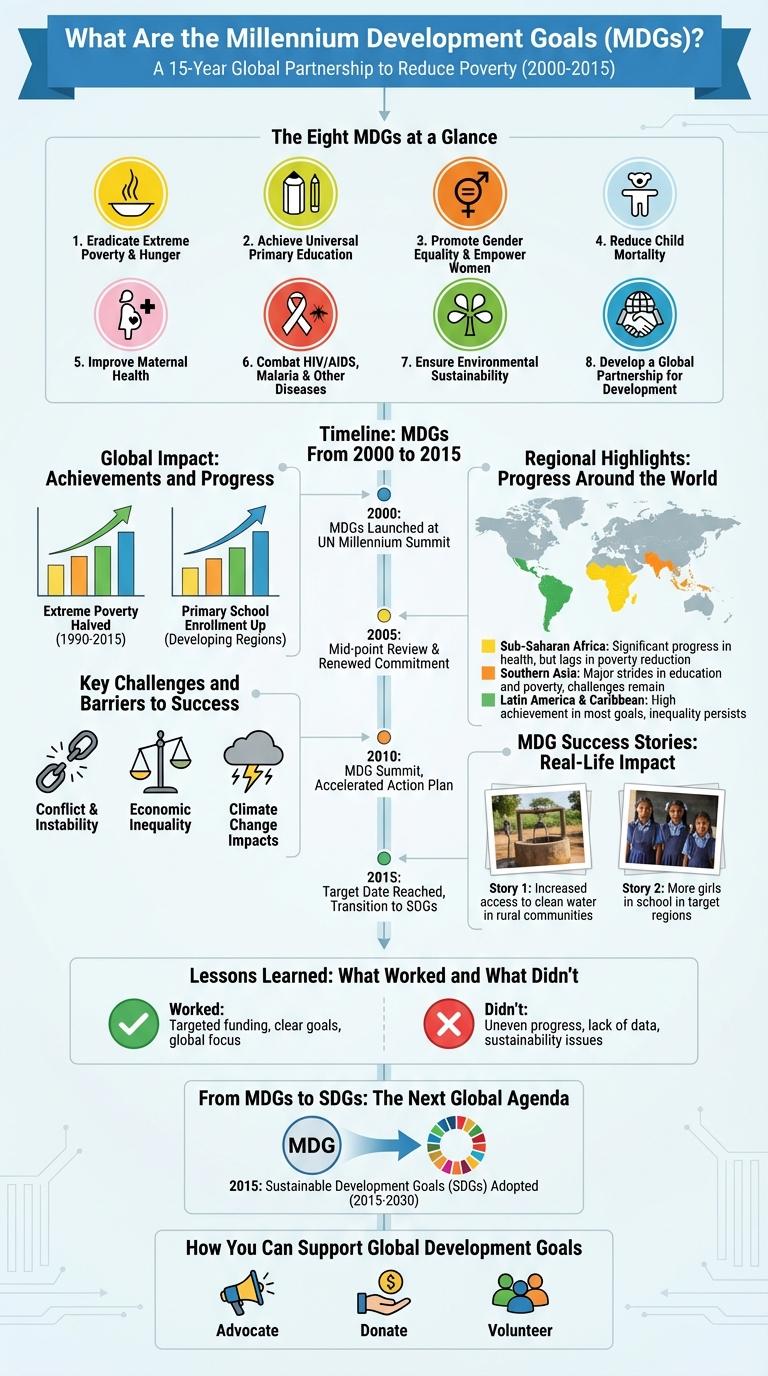
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) represent a global effort to address critical issues such as poverty, education, and health by 2015. This infographic visually highlights key targets, progress statistics, and challenges encountered throughout the initiative. Clear data presentation helps audiences grasp the impact and ongoing relevance of these international development goals.
What Are the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs)?
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) are eight international development targets established by the United Nations in 2000. They aimed to address critical global issues by 2015.
- Poverty Reduction - Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger worldwide with measurable targets to reduce the number of people living on less than $1.25 a day.
- Education Access - Achieve universal primary education by ensuring that all children complete a full course of primary schooling.
- Gender Equality - Promote gender equality and empower women by eliminating gender disparity in education and employment opportunities.
The MDGs served as a framework for global cooperation and progress towards sustainable development and human well-being.
