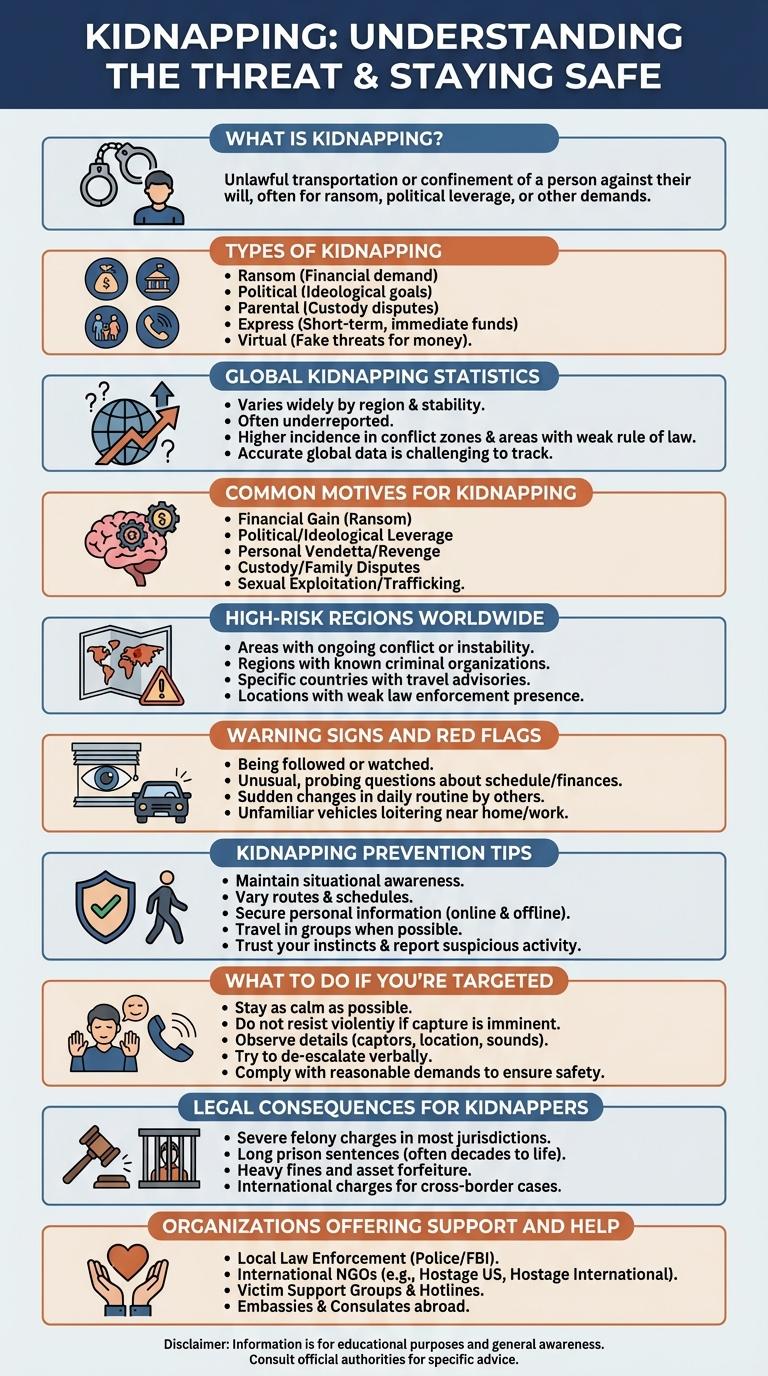
Kidnapping is a serious crime involving the unlawful abduction or detention of a person against their will. This infographic highlights key statistics, common motives, and safety tips to raise awareness and help prevent such incidents. Understanding patterns and preventive measures is crucial for protecting individuals and communities from the dangers of kidnapping.
What is Kidnapping?
Kidnapping involves unlawfully seizing and detaining a person against their will. It is a criminal act often driven by motives such as ransom, coercion, or exploitation.
- Legal Definition - Kidnapping is defined as the illegal taking and holding of a person typically to demand a ransom or exert influence.
