Infographics about equality visually present key data and concepts that highlight disparities and promote fairness across different social groups. They use clear graphics and concise information to engage audiences, making complex issues more accessible and understandable. By raising awareness, these infographics encourage informed discussions and actions towards achieving equal rights and opportunities.
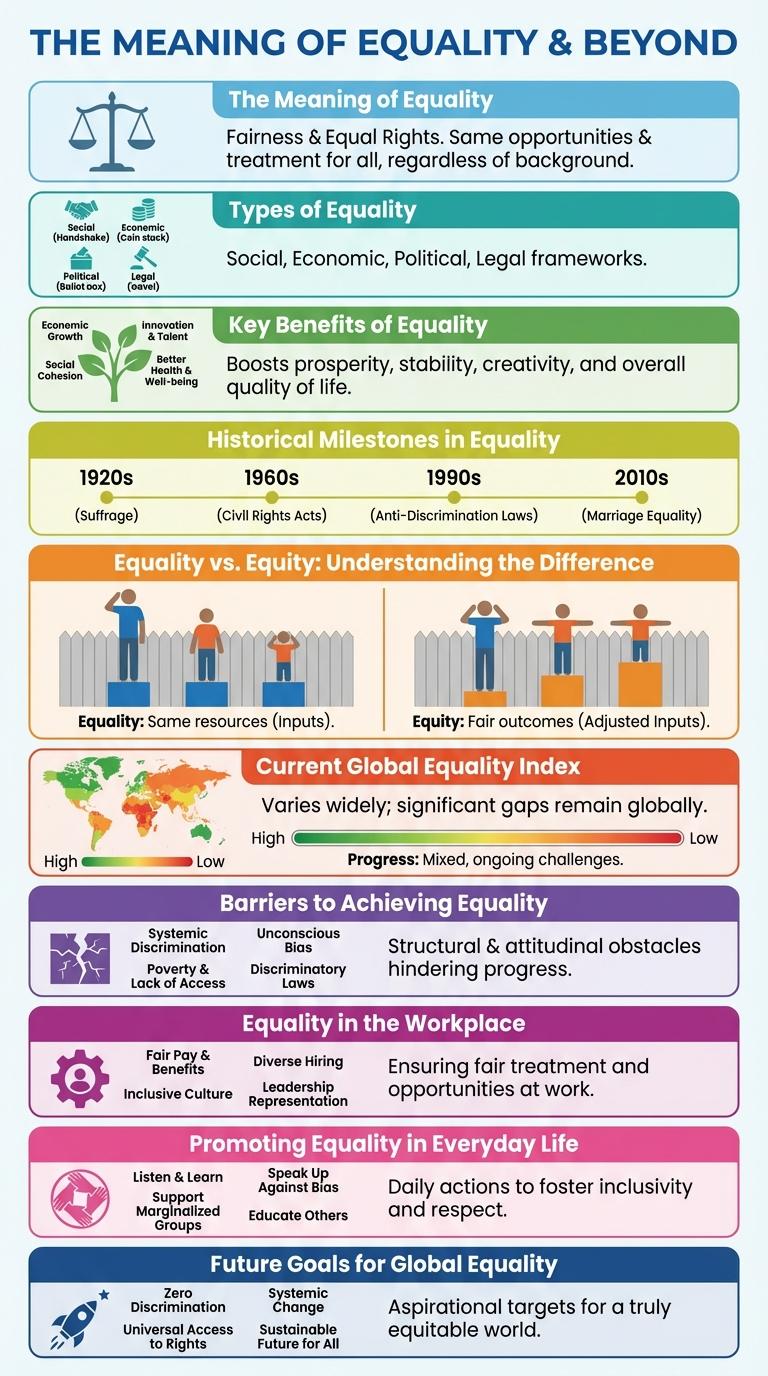
The Meaning of Equality
Equality means ensuring that every individual has the same rights, opportunities, and access to resources regardless of their background or identity. It promotes fairness by eliminating discrimination and bias in social, economic, and political settings. True equality fosters inclusive communities where diversity is respected and valued.
