Citizenship embodies the rights, responsibilities, and privileges granted to individuals within a nation. Infographics effectively visualize the complex aspects of citizenship, highlighting key elements like legal status, civic duties, and social benefits. This format simplifies understanding by combining data, statistics, and symbolic imagery for clearer comprehension.
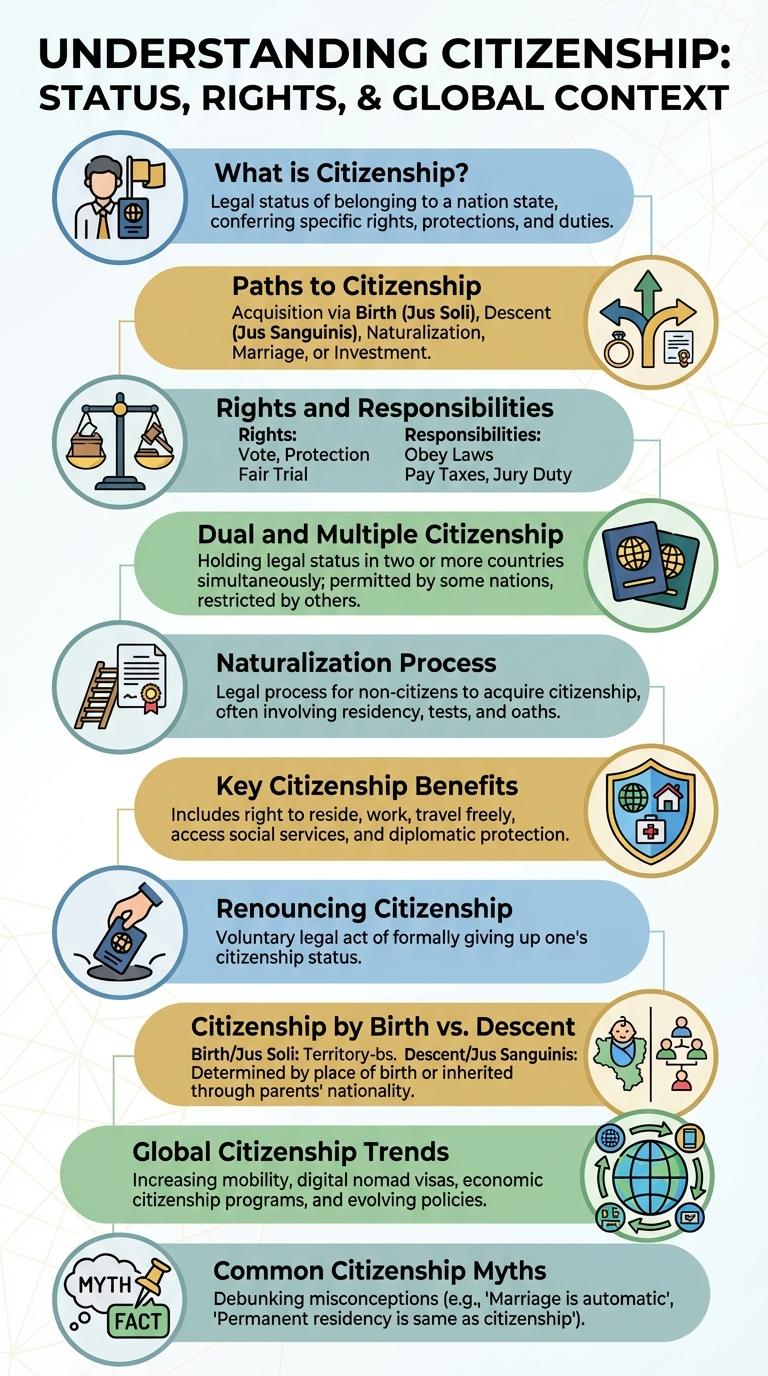
What is Citizenship?
Citizenship is the legal status that grants an individual the rights and responsibilities within a specific country. It defines the relationship between the individual and the state, including rights like voting and access to social services. Citizenship also entails duties such as obeying laws and participating in civic activities.
Paths to Citizenship
What are the main paths to citizenship? Citizenship can be obtained through birthright, naturalization, or descent from citizen parents. Each path requires specific eligibility criteria and documentation to complete the process.
Rights and Responsibilities
Citizenship grants individuals the essential rights that empower them to participate fully in society, including voting, access to public services, and freedom of speech. These rights ensure equal treatment and protection under the law for all citizens.
With citizenship come important responsibilities such as obeying laws, paying taxes, and serving on juries when called upon. Fulfilling these duties helps maintain social order and contributes to the common good of the community.
Dual and Multiple Citizenship
Dual and multiple citizenship allow individuals to legally belong to two or more countries simultaneously. This status can provide extensive rights, responsibilities, and opportunities across nations.
Understanding the complexities and benefits of dual and multiple citizenship is essential for global travelers and expatriates.
- Definition of Dual Citizenship - Legally holding citizenship from two countries at the same time.
- Definition of Multiple Citizenship - Holding three or more citizenships simultaneously, expanding global identity.
- Benefits of Dual Citizenship - Enables access to social services, work rights, and voting in both countries.
Naturalization Process
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Eligibility | Meet residency and legal requirements, typically 5 years as a permanent resident. |
| Application | Submit Form N-400 with supporting documents and fees to the U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS). |
| Biometrics Appointment | Attend appointment for fingerprinting and background check. |
| Interview and Testing | Complete an interview assessing English skills and knowledge of U.S. history and government. |
| Oath of Allegiance | Take the Oath of Allegiance in a formal ceremony to become a U.S. citizen. |
Key Citizenship Benefits
Citizenship grants individuals full rights and responsibilities within a country. It provides access to essential services and legal protections that non-citizens may not receive.
Key benefits of citizenship include the right to vote in national and local elections, influencing government decisions directly. Citizens gain eligibility for public sector jobs and social welfare programs. Furthermore, citizenship ensures protection under the country's laws both domestically and abroad.
Renouncing Citizenship
Renouncing citizenship is the formal process of voluntarily giving up one's nationality. This act can have significant legal and financial consequences.
- Voluntary Act - Individuals choose to renounce citizenship to avoid taxes or gain a different nationality.
- Legal Process - Requires submission of formal documents to the relevant government authority and approval.
- Loss of Rights - Renouncers forfeit rights such as voting, obtaining a passport, and social benefits.
Citizenship by Birth vs. Descent
Citizenship by birth grants nationality to individuals born within a country's territory, often referred to as jus soli. This method provides automatic citizenship regardless of the parents' nationality.
Citizenship by descent, known as jus sanguinis, is acquired through the nationality of one or both parents. This method allows individuals born abroad to inherit citizenship from their parents.
Global Citizenship Trends
Global citizenship is rapidly evolving with increasing awareness of environmental and social issues worldwide. More people are engaging in cross-cultural exchanges, advocating for human rights, and participating in global initiatives. Digital connectivity and international education play key roles in fostering a sense of shared responsibility across borders.
