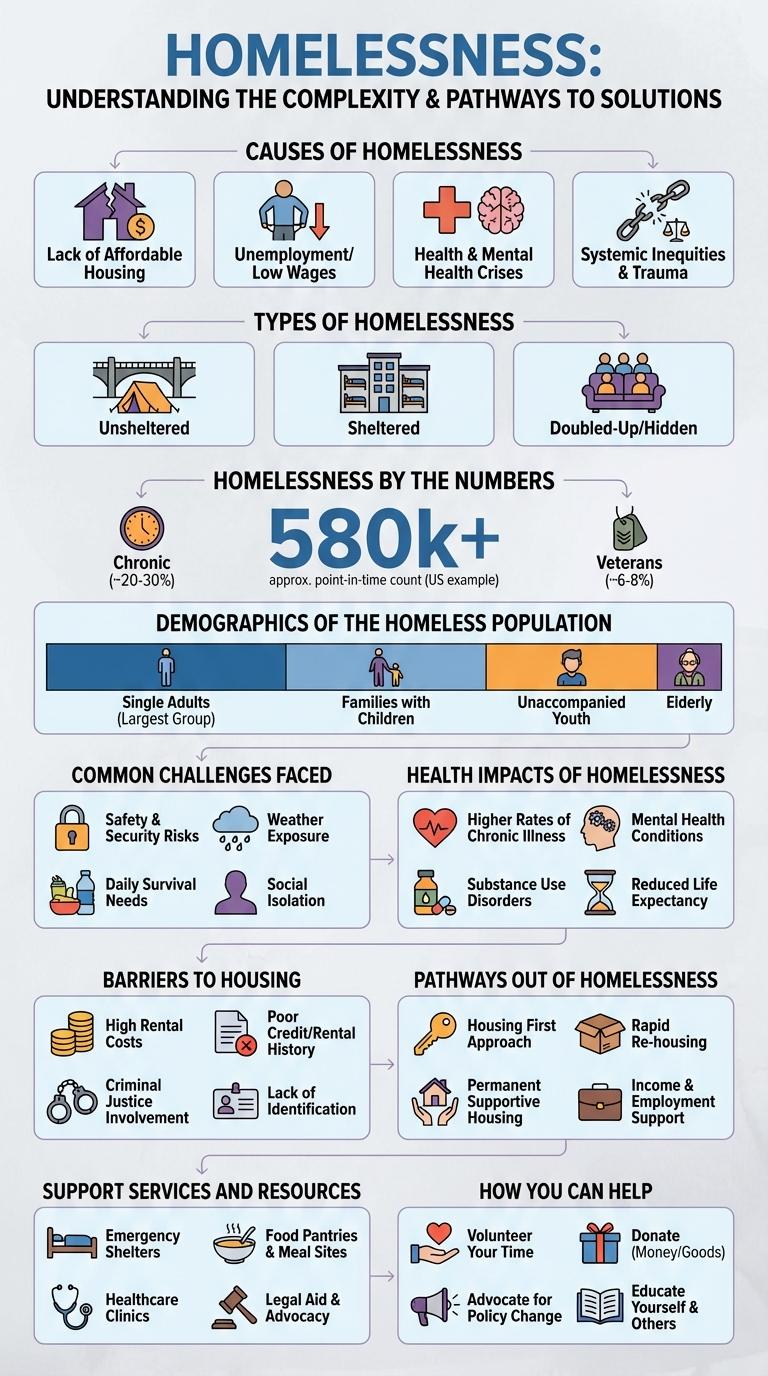
Homelessness remains a pressing social issue affecting millions worldwide, with diverse causes ranging from economic instability to mental health challenges. Visual data representations offer clear insights into the demographics, root causes, and possible solutions for homelessness. This infographic breaks down key statistics and trends, highlighting the urgent need for comprehensive support and policy change.
Causes of Homelessness
Homelessness arises from a complex interplay of economic, social, and personal factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for effective intervention and policy-making.
Key causes include poverty, lack of affordable housing, and unemployment. Mental health issues and substance abuse contribute significantly to prolonged homelessness. Systemic barriers such as discrimination and inadequate social support also play a major role.