- Methods - Perpetrators may use force, threats, deception, or coercion to abduct victims.
- Consequences - Victims face severe physical, psychological, and emotional trauma due to kidnapping.
Law enforcement agencies worldwide prioritize kidnapping cases due to their urgent, life-threatening nature.
Types of Kidnapping
Kidnapping involves unlawfully seizing and holding a person against their will. Common types include parental kidnapping, where a child is taken by a non-custodial parent; stranger abduction, often motivated by ransom or exploitation; and express kidnapping, which involves quick abduction for immediate financial gain. Each type varies in motive, method, and impact on victims and families.
Global Kidnapping Statistics
Kidnapping remains a significant global issue, with thousands of cases reported annually across various continents. The highest incidence rates occur in regions affected by political instability and organized crime.
According to recent data, around 200,000 kidnappings are documented worldwide each year, with a substantial percentage involving ransom demands. Children and young adults constitute the majority of victims, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced preventive measures.
Common Motives for Kidnapping
Kidnapping is a serious crime driven by various underlying motives. Understanding these motives helps in prevention and awareness efforts.
Common motives for kidnapping often revolve around financial gain, coercion, or psychological factors.
- Ransom Demands - Kidnappers frequently seek money by holding victims hostage until a ransom is paid.
- Political Leverage - Kidnapping is used to intimidate or gain concessions from governments or organizations.
- Personal Vendettas - Individuals may kidnap to exact revenge or resolve personal conflicts.
High-Risk Regions Worldwide
Kidnapping incidents occur with varying frequency across different regions worldwide, often influenced by socio-economic and political factors. Certain areas exhibit notably higher risks due to ongoing conflicts, weak law enforcement, and organized crime activities.
Regions such as Latin America, Sub-Saharan Africa, South Asia, and parts of the Middle East report the highest rates of kidnapping cases annually. These high-risk zones present significant challenges for governments and international agencies aiming to combat abductions and protect citizens.
Warning Signs and Red Flags
Kidnapping warning signs often include sudden changes in a child's behavior, such as fear of being alone or reluctance to go with certain individuals. Unexplained injuries, secretive actions, and unusual gifts or money can also be red flags. Awareness of these indicators helps caregivers and authorities intervene before abduction occurs.
Kidnapping Prevention Tips
| Kidnapping Prevention Tips | Description |
|---|---|
| Stay Alert | Be aware of your surroundings and trust your instincts in unfamiliar environments. |
| Never Walk Alone | Travel with a companion, especially at night or in isolated areas. |
| Keep Personal Information Private | Avoid sharing your address, schedule, or location details with strangers. |
| Use Safety Apps | Install GPS tracking or emergency alert apps on your smartphone for quick assistance. |
| Inform Trusted Contacts | Share your daily routes and plans with family or friends for added security. |
What To Do If You're Targeted
Kidnapping is a serious threat that requires quick thinking and a clear plan of action. Knowing the right steps to take can significantly increase your chances of staying safe.
- Stay Calm - Keeping a clear head helps you assess the situation and avoid panic, making it easier to make safe decisions.
- Make Noise - Drawing attention by shouting or using a personal alarm can deter kidnappers and attract help.
- Remember Details - Observing and memorizing the kidnapper's appearance, surroundings, and vehicle aids law enforcement in their search.
Legal Consequences for Kidnappers
What are the legal consequences faced by kidnappers? Kidnapping is a serious criminal offense that carries severe penalties under the law. Perpetrators may face long prison sentences, heavy fines, and lasting legal repercussions.
| Legal Consequence | Description |
|---|---|
| Imprisonment | Kidnappers can be sentenced to decades in prison depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the crime. |
| Fines | Monetary penalties can range from thousands to millions of dollars. |
| Restitution | Courts may order kidnappers to compensate victims for emotional and physical damages. |
| Life Imprisonment | In cases involving aggravating factors, kidnappers might receive life sentences without parole. |
| Death Penalty | Some jurisdictions impose capital punishment for kidnapping resulting in murder or severe harm. |
Legal systems prioritize protecting victims and deterring kidnapping. The consequences help reinforce public safety and uphold justice globally.