The Eight MDGs at a Glance
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) consist of eight international development targets established by the United Nations in 2000. These goals aim to address critical global issues such as poverty, education, and health by 2015. The eight MDGs provide a framework for measuring progress towards improving the lives of people worldwide.
| MDG | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| 1 | Eradicate extreme poverty and hunger |
| 2 | Achieve universal primary education |
| 3 | Promote gender equality and empower women |
| 4 | Reduce child mortality |
| 5 | Improve maternal health |
| MDG | Focus Area |
|---|---|
| 6 | Combat HIV/AIDS, malaria, and other diseases |
| 7 | Ensure environmental sustainability |
| 8 | Develop a global partnership for development |
Timeline: MDGs From 2000 to 2015
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) were a global initiative launched in 2000 by the United Nations to address critical issues like poverty, education, and health by 2015. The timeline highlights key milestones, including the adoption of the MDGs in 2000, mid-term reviews in 2005 and 2010, and the final assessment in 2015. This infographic illustrates the progress made across eight specific goals through measurable targets, shaping international development policy throughout the 15-year period.
Global Impact: Achievements and Progress
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) brought unprecedented global efforts to tackle poverty and improve health by 2015. These goals mobilized resources and policies that led to significant progress in various sectors worldwide.
The global impact of the MDGs is marked by measurable achievements in health, education, and poverty reduction. Countries across continents experienced improved living conditions and sustainable development outcomes through coordinated international action.
- Reduction in extreme poverty - The proportion of people living on less than $1.25 a day dropped from 47% in 1990 to 14% in 2015, lifting over 1 billion people out of extreme poverty.
- Universal primary education - Enrollment rates in primary education increased to 91% globally, enhancing literacy and access to learning for millions of children.
- Decline in child mortality - Under-five mortality rates fell by more than half, saving approximately 10 million children's lives between 1990 and 2015.
Key Challenges and Barriers to Success
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) faced significant obstacles that hindered their full achievement by 2015. Addressing these challenges is critical for ongoing global development efforts.
- Poverty and Inequality - Persistent poverty and widening inequality limited access to education, healthcare, and basic services.
- Political Instability - Conflicts and weak governance disrupted development programs and resource allocation.
- Resource Constraints - Insufficient funding and limited infrastructure weakened implementation of MDG initiatives.
Regional Highlights: Progress Around the World
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) have driven significant improvements in health, education, and poverty reduction worldwide. Regional progress highlights diverse achievements, reflecting tailored strategies and investments across continents.
Sub-Saharan Africa achieved notable gains in reducing extreme poverty and improving access to primary education, yet challenges remain in maternal health and sanitation. Asia-Pacific regions excelled in eradicating hunger and increasing gender parity in schools. Latin America made strides in environmental sustainability and reducing child mortality rates through targeted social programs.
MDG Success Stories: Real-Life Impact
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) set ambitious targets to address global challenges like poverty, education, and health by 2015. Many countries achieved remarkable progress, improving lives worldwide through focused efforts and international cooperation.
MDG success stories highlight reductions in extreme poverty, increased access to primary education, and significant declines in child mortality rates. These real-life impacts demonstrate the power of unified global action in driving sustainable development.
Lessons Learned: What Worked and What Didn't
The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) significantly reduced global poverty and improved access to education and healthcare. Successes were driven by strong international cooperation and targeted development programs.
Challenges included uneven progress across regions and difficulty addressing environmental sustainability. Lessons learned emphasize the need for inclusive policies and robust data collection for future goals.
From MDGs to SDGs: The Next Global Agenda
What marks the transition from the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) to the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)? The MDGs, established in 2000, targeted eight specific global issues aiming for achievement by 2015. The SDGs, adopted in 2015, expanded the scope to 17 interconnected goals addressing broader sustainability challenges.
How do the SDGs differ in approach compared to the MDGs? The SDGs emphasize inclusivity, universal applicability, and integration of economic, social, and environmental dimensions. This comprehensive framework engages all countries, unlike the MDGs which primarily focused on developing nations.
What are the core themes that SDGs address beyond the MDGs? While MDGs focused on poverty, education, and health, the SDGs also target climate action, clean energy, sustainable cities, and peace and justice. This evolution reflects a holistic approach to global development and sustainability.
| Goal Type | Number of Goals |
|---|---|
| Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) | 8 |
| Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | 17 |
What is the timeframe for achieving the SDGs? The SDGs set targets for 2015 to 2030, promoting a 15-year plan for sustainable development globally. The agenda calls for collaborative efforts among governments, organizations, and communities worldwide.
