awareness and promote inclusivity.
Which techniques improve fairness during hiring and evaluation? Blind recruitment removes identifying information to focus on qualifications. Standardized evaluation criteria ensure consistent assessment across candidates.
How does feedback contribute to reducing bias over time? Continuous feedback provides opportunities to identify and correct biased behavior. Encouraging open dialogues fosters a culture of accountability and improvement.
What tools assist in detecting and managing bias? Data analytics can reveal patterns indicating bias in processes. Bias detection software supports objective review and helps maintain fairness.
Bias in the Workplace
Bias in the workplace affects decision-making processes, leading to unequal opportunities and reduced employee morale. Common types include gender bias, racial bias, and ageism, which impact hiring, promotions, and team dynamics.
Organizations with high bias levels report lower productivity and increased turnover rates. Implementing bias training, diverse hiring panels, and inclusive policies helps create fairer, more innovative work environments.
