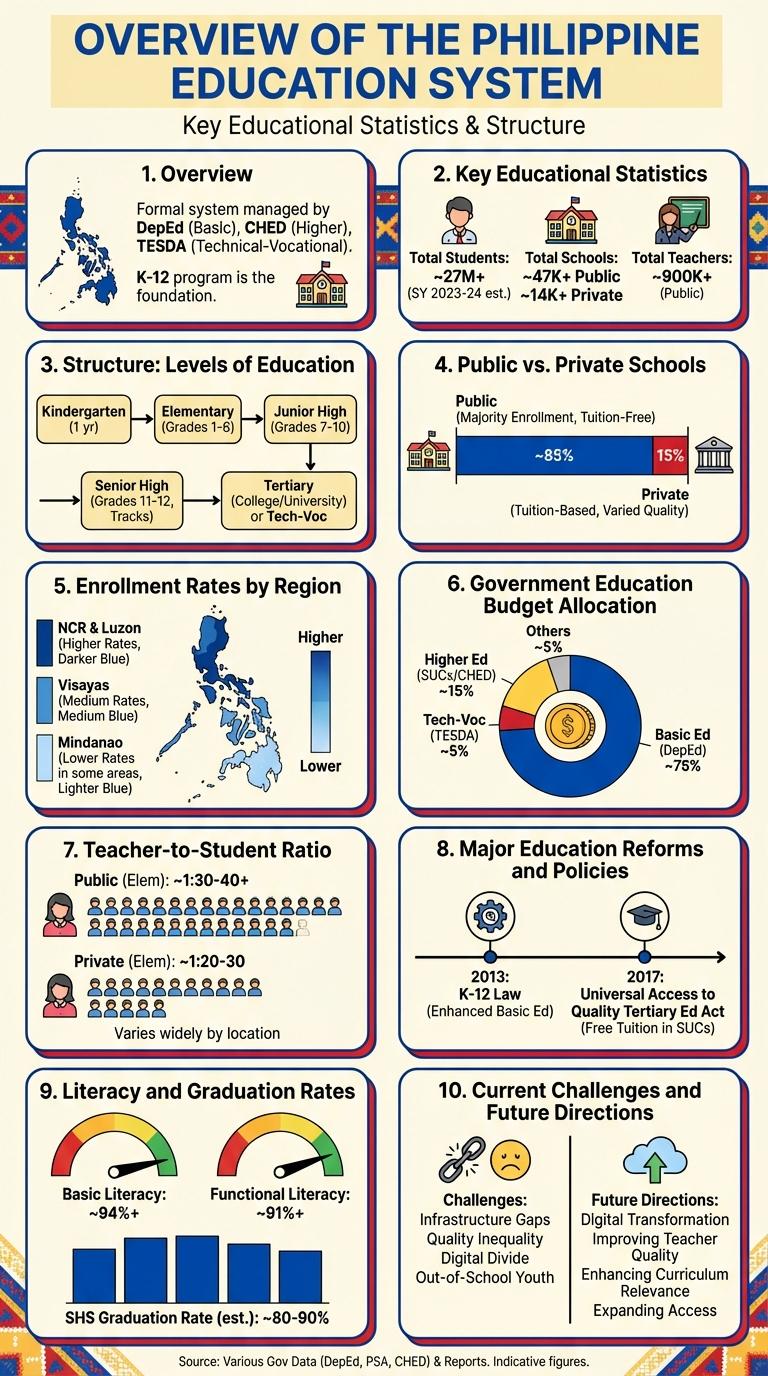
Education in the Philippines is a dynamic system that shapes the nation's future through accessible learning opportunities and diverse academic programs. This infographic highlights key statistics, challenges, and milestones in Philippine education, offering a comprehensive overview of enrollment rates, literacy levels, and government initiatives. Understanding these elements provides valuable insight into the progress and ongoing efforts to enhance the quality of education across the country.
Overview of the Philippine Education System
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Governing Body | Department of Education (DepEd), Commission on Higher Education (CHED) |
| Education Levels | Basic Education (K-12), Senior High School, Higher Education |
| K-12 Program | Mandatory Kindergarten plus 12 years of basic education including 6 years primary, 4 years junior high, 2 years senior high |
| Language of Instruction | English and Filipino, with mother tongue as medium in early grades |
| Academic Year | June to March, divided into two semesters |
Key Educational Statistics
The education system in the Philippines serves over 27 million students across various levels. The Department of Education manages primary and secondary education, while the Commission on Higher Education oversees tertiary education.
