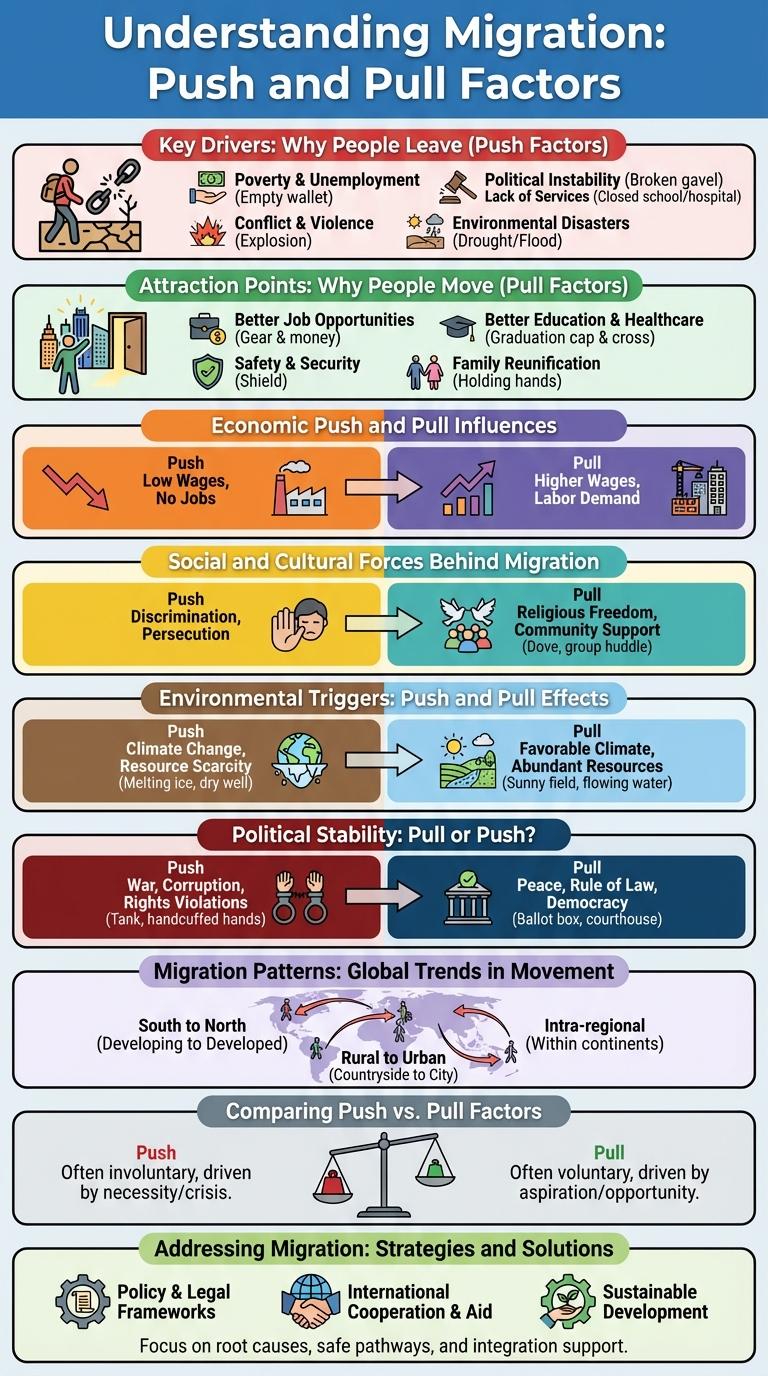
Push and pull factors play a crucial role in shaping migration patterns by influencing why people leave their homes or are attracted to new destinations. Understanding these factors helps explain the complex economic, social, and environmental reasons behind population movements. This infographic visually breaks down the key elements that drive migration decisions worldwide.
Understanding Migration: Push and Pull Factors
Migration is influenced by various push and pull factors that drive people to leave their home countries or attract them to new destinations. Push factors are negative conditions that compel individuals to move away, while pull factors are positive attributes that draw them toward a specific location.