Types of Equality
What are the main types of equality in society?
Equality refers to the state where individuals have fair and equal access to opportunities and resources. Different types of equality focus on various aspects such as rights, treatment, and access.
| Type of Equality | Description |
|---|---|
| Social Equality | Ensures equal status and opportunities in social settings regardless of background or identity. |
| Economic Equality | Focuses on reducing income and wealth disparities among members of society. |
| Political Equality | Guarantees equal participation rights in political processes and decision-making. |
| Legal Equality | Means all individuals are subject to the same laws without discrimination. |
| Gender Equality | Promotes equal rights, responsibilities, and opportunities regardless of gender. |
Key Benefits of Equality
Equality fosters social harmony and drives sustainable economic growth by ensuring fair opportunities for all. Embracing equality enhances innovation and strengthens communities through diverse perspectives.
- Improved Social Cohesion - Equality reduces conflicts and promotes mutual respect across different groups.
- Economic Prosperity - Equal access to resources and education boosts productivity and economic development.
- Innovation and Creativity - Diverse teams lead to more innovative solutions and broader viewpoints.
Historical Milestones in Equality
Historical milestones in equality have shaped the modern fight for social justice worldwide. Key moments include the abolition of slavery in the 19th century, women's suffrage movements in the early 20th century, and the Civil Rights Act of 1964 in the United States. Each milestone represents a step towards greater legal and social recognition of equal rights for all individuals.
| Year | Milestone |
|---|---|
| 1865 | Abolition of Slavery (13th Amendment, USA) |
| 1920 | Women's Suffrage (19th Amendment, USA) |
| 1964 | Civil Rights Act (USA) |
| 1948 | Universal Declaration of Human Rights |
| 1995 | Beijing Declaration on Women's Rights |
Equality vs. Equity: Understanding the Difference
Equality means giving everyone the same resources or opportunities regardless of their individual needs. It aims for fairness by treating all people identically.
Equity involves distributing resources based on the unique needs and circumstances of individuals to achieve fair outcomes. It recognizes that different people may require different support to reach equal opportunities.
Current Global Equality Index
The Current Global Equality Index measures disparities across income, gender, education, and health worldwide. It highlights progress and areas needing urgent attention to promote fairness and inclusion.
- Global Score - The 2024 Global Equality Index stands at 67 out of 100, indicating moderate overall equality.
- Income Equality - Income inequality remains high with a score of 54, reflecting significant wealth gaps between populations.
- Gender Equality - Gender parity improved slightly to 72, driven by greater access to education and employment opportunities for women.
Countries scoring above 80 show exemplary equality efforts, while regions below 50 require targeted policies to close critical gaps.
Barriers to Achieving Equality
Barriers to achieving equality include systemic discrimination and unequal access to resources. These obstacles create persistent gaps in opportunities for marginalized groups.
Social biases and institutional policies often reinforce inequality, limiting social mobility. Addressing these barriers requires targeted interventions and inclusive reforms.
Equality in the Workplace
Equality in the workplace ensures all employees receive fair treatment regardless of gender, race, or background. Promoting diversity leads to increased innovation, productivity, and employee satisfaction.
- Equal Pay - Employees in similar roles should receive equivalent compensation to promote fairness and reduce wage gaps.
- Diverse Hiring Practices - Inclusive recruitment strategies enhance workforce variety and reflect a global market perspective.
- Anti-Discrimination Policies - Enforcing strict policies helps create a safe, respectful work environment free from bias and harassment.
Promoting Equality in Everyday Life
| Action | Description |
|---|---|
| Respect Diversity | Recognize and value different cultural backgrounds, perspectives, and experiences in daily interactions. |
| Challenge Bias | Identify and address personal and systemic prejudices to create fair opportunities for all. |
| Inclusive Language | Use words that respect all genders, races, abilities, and identities to foster inclusion. |
| Equal Opportunities | Support fair access to education, employment, and resources for every individual. |
| Community Engagement | Participate in initiatives that promote social equality and inclusive environments. |