The literacy rate in the Philippines stands at approximately 98%, reflecting strong national efforts to improve education access. Public schools enroll about 85% of students, with private and alternative education catering to the remainder.
Structure: Levels of Education
The education system in the Philippines is divided into distinct levels: Early Childhood Education, Basic Education, and Higher Education. Basic Education consists of Kindergarten, 6 years of Elementary School, 4 years of Junior High School, and 2 years of Senior High School. Higher Education includes undergraduate, graduate, and postgraduate programs offered by universities and colleges nationwide.
Public vs. Private Schools
How do public and private schools in the Philippines differ in terms of enrollment and resources? Public schools serve approximately 84% of Filipino students, offering free education funded by the government. Private schools, though catering to about 16%, often provide more specialized programs and resources due to tuition fees.
What is the difference in student-teacher ratio between public and private schools in the Philippines? Public schools have an average student-teacher ratio of 30:1, which can affect individual attention. Private schools maintain a lower ratio around 20:1, supporting more personalized instruction.
| School Type | Key Features |
|---|---|
| Public Schools | Government-funded, free tuition, higher enrollment, larger class sizes |
| Private Schools | Tuition-based, smaller classes, specialized curricula, better facilities |
What challenges do public schools face compared to private schools in the Philippines? Limited funding often results in outdated facilities and learning materials in public schools. Private schools benefit from higher budgets allowing advanced technology and extracurricular options.
How does the government support education quality in public schools? The Department of Education implements policies and programs to enhance teaching quality and infrastructure. Grants and training aim to reduce disparities with private school resources over time.
Enrollment Rates by Region
The Philippines exhibits varied enrollment rates across its 17 regions, reflecting diverse socio-economic and geographic factors. Regions with urban centers tend to have higher enrollment rates compared to remote and rural areas.
National enrollment stands at approximately 85% for elementary education and 75% for secondary education. Notably, the National Capital Region (NCR) leads with enrollment rates above 90%, while some Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) provinces report rates below 60%.
Government Education Budget Allocation
The Government of the Philippines allocates a substantial portion of its national budget to education, reflecting its commitment to improving learning outcomes. In 2024, the Department of Education (DepEd) received approximately P900 billion, representing around 19% of the total national budget. This funding supports public schools, teacher salaries, learning materials, and infrastructure development nationwide.
Teacher-to-Student Ratio
The teacher-to-student ratio in the Philippines remains a critical indicator of educational quality and accessibility. This ratio measures the average number of students assigned to each teacher in schools across the country.
Recent data from the Department of Education shows an average ratio of approximately 1:30 in public schools, which is higher than the international standard of 1:20. High ratios often lead to challenges in providing personalized instruction and maintaining classroom management. Efforts to recruit more qualified teachers aim to improve this ratio and enhance the overall learning experience for Filipino students.
Major Education Reforms and Policies
The Philippines has implemented significant education reforms to improve quality and accessibility across all levels. These policies aim to address educational gaps and align the curriculum with global standards.
- Enhanced Basic Education Act (K-12 Program) - Extended basic education from 10 to 12 years, including senior high school to better prepare students for college and employment.
- Universal Access to Quality Tertiary Education Act - Provides free tuition and other fees for students in state universities and colleges nationwide.
- Alternative Learning System (ALS) - Offers non-formal education programs to out-of-school youth and adult learners for basic literacy and skills development.
Literacy and Graduation Rates
The education system in the Philippines shows significant progress in literacy and graduation rates over recent years. These key metrics highlight the country's ongoing efforts to improve universal access to quality education.
Literacy rates and graduation rates serve as critical indicators of educational attainment in the Philippines.
- Literacy Rate - The Philippines boasts a literacy rate of approximately 98.2% among individuals aged 15 and above, reflecting widespread basic reading and writing skills.
- Elementary School Graduation Rate - Around 92% of students complete elementary education, demonstrating strong retention at the primary level.
- Secondary School Graduation Rate - About 75% of students graduate from high school, indicating ongoing challenges in maintaining enrollment through the secondary stage.
