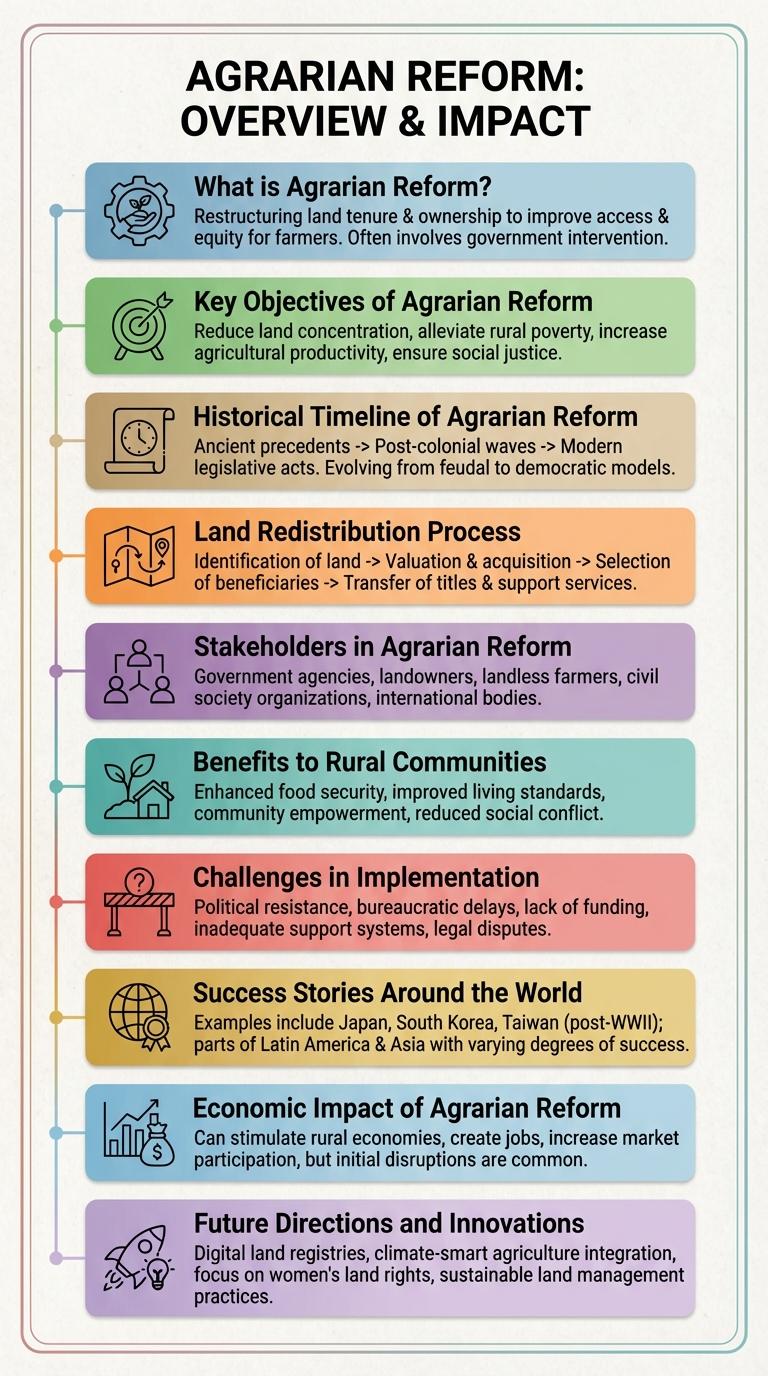
Agrarian reform transforms land ownership to promote equitable distribution and improve agricultural productivity. This infographic highlights key policies, historical milestones, and social impacts of agrarian reform worldwide. Understanding these elements reveals how land redistribution fosters rural development and poverty reduction.
What is Agrarian Reform?
What is Agrarian Reform?
Agrarian reform refers to the legal measures implemented to redistribute land from large landowners to landless farmers and tenants. This process aims to promote social equity, improve agricultural productivity, and reduce rural poverty.
Key Objectives of Agrarian Reform
Agrarian reform aims to redistribute land to promote social equity and improve the livelihoods of rural farmers. Key objectives include ensuring land ownership for landless farmers, increasing agricultural productivity, and reducing rural poverty. The reform also seeks to stabilize rural communities and empower marginalized groups through equitable access to land resources.
Historical Timeline of Agrarian Reform
Agrarian reform has played a crucial role in reshaping land ownership and promoting social justice in rural areas worldwide. Key milestones include the Mexican Land Reform in the early 20th century, the Philippine Agrarian Reform Program initiated in the 1970s, and recent efforts in countries like India and Brazil to redistribute land to marginalized farmers. These reforms reflect ongoing struggles for equitable land distribution and sustainable agricultural development.
Land Redistribution Process
The land redistribution process is a key component of agrarian reform designed to provide land to landless farmers. It aims to promote social justice and improve agricultural productivity by reallocating land from large landowners to tenant farmers and landless workers.
The process typically starts with identifying land suitable for redistribution, including idle or underutilized lands. Beneficiaries are selected based on eligibility criteria, prioritizing small farmers and marginalized groups. Land titles are then transferred to the new owners, granting them secure tenure and access to government support services.
Stakeholders in Agrarian Reform
Agrarian reform aims to redistribute land to promote equitable ownership and improve agricultural productivity. Various stakeholders play critical roles in implementing and benefiting from these reforms.
- Farmers and Landless Workers - Primary beneficiaries who gain access to land for cultivation and livelihood improvement.
- Government Agencies - Responsible for policy formulation, land distribution, and monitoring reform implementation.
- Landowners - Previous holders of land who may be subject to redistribution under agrarian reform policies.
- Civil Society Organizations - Advocate for farmers' rights and support capacity-building within agrarian communities.
- Local Government Units - Facilitate local implementation and mediate between stakeholders during reform processes.
Benefits to Rural Communities
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Increased Land Ownership | Redistribution of land empowers farmers with secure titles, promoting investment and long-term planning. |
| Improved Agricultural Productivity | Access to land enables the adoption of modern farming techniques, enhancing crop yields and food security. |
| Economic Empowerment | Land ownership fosters income opportunities, reducing poverty and improving living standards in rural areas. |
| Community Development | Stronger rural economies support better infrastructure, education, and health services for farming communities. |
| Social Equity | Agrarian reform promotes fairness by addressing land inequality and supporting marginalized farmers. |
Challenges in Implementation
Agrarian reform aims to redistribute land to promote equity and improve agricultural productivity. Implementation faces significant obstacles that hinder its success and impact on rural communities.
Land ownership disputes and bureaucratic delays often stall the reform process. Limited resources and resistance from powerful landowners further complicate enforcement and sustainability.
Success Stories Around the World
Agrarian reform has transformed rural communities globally by redistributing land to empower small farmers and reduce inequality. Successful initiatives have boosted agricultural productivity and improved livelihoods across diverse regions.
In South Korea, land reform in the 1950s redistributed land from landlords to tenant farmers, fostering rapid economic growth. Brazil's agrarian reform programs have provided land rights and support services to thousands of rural families, enhancing food security.
Economic Impact of Agrarian Reform
Agrarian reform significantly transforms rural economies by redistributing land to foster equitable agricultural productivity. This process enhances income distribution and stimulates economic development in farming communities.
- Increased Agricultural Output - Redistribution of land promotes efficient land use, resulting in higher crop yields and food production.
- Poverty Reduction - Providing land to smallholder farmers improves livelihoods and reduces rural poverty levels.
- Rural Employment Growth - Agrarian reform boosts job opportunities in agriculture and related sectors, driving local economic activity.