Types of Homelessness
| Type of Homelessness | Description |
|---|---|
| Chronic Homelessness | Long-term or repeated homelessness coupled with a disabling condition, often requiring comprehensive healthcare and social services. |
| Transitional Homelessness | Short-term homelessness often caused by a sudden crisis or loss of housing, typically resolved with temporary shelter and support. |
| Episodic Homelessness | Frequent episodes of homelessness, often linked to health issues like mental illness or substance abuse, requiring targeted interventions. |
| Hidden Homelessness | Individuals who do not access shelters and instead stay with friends or family, often underreported in official statistics. |
| Family Homelessness | Homelessness affecting families with children, requiring coordinated support for housing stability, education, and healthcare. |
Homelessness by the Numbers
Homelessness affects millions worldwide, reflecting complex social and economic challenges. Accurate data highlights the scale and demographics of this urgent issue.
- 580,000 People Experiencing Homelessness - The United States reported over half a million individuals without stable housing on a single night in 2023.
- 35% Family Households - Families with children constitute more than one-third of the homeless population, underscoring the vulnerability of youth in homelessness.
- 50% Chronically Homeless - Half of all homeless individuals face long-term or repeated episodes of homelessness combined with disabling conditions.
Addressing homelessness requires comprehensive policies targeting prevention, shelter access, and permanent supportive housing solutions.
Demographics of the Homeless Population
Homelessness affects diverse demographic groups across the United States, with the majority being individuals aged 25 to 54. According to the 2023 Annual Homeless Assessment Report, approximately 37% of the homeless population are families with children, highlighting the prevalence among young and middle-aged adults.
Racial disparities are significant, with Black individuals representing 39% of the homeless population, despite comprising about 13% of the general population. Veterans account for nearly 6% of those experiencing homelessness, reflecting ongoing challenges in securing stable housing post-service.
Common Challenges Faced
Homelessness presents numerous challenges, including lack of access to stable housing, inadequate healthcare, and limited employment opportunities. Many individuals face food insecurity, mental health issues, and social stigma. These obstacles create a cycle that makes escaping homelessness difficult and requires comprehensive support services.
Health Impacts of Homelessness
Homelessness significantly worsens health outcomes, affecting physical and mental well-being. Access to basic healthcare services remains a major challenge for homeless populations.
- Chronic Illness Prevalence - Homeless individuals experience higher rates of chronic illnesses such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and respiratory conditions compared to housed populations.
- Mental Health Disorders - The incidence of depression, anxiety, and substance use disorders is disproportionately high among people experiencing homelessness.
- Limited Healthcare Access - Barriers like lack of insurance, transportation, and stigma limit healthcare utilization by homeless populations, worsening health outcomes.
Barriers to Housing
Barriers to housing significantly contribute to the persistence of homelessness. These obstacles include financial constraints, lack of affordable housing, and systemic issues within the housing market.
Many individuals face challenges such as poor credit history, insufficient income, and legal barriers that prevent access to stable housing. Addressing these factors is critical to reducing homelessness and ensuring safe living conditions for all.
Pathways Out of Homelessness
What are effective pathways out of homelessness?
Housing First programs prioritize providing stable housing before addressing other challenges. Support services like job training, mental health care, and substance abuse treatment improve long-term outcomes.
How does employment contribute to exiting homelessness?
Securing employment provides financial stability and promotes self-sufficiency. Vocational training and job placement programs are key to helping individuals re-enter the workforce.
Why is access to healthcare essential for homeless individuals?
Access to comprehensive healthcare addresses physical and mental health needs critical for stability. Chronic conditions and untreated mental illness often perpetuate homelessness.
What role do supportive housing services play?
Supportive housing combines affordable housing with on-site services to maintain housing stability. This approach reduces repeated homelessness and hospitalizations.
How can community involvement aid in ending homelessness?
Community engagement fosters awareness, resources, and volunteer support. Collaborative efforts among government, nonprofits, and citizens enhance service delivery and innovation.
Support Services and Resources
Support services for homelessness include emergency shelters, food banks, and healthcare programs designed to address immediate needs. Resources such as job training, mental health counseling, and substance abuse treatment play a critical role in helping individuals achieve long-term stability. Community organizations and government agencies collaborate to provide these essential services, aiming to reduce homelessness and promote self-sufficiency.