Common push factors include economic hardship, political instability, and environmental challenges. Pull factors often consist of better job opportunities, political stability, and improved living conditions.
Key Drivers: Why People Leave (Push Factors)
Migration is significantly influenced by various push factors that compel individuals to leave their home countries. These key drivers often relate to economic hardship, political instability, and social pressures.
Economic challenges such as unemployment and poverty push people to seek better opportunities elsewhere. Political instability, including conflict and persecution, forces individuals to escape unsafe environments. Social factors like lack of education and healthcare also motivate migration to improve living conditions.
Attraction Points: Why People Move (Pull Factors)
What attracts people to migrate to new locations? Pull factors such as better job opportunities and improved living conditions draw individuals to move. Access to quality education and healthcare also serves as strong incentives for migration.
Economic Push and Pull Influences
Economic push factors in migration include unemployment, low wages, and poor job opportunities that drive individuals to leave their home countries. Economic pull factors attract migrants through higher wages, better employment prospects, and improved living standards in destination areas. Infographics visually highlight these influences, helping to understand migration patterns and economic motivations worldwide.
Social and Cultural Forces Behind Migration
Social and cultural forces significantly influence migration patterns by shaping individuals' decisions to leave or settle in new locations. These forces encompass factors related to family ties, community networks, and cultural acceptance.
- Family Reunification - Migration often occurs to join family members who have previously relocated, providing emotional support and social stability.
- Community Networks - Established ethnic or cultural communities in destination areas attract migrants by offering familiar language, customs, and assistance.
- Cultural Acceptance - Societies with inclusive attitudes encourage migration by reducing discrimination and enabling smoother integration for newcomers.
Environmental Triggers: Push and Pull Effects
Environmental triggers significantly influence migration patterns through push and pull effects. Push factors include natural disasters, droughts, and environmental degradation that force people to leave their homelands. Pull factors such as better climate conditions, abundant natural resources, and safer environments attract migrants to new locations.
Political Stability: Pull or Push?
Political stability plays a crucial role in migration decisions, acting as either a pull or push factor. People often move to countries with stable governments or flee regions experiencing political unrest.
- Political Stability as a Pull Factor - Stable governments create safe environments attracting migrants seeking security and opportunities.
- Political Instability as a Push Factor - Political violence, corruption, and unrest force residents to leave for safer locations.
- Impact on Economic and Social Conditions - Political stability supports economic growth and social services, enhancing migration appeal.
Migration Patterns: Global Trends in Movement
| Push Factors | Pull Factors |
|---|---|
| Economic instability and unemployment in home countries | Availability of job opportunities in destination countries |
| Political conflicts and persecution | Political stability and protection of human rights |
| Environmental disasters and climate change impacts | Safer environments and disaster-resilient infrastructure |
| Poor access to education and healthcare services | Better educational institutions and advanced healthcare systems |
| Social discrimination and lack of freedom | Social inclusion and freedom of expression |
Migration patterns reveal global trends in human movement driven by diverse push and pull factors. Push factors compel individuals to leave their countries due to adverse conditions such as economic instability, armed conflicts, environmental crises, limited social services, and discriminatory practices. Pull factors attract migrants to new locations by offering enhanced economic prospects, political safety, improved living conditions, quality education and healthcare, and inclusive societies.
Major migration routes connect developing regions in Africa, Asia, and Latin America to developed economies in North America, Europe, and Oceania. Increasing climate migrations underscore growing environmental challenges influencing population displacement. Understanding these factors is essential for policymakers to manage migration flows and support sustainable development globally.
Comparing Push vs. Pull Factors
Migration is driven by various push and pull factors that influence individuals to leave their home country or settle in a new one. Understanding these factors helps explain the reasons behind human movement on a global scale.
- Push Factors - These are negative conditions such as conflict, poverty, and natural disasters that compel people to leave their origin.
- Pull Factors - Positive attributes like economic opportunities, political stability, and better living conditions attract migrants to a destination.
- Contrast in Motivation - Push factors force migration out of necessity, while pull factors encourage migration by presenting desirable options.
Analyzing push and pull factors provides insight into the complex motives behind migration patterns worldwide.
